|
Hypertrophy
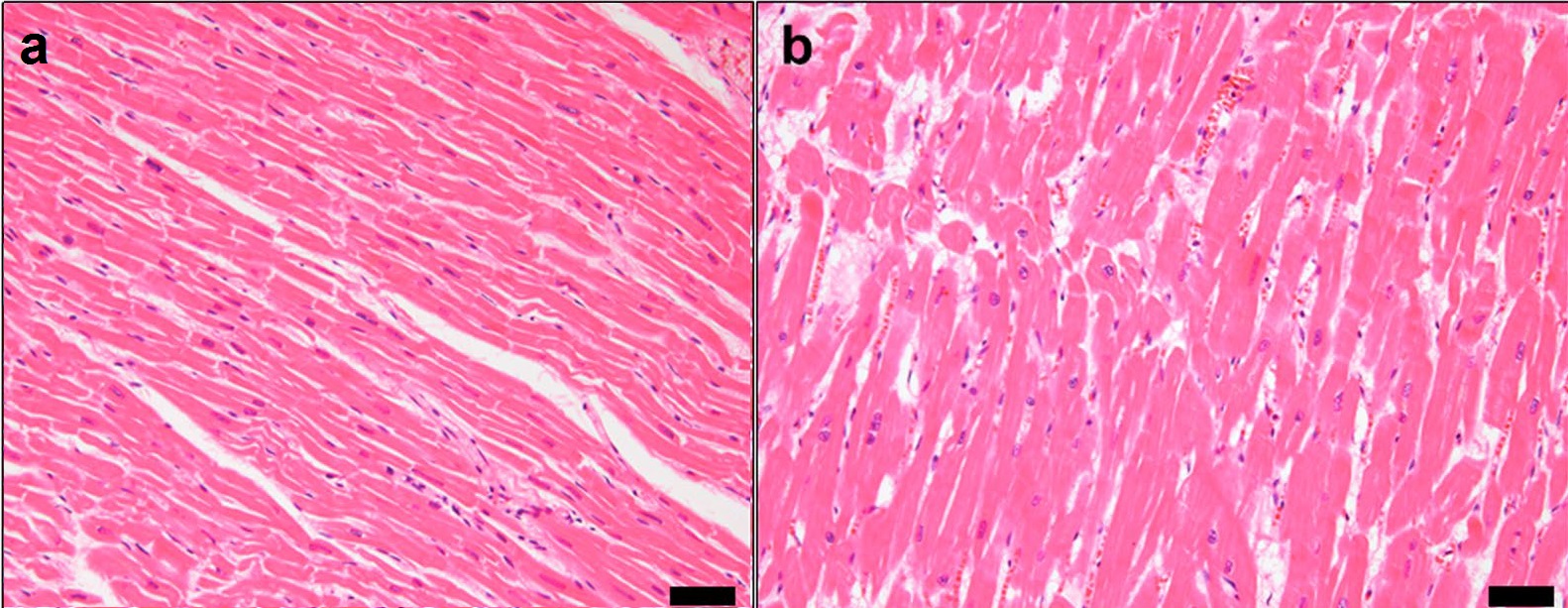
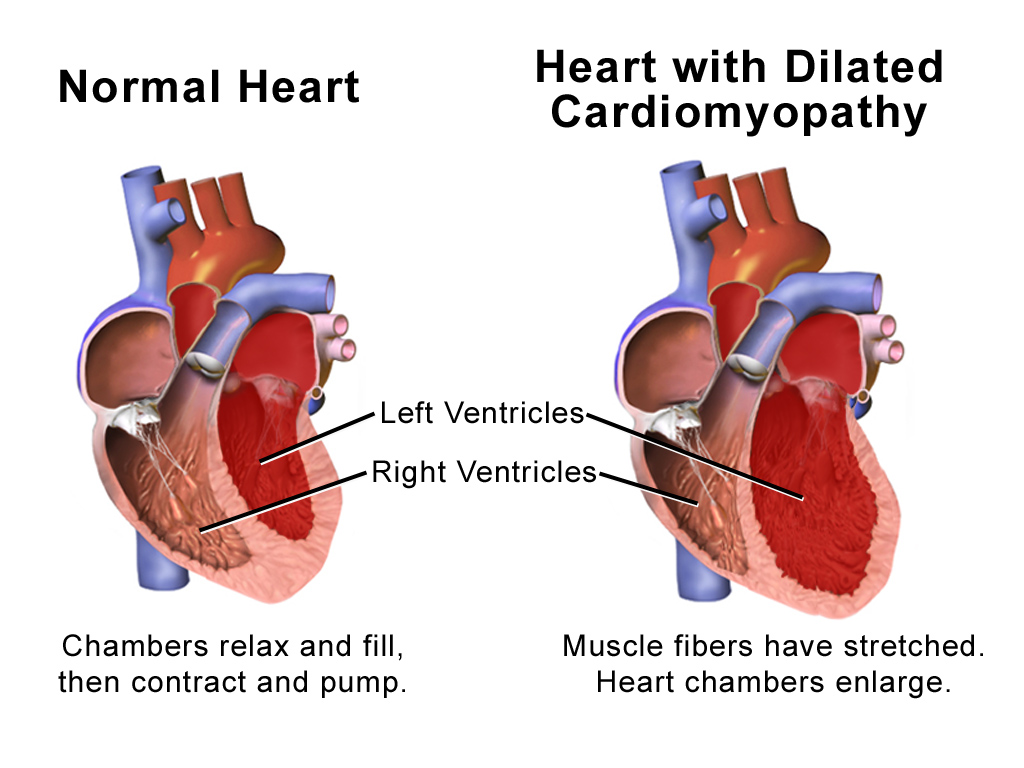
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells. It is distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number.Updated by Linda J. Vorvick. 8/14/1Hyperplasia/ref> Although hypertrophy and hyperplasia are two distinct processes, they frequently occur together, such as in the case of the hormonally-induced proliferation and enlargement of the cells of the uterus during pregnancy. Eccentric hypertrophy is a type of hypertrophy where the walls and chamber of a hollow organ undergo growth in which the overall size and volume are enlarged. It is applied especially to the left ventricle of heart. Sarcomeres are added in series, as for example in dilated cardiomyopathy (in contrast to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a type of concentric hypertrophy, where sarcomeres are added in parallel). Gallery File:*+ * Photographic documentation on sexual education - Hypertrophy o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is thickening of the heart muscle of the left ventricle of the heart, that is, left-sided ventricular hypertrophy and resulting increased left ventricular mass. Causes While ventricular hypertrophy occurs naturally as a reaction to aerobic exercise and strength training, it is most frequently referred to as a pathological reaction to cardiovascular disease, or high blood pressure. It is one aspect of ventricular remodeling. While LVH itself is not a disease, it is usually a marker for disease involving the heart. Disease processes that can cause LVH include any disease that increases the afterload that the heart has to contract against, and some primary diseases of the muscle of the heart. Causes of increased afterload that can cause LVH include aortic stenosis, aortic insufficiency and hypertension. Primary disease of the muscle of the heart that cause LVH are known as hypertrophic cardiomyopathies, which can lead into heart failure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventricular Hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy (VH) is thickening of the walls of a ventricle (lower chamber) of the heart. Although left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is more common, right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH), as well as concurrent hypertrophy of both ventricles can also occur. Ventricular hypertrophy can result from a variety of conditions, both adaptive and maladaptive. For example, it occurs in what is regarded as a physiologic, adaptive process in pregnancy in response to increased blood volume; but can also occur as a consequence of ventricular remodeling following a heart attack. Importantly, pathologic and physiologic remodeling engage different cellular pathways in the heart and result in different gross cardiac phenotypes. Presentation In individuals with eccentric hypertrophy there may be little or no indication that hypertrophy has occurred as it is generally a healthy response to increased demands on the heart. Conversely, concentric hypertrophy can make itself known in a vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
Right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH) is a condition defined by an abnormal enlargement of the cardiac muscle surrounding the right ventricle. The right ventricle is one of the four chambers of the heart. It is located towards the lower-end of the heart and it receives blood from the right atrium and pumps blood into the lungs. Since RVH is an enlargement of muscle it arises when the muscle is required to work harder. Therefore, the main causes of RVH are pathologies of systems related to the right ventricle such as the pulmonary artery, the tricuspid valve or the airways. RVH can be benign and have little impact on day-to-day life or it can lead to conditions such as heart failure, which has a poor prognosis. Signs and symptoms Symptoms Although presentations vary, individuals with right ventricular hypertrophy can experience symptoms that are associated with pulmonary hypertension, heart failure and/or a reduced cardiac output. These include: * Difficulty breathing on exertio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
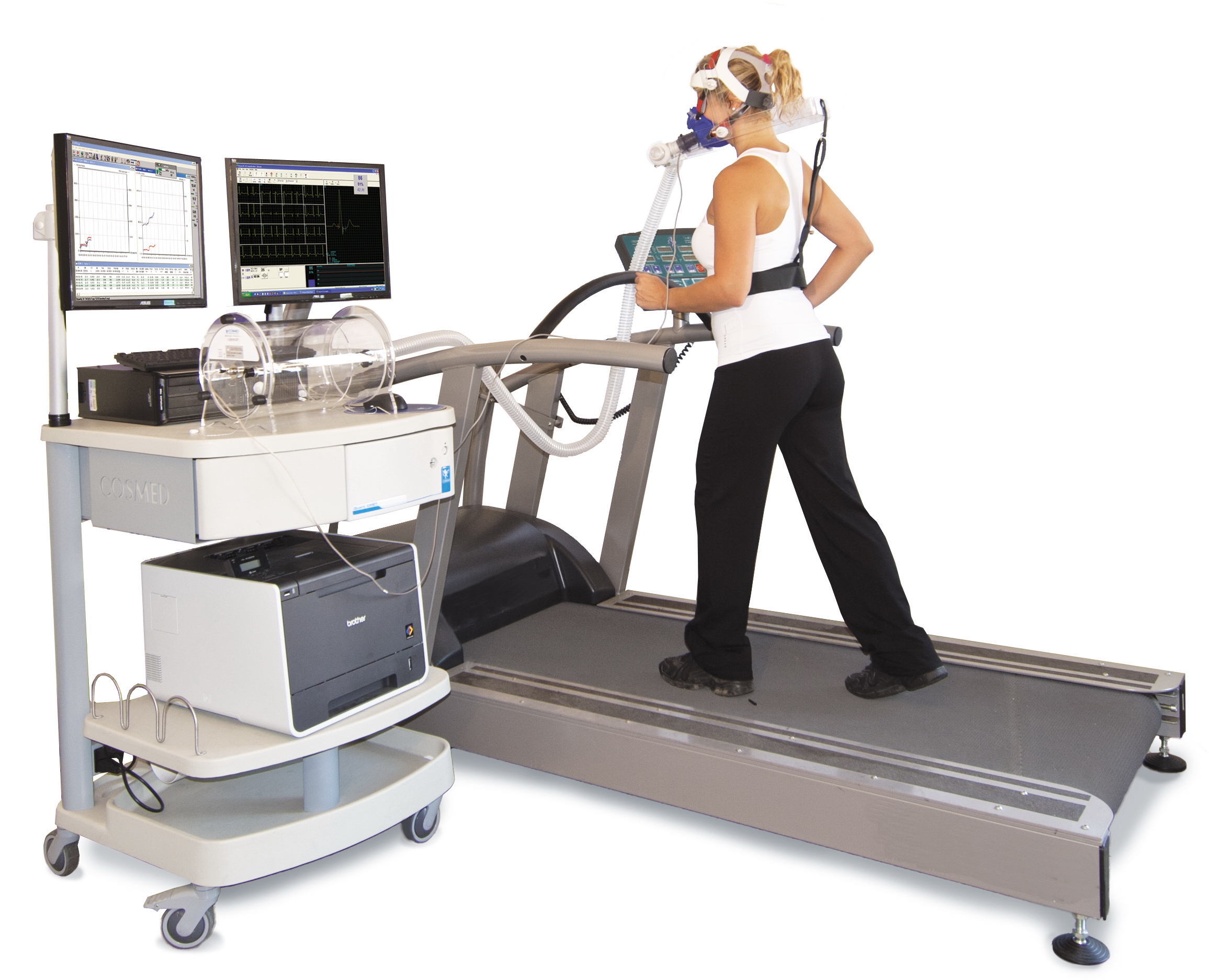
Physical Exercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness. It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic skills, weight loss or maintenance, improve health, or simply for enjoyment. Many individuals choose to exercise outdoors where they can congregate in groups, socialize, and improve well-being as well as mental health. In terms of health benefits, the amount of recommended exercise depends upon the goal, the type of exercise, and the age of the person. Even doing a small amount of exercise is healthier than doing none. Classification Physical exercises are generally grouped into three types, depending on the overall effect they have on the human body: * Aerobic exercise is any physical activity that uses large muscle groups and causes the body to use more oxygen than it would while resting. The goal of aerobic exercise is to in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Hypertrophy
Muscle hypertrophy or muscle building involves a hypertrophy or increase in size of skeletal muscle through a growth in size of its component cells. Two factors contribute to hypertrophy: sarcoplasmic hypertrophy, which focuses more on increased muscle glycogen storage; and myofibrillar hypertrophy, which focuses more on increased myofibril size. It is the most major part of the bodybuilding-related activities. Hypertrophy stimulation A range of stimuli can increase the volume of muscle cells. These changes occur as an adaptive response that serves to increase the ability to generate force or resist fatigue in anaerobic conditions. Strength training Strength training (resistance training) causes neural and muscular adaptations which increase the capacity of an athlete to exert force through voluntary muscular contraction: After an initial period of neuro-muscular adaptation, the muscle tissue expands by creating sarcomeres (contractile elements) and increasing non-contractile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Biological Development Disorders
References Bibliography * Reece JB, Urry LA, Cain ML, Wasserman SA, Minorsky PV, Jackson RB. Campbell Biology (10th ed.). Addison Wesley Longman; 2014. {{DEFAULTSORT:Biological development disorders Lists of diseases Disability-related lists Biological nomenclature Medical terminology Lists of biology lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperplasia
Hyperplasia (from ancient Greek ὑπέρ ''huper'' 'over' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'), or hypergenesis, is an enlargement of an organ or tissue caused by an increase in the amount of organic tissue that results from cell proliferation. It may lead to the gross enlargement of an organ, and the term is sometimes confused with benign neoplasia or benign tumor. Hyperplasia is a common preneoplastic response to stimulus. Microscopically, cells resemble normal cells but are increased in numbers. Sometimes cells may also be increased in size (hypertrophy). Hyperplasia is different from hypertrophy in that the adaptive cell change in hypertrophy is an increase in the ''size'' of cells, whereas hyperplasia involves an increase in the ''number'' of cells. Causes Hyperplasia may be due to any number of causes, including proliferation of basal layer of epidermis to compensate skin loss, chronic inflammatory response, hormonal dysfunctions, or compensation for damage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concentric Hypertrophy
Concentric hypertrophy is a hypertrophic growth of a hollow organ without overall enlargement, in which the walls of the organ are thickened and its capacity or volume is diminished. Sarcomeres are added in parallel, as for example occurs in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. In the heart, concentric hypertrophy is related to increased pressure overload of the heart, often due to hypertension and/or aortic stenosis. The consequence is a decrease in ventricular compliance and diastolic dysfunction, followed eventually by ventricular failure and systolic dysfunction Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a .... Laplace's law for a sphere states wall stress (T) is proportionate to the product of the transmural pressure (P) and cavitary radius (r) and inversely proportionate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a condition in which the heart becomes enlarged and cannot pump blood effectively. Symptoms vary from none to feeling tired, leg swelling, and shortness of breath. It may also result in chest pain or fainting. Complications can include heart failure, heart valve disease, or an irregular heartbeat. Causes include genetics, alcohol, cocaine, certain toxins, complications of pregnancy, and certain infections. Coronary artery disease and high blood pressure may play a role, but are not the primary cause. In many cases the cause remains unclear. It is a type of cardiomyopathy, a group of diseases that primarily affects the heart muscle. The diagnosis may be supported by an electrocardiogram, chest X-ray, or echocardiogram. In those with heart failure, treatment may include medications in the ACE inhibitor, beta blocker, and diuretic families. A low salt diet may also be helpful. In those with certain types of irregular heartbeat, blood thinners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Ventricle
A ventricle is one of two large chambers toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by the at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exercise Physiology
Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise. It is one of the allied health professions, and involves the study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to exercise. Exercise physiologists are the highest qualified exercise professionals and utilise education, lifestyle intervention and specific forms of exercise to rehabilitate and manage acute and chronic injuries and conditions. Understanding the effect of exercise involves studying specific changes in muscular, cardiovascular, and neurohumoral systems that lead to changes in functional capacity and strength due to endurance training or strength training. The effect of training on the body has been defined as the reaction to the adaptive responses of the body arising from exercise or as "an elevation of metabolism produced by exercise". Exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or reverse disease progression. History Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tissues (biology)
Tissue may refer to: Biology * Tissue (biology), an ensemble of similar (or dissimilar in structure but same in origin) cells that together carry out a specific function * '' Triphosa haesitata'', a species of geometer moth ("tissue moth") found in North America * '' Triphosa dubitata'', a species of geometer moth ("tissue") found in Afro-Eurasia Paper products * Tissue paper, a type of thin, gauzy translucent paper used for wrapping and cushioning items ** Facial tissue, tissue paper used for cleaning the face ** Japanese tissue, tissue paper from Japan made of vegetable fibers ** Toilet paper, tissue paper used for cleaning the anus ** Wrapping tissue, tissue paper used for wrapping and cushioning items Other * Aerial tissue, an acrobatic art form and one of the circus arts * "The Tissue (Tomaranai Seishun) is the third single by the Japanese girl idol group Shiritsu Ebisu Chugaku (or fourth counting one cover single), released in Japan on April 27, 2011 on the indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |