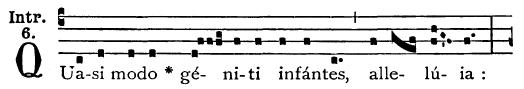|
Hypoionian Mode
The Hypoionian mode, literally meaning "below Ionian", is the name assigned by Henricus Glareanus in his ''Dodecachordon'' (1547) to the plagal mode on C, which uses the diatonic octave species from G to the G an octave higher, divided at its final, C. This is roughly the same as playing all the white notes of a piano from G to G: G A B C , (C) D E F G. Glarean regarded compositions with F as the final and a one-flat signature as transpositions of the Ionian or Hypoionian mode (depending on the ambitus In ancient Roman law, ''ambitus'' was a crime of political corruption, mainly a candidate's attempt to influence the outcome (or direction) of an election through bribery or other forms of soft power. The Latin word ''ambitus'' is the origin ...). Most of his contemporaries, however, appear to have continued considering such compositions as being in the fifth and sixth modes ( Lydian and Hypolydian), which had been regarded since the beginnings of medieval modal theory as pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixolydian Mode G
Mixolydian mode may refer to one of three things: the name applied to one of the ancient Greek ''harmoniai'' or ''tonoi'', based on a particular octave species or scale; one of the medieval church modes; or a modern musical mode or diatonic scale, related to the medieval mode. (The Hypomixolydian mode of medieval music, by contrast, has no modern counterpart.) The modern diatonic mode is the scale forming the basis of both the rising and falling forms of Harikambhoji in Carnatic music, the classical music form of southern India. Greek Mixolydian The idea of a Mixolydian mode comes from the music theory of ancient Greece. The invention of the ancient Greek Mixolydian mode was attributed to Sappho, the poet and musician. However, what the ancient Greeks thought of as Mixolydian is very different from the modern interpretation of the mode. The prefix ''mixo''- (μιξο-) means "half", referring to its resemblance to the Lydian mode. In Greek theory, the Mixolydian ''tonos'' (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henricus Glareanus
Heinrich Glarean also styled Glareanus (born as Heinrich Loriti on 28 February or 3 June 1488 – 28 March 1563) was a Swiss music theorist, poet and humanist. He was born in Mollis (in the canton of Glarus, hence his name) and died in Freiburg im Breisgau. Biography Glarean was born as Heinrich Loriti in Mollis in Canton Glarus to a politician. As a boy, he took care of cattle and received a good education. After a thorough early training in music, Glarean enrolled in the University of Cologne, where he studied theology, philosophy, and mathematics as well as music. It was there that he wrote a famous poem as a tribute to Emperor Maximilian I. Shortly afterwards, in Basle, he met Erasmus and the two humanists became lifelong friends. Glarean's first publication on music, a modest volume entitled ''Isagoge in musicen'', was in 1516. In it he discusses the basic elements of music; probably it was used for teaching. But his most famous book, and one of the most famous and influentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregorian Mode
A Gregorian mode (or church mode) is one of the eight systems of pitch organization used in Gregorian chant. History The name of Pope Gregory I was attached to the variety of chant that was to become the dominant variety in medieval western and central Europe (the diocese of Milan was the sole significant exception) by the Frankish cantors reworking Roman ecclesiastical song during the Carolingian period. The theoretical framework of modes arose later to describe the tonal structure of this chant repertory, and is not necessarily applicable to the other European chant dialects ( Old Roman, Mozarabic, Ambrosian, etc.). The repertory of Western plainchant acquired its basic forms between the sixth and early ninth centuries, but there are neither theoretical sources nor notated music from this period. By the late eighth century, a system of eight modal categories, for which there was no precedent in Ancient Greek theory, came to be associated with the repertory of Gregorian chant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatonic
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are most often used to characterize Scale (music), scales, and are also applied to musical instruments, Interval (music), intervals, Chord (music), chords, Musical note, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, especially when applied to contrasting features of the Common practice period, common practice music of the period 1600–1900. These terms may mean different things in different contexts. Very often, ''diatonic'' refers to musical elements derived from the modes and transpositions of the "white note scale" C–D–E–F–G–A–B. In some usages it includes all forms of heptatonic scale that are in common use in Western music (the major, and all forms of the minor). ''Chromatic'' most often refers to structures derived from the twelve-note chromatic scale, which consists of all semitones. Historically, however, it had other senses, referring in Ancient Greek music theory to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octave Species
In the musical system of ancient Greece, an octave species (εἶδος τοῦ διὰ πασῶν, or σχῆμα τοῦ διὰ πασῶν) is a specific sequence of intervals within an octave. In ''Elementa harmonica'', Aristoxenus classifies the species as three different genera, distinguished from each other by the largest intervals in each sequence: the diatonic, chromatic, and enharmonic genera, whose largest intervals are, respectively, a whole tone, a minor third, and a ditone; quarter tones and semitones complete the tetrachords. The concept of octave species is very close to tonoi and akin to musical scale and mode, and was invoked in Medieval and Renaissance theory of Gregorian mode and Byzantine Octoechos. Ancient Greek theory Greek theorists used two terms interchangeably to describe what we call species: ''eidos'' (εἶδος) and ''skhēma'' (σχῆμα), defined as "a change in the arrangement of incomposite ntervalsmaking up a compound magnitude while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambitus (music)
Ambitus () is a Latin term literally meaning ''enclos r'', and in Medieval Latin means the "range" of a melodic line, most usually referring to the range of scale degrees attributed to a given mode, particularly in Gregorian chant. In Gregorian chant specifically, the ambitus is the range, or the distance between the highest and lowest note. Different chants vary widely in their ambitus. Even relatively florid chants like Alleluias may have a narrow ambitus. Earlier writers termed the modal ambitus "perfect" when it was a ninth or tenth (that is, an octave plus one or two notes, either at the top or bottom or both), but from the late fifteenth century onward "perfect ambitus" usually meant one octave, and the ambitus was called "imperfect" when it was less, and "pluperfect" when it was more than an octave. All of the church modes are distinguished in part by their ambitus. The plagal modes have the final in the middle of the ambitus, while the authentic modes generally go no more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lydian Mode
The modern Lydian mode is a seven-tone musical scale formed from a rising pattern of pitches comprising three whole tones, a semitone, two more whole tones, and a final semitone. : Because of the importance of the major scale in modern music, the Lydian mode is often described as the scale that begins on the fourth scale degree of the major scale, or alternatively, as the major scale with the fourth scale degree raised half a step. This sequence of pitches roughly describes the scale underlying the fifth of the eight Gregorian (church) modes, known as Mode V or the authentic mode on F, theoretically using B but in practice more commonly featuring B. The use of the B as opposed to B would have made such piece in the modern day F major scale. Ancient Greek Lydian The name Lydian refers to the ancient kingdom of Lydia in Anatolia. In Greek music theory, there was a Lydian scale or "octave species" extending from ''parhypate hypaton'' to ''trite diezeugmenon'', equivalent in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypolydian Mode
The Hypolydian mode, literally meaning "below Lydian", is the common name for the sixth of the eight church modes of medieval music theory. The name is taken from Ptolemy of Alexandria's term for one of his seven ''tonoi'', or transposition keys. This mode is the plagal counterpart of the authentic fifth mode. In medieval theory the Hypolydian mode was described either as (1) the diatonic octave species from C to the C an octave higher, divided at the final F (C–D–E–F + F–G–A–B–C) or (2) a mode with F as final and an ambitus from the C below the final to the D above it. The third above the final, A—corresponding to the reciting tone or "tenor" of the sixth psalm tone—was regarded as having an important melodic function in this mode. The sequence of intervals was therefore divided by the final into a lower tetrachord of tone-tone-semitone, and an upper pentachord of tone-tone-tone-semitone. However, from as early as the time of Hucbald Hucbald ( – 20 June ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harold Powers
Harold Stone Powers (August 5, 1928 – March 15, 2007) was an American musicologist, ethnomusicologist, and music theorist. Career Born in New York City on August 5, 1928, he earned his B.Mus. in piano from Syracuse University in 1950 and an MFA in composition and musicology from Princeton University in 1952. As a Fulbright Fellow, he studied Indian music in Madras for two years before continuing at Princeton where he received a Ph.D. in musicology. His dissertation was on “The Background of the South Indian Raga System.” Powers taught at Harvard University from 1958 to 1960 and at the University of Pennsylvania from 1961 to 1973 before returning to Princeton where he was named the Scheide Professor of Music History in 1995 and in 2001 assumed Emeritus status. Powers returned to India several times to study music there on John D. Rockefeller III and Fulbright Senior fellowships. Powers was known for intensive study of both Renaissance music and music theory and several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanley Sadie
Stanley John Sadie (; 30 October 1930 – 21 March 2005) was an influential and prolific British musicologist, music critic, and editor. He was editor of the sixth edition of the '' Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' (1980), which was published as the first edition of ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians''. Along with Thurston Dart, Nigel Fortune and Oliver Neighbour he was one of Britain's leading musicologists of the post-World War II generation. Career Born in Wembley, Sadie was educated at St Paul's School, London, and studied music privately for three years with Bernard Stevens. At Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge he read music under Thurston Dart. Sadie earned Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Music degrees in 1953, a Master of Arts degree in 1957, and a PhD in 1958. His doctoral dissertation was on mid-eighteenth-century British chamber music. After Cambridge, he taught at Trinity College of Music, London (1957–1965). Sadie then turned to musi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Tyrrell (musicologist)
John Tyrrell (17 August 1942 – 4 October 2018) was a British musicologist. He published several books on Leoš Janáček, including an authoritative and largely definitive two-volume biography. Early life Tyrrell was born in Salisbury, Southern Rhodesia (now Harare, Zimbabwe), he studied at the universities of Cape Town, Oxford and Brno. He pursued his Bachelor of Music at the University of Cape Town following which he moved to Oxford University to pursue a doctoral degree under the supervision of Edmund Rubbra Career Tyrrell started his career working in an editorial capacity at The Musical Times. He was a Lecturer in Music at the University of Nottingham (1976), becoming Reader in Opera Studies (1987) and Professor (1996). From 1996 to 2000 he was Executive Editor of the second edition of ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' (2001). From 2000-08, he was Research Professor at Cardiff University. He received numerous awards and honours throughout his career. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |