|
Hypoplectrus Unicolor
''Hypoplectrus unicolor'', the butter hamlet or yellowtail hamlet, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a sea bass from the subfamily Serraninae which is part of the family Serranidae, which also includes the groupers and anthias. It occurs in the western central Atlantic Ocean and occasionally makes its way into the aquarium trade. Description ''Hypplectrus unicolor'' has a deep body and head which is highly laterally compressed with a straight forehead and a rather short snout and a protrusible upper jaw. It has an angular preoperculum which has serrations on its edge and a number of small forward pointing spines on its lower margin close to the angle. The continuous dorsal fin has ten spines and 14-17 soft rays. It has long pelvic fins which extend as far as or beyond the anus. The caudal fin is slightly forked. The body is greyish white to yellow in colour with the back being darker, with a sizeable black saddle-like marking on the base of the caudal fin, this extends ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Julius Walbaum
Johann Julius Walbaum (30 June 1724 – 21 August 1799) was a German physician, naturalist and fauna taxonomist. Works As an ichthyologist, he was the first to describe many previously unknown fish species from remote parts of the globe, such as the Great Barracuda (''Sphyraena barracuda''), the Chum salmon (''Oncorhynchus keta'') from the Kamchatka River in Siberia, and the curimatá-pacú (''Prochilodus marggravii'') from the São Francisco River in Brazil. He was also the first to observe gloves as a preventative against infection in medical surgery. In 1758, the gloves he observed were made from the cecum of the sheep, rather than rubber, which had not yet been discovered. Legacy The Natural History Museum in Lübeck, opened in 1893, was based on Walbaum's extensive scientific collection, which was lost during the Second World War World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cedar Key
Cedar Key is a city in Levy County, Florida, United States. The population was 702 at the 2010 census. The Cedar Keys are a cluster of islands near the mainland. Most of the developed area of the city has been on Way Key since the end of the 19th century. The Cedar Keys are named for the eastern red cedar ''Juniperus virginiana'', once abundant in the area. History Early While evidence suggests human occupation as far back as 500 BC, the first maps of the area date to 1542, when it was labeled "Las Islas Sabines" by a Spanish cartographer. An archaeological dig at Shell Mound, north of Cedar Key, found artifacts dating back to 500 BC in the top of the mound. The only ancient burial found in Cedar Key was a 2,000-year-old skeleton found in 1999. Arrow heads and spear points dating from the Paleo period (12,000 years old) were collected by Cedar Key historian St. Clair Whitman and are displayed at the Cedar Key Museum State Park. Followers of William Augustus Bowles, self-decl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sessility (motility)
Sessility is the biological property of an organism describing its lack of a means of self-locomotion. Sessile organisms for which natural ''motility'' is absent are normally immobile. This is distinct from the botanical concept of sessility, which refers to an organism or biological structure attached directly by its base without a stalk. Sessile organisms can move via external forces (such as water currents), but are usually permanently attached to something. Organisms such as corals lay down their own substrate from which they grow. Other sessile organisms grow from a solid such as a rock, dead tree trunk, or a man-made object such as a buoy or ship's hull. Mobility Sessile animals typically have a motile phase in their development. Sponges have a motile larval stage and become sessile at maturity. Conversely, many jellyfish develop as sessile polyps early in their life cycle. In the case of the cochineal, it is in the nymph stage (also called the crawler stage) that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths." Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms (e.g., bacteria and fungi) as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud. Description Oceans The benthic region of the ocean begins at the shore line (intertidal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foureye Butterflyfish
The foureye butterflyfish (''Chaetodon capistratus'') is a butterflyfish (family Chaetodontidae). It is alternatively called the four-eyed butterflyfish. This species is found in the Western Atlantic from Massachusetts, USA and Bermuda to the West Indies and northern South America. ''Chaetodon capistratus'' is the type species of ''Chaetodon''. If this genus is split up as some have proposed, it will retain its present name like its closest relatives, which include the banded butterflyfish (''C. striatus'') and the spot-finned butterflyfish (''C. ocellatus''). Description and ecology Foureye butterflyfish are deep-bodied and laterally compressed, with a single dorsal fin and a small mouth with tiny, bristle like teeth. The body is light grey, sometimes with a yellowish hue, and dark forward-pointing chevrons. The ventral fins are yellow. The species gets its common name from a large dark spot on the rear portion of each side of the body. This spot is surrounded by a brilliant wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mimicry
In evolutionary biology, mimicry is an evolved resemblance between an organism and another object, often an organism of another species. Mimicry may evolve between different species, or between individuals of the same species. Often, mimicry functions to protect a species from predators, making it an anti-predator adaptation. Mimicry evolves if a receiver (such as a predator) perceives the similarity between a mimic (the organism that has a resemblance) and a model (the organism it resembles) and as a result changes its behaviour in a way that provides a selective advantage to the mimic. The resemblances that evolve in mimicry can be visual, acoustic, chemical, tactile, or electric, or combinations of these sensory modalities. Mimicry may be to the advantage of both organisms that share a resemblance, in which case it is a form of mutualism; or mimicry can be to the detriment of one, making it parasitic or competitive. The evolutionary convergence between groups is driven by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
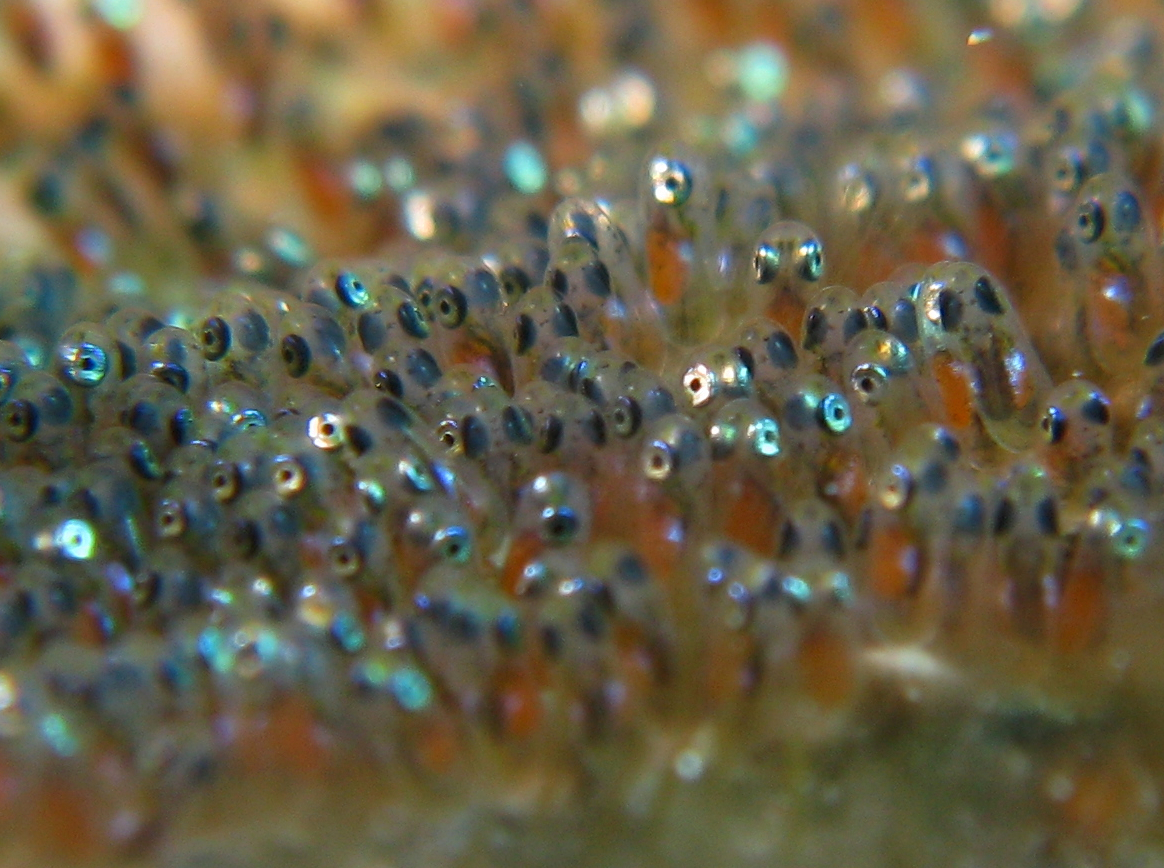
Spawn (biology)
Spawn is the Egg cell, eggs and Spermatozoa, sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of releasing the eggs and sperm, and the act of both sexes is called spawning. Most aquatic animals, except for aquatic mammals and marine reptile, reptiles, reproduce through the process of spawning. Spawn consists of the reproductive cells (gametes) of many aquatic animals, some of which will become fertilized and produce offspring. The process of spawning typically involves females releasing Ovum, ova (unfertilized eggs) into the water, often in large quantities, while males simultaneously or sequentially release spermatozoa (milt) to fertilize the eggs. Most fish reproduce by spawning, as do most other aquatic animals, including crustaceans such as crabs and shrimps, molluscs such as oysters and squid, echinoderms such as sea urchins and sea cucumbers, amphibians such as frogs and newts, aquatic insects such as mayflies and mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
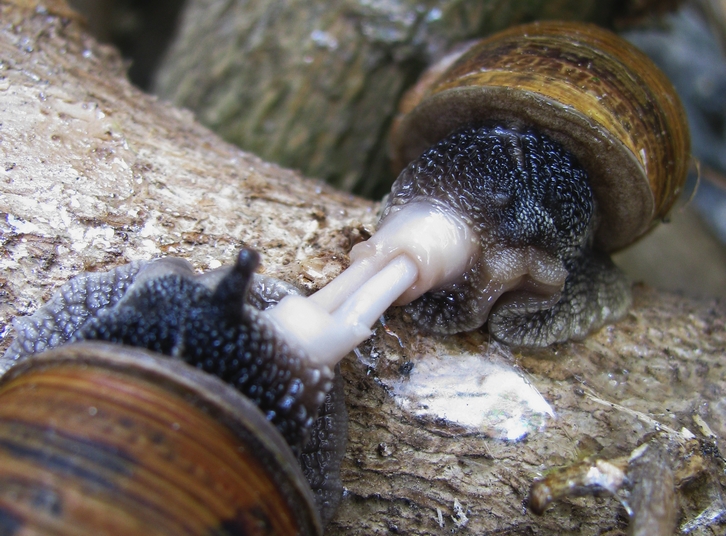
Hermaphrodite
In reproductive biology, a hermaphrodite () is an organism that has both kinds of reproductive organs and can produce both gametes associated with male and female sexes. Many Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic groups of animals (mostly invertebrates) do not have separate sexes. In these groups, hermaphroditism is a normal condition, enabling a form of sexual reproduction in which either partner can act as the female or male. For example, the great majority of tunicata, tunicates, pulmonate molluscs, opisthobranch, earthworms, and slugs are hermaphrodites. Hermaphroditism is also found in some fish species and to a lesser degree in other vertebrates. Most plants are also hermaphrodites. Animal species having different sexes, male and female, are called Gonochorism, gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphrodite. There are also species where hermaphrodites exist alongside males (called androdioecy) or alongside females (called gynodioecy), or all three exist in the same species ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoplectrus
''Hypoplectrus'' is a genus of fishes commonly known as hamlets, found mainly in coral reefs in the Caribbean Sea and the Gulf of Mexico, particularly around Florida and the Bahamas. They are a popular choice for hobbyist saltwater aquariums, and come in a variety of colors. Species There are currently 17 recognized species in this genus: * '' Hypoplectrus aberrans'' Poey, 1868 (Yellowbelly hamlet) * '' Hypoplectrus atlahua'' Tavera & Acero P, 2013 (Jarocho hamlet) Tavera, J. & Acero P., A. (2013): Description of a new species of ''Hypoplectrus'' (Perciformes: Serranidae) from the Southern Gulf of Mexico. ''aqua, International Journal of Ichthyology, 19 (1): 29-38.'' * '' Hypoplectrus castroaguirrei'' Del-Moral-Flores, J. L. Tello-Musi & J. A. Martínez-Pérez, 2012 * '' Hypoplectrus chlorurus'' G. Cuvier, 1828 (Yellowtail hamlet) * ''Hypoplectrus ecosur'' Victor, 2012 * '' Hypoplectrus floridae'' Victor, 2012 * '' Hypoplectrus gemma'' Goode & T. H. Bean, 1882 (Blue ham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mangrove
A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows in coastal saline water, saline or brackish water. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in several plant families. They occur worldwide in the tropics and subtropics and even some temperate coastal areas, mainly between latitudes 30° N and 30° S, with the greatest mangrove area within 5° of the equator. Mangrove plant families first appeared during the Late Cretaceous to Paleocene epochs, and became widely distributed in part due to the plate tectonics, movement of tectonic plates. The oldest known fossils of Nypa fruticans, mangrove palm date to 75 million years ago. Mangroves are salt-tolerant trees, also called halophytes, and are adapted to live in harsh coastal conditions. They contain a complex salt filtration system and a complex root system to cope with saltwater immersion and wave action. They are ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivory
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose food and energy requirements derive from animal tissues (mainly muscle, adipose tissue, fat and other soft tissues) whether through predation, hunting or scavenger, scavenging. Nomenclature Mammal order The technical term for mammals in the order (biology), order Carnivora is ''carnivoran'', and they are so-named because most member species in the group have a carnivorous diet, but the similarity of the name of the order and the name of the diet causes confusion. Many but not all carnivorans are meat eaters; a few, such as the felidae, large and small cats (felidae) are ''obligate'' carnivores (see below). Other classes of carnivore are highly variable. The Ursidae, Ursids, for example: While the Arctic polar bear eats meat almost exclusively (more than 90% of its diet is meat), almost all other bear species are omnivore, om ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)