|
Hyperbolic Asteroid
A hyperbolic asteroid is any sort of asteroid or non-cometary astronomical object observed to have an orbit not bound to the Sun and will have an orbital eccentricity greater than 1 when near perihelion. Unlike hyperbolic comets, they have not been seen out-gassing light elements, and therefore have no cometary coma. Most of these objects will only be weakly hyperbolic and will not be of interstellar origin. Orbit explanation The planets and most satellites of the solar system revolve in an almost circular motion – called an elliptical orbit – around the Sun or their parent planet, so their orbital eccentricity is generally much closer to 0 than to 1. In mathematics, by definition, an eccentricity (''e'') of 1 characterizes a parabola, and ''e'' > 1, a hyperbola. Some comets are on parabolic and hyperbolic orbits. This means that these hyperbolic asteroids all have an orbital eccentricity greater than 1. Known hyperbolic asteroids So far most hyperbolic asteroids discover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere. Of the roughly one million known asteroids the greatest number are located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, approximately 2 to 4 AU from the Sun, in the main asteroid belt. Asteroids are generally classified to be of three types: C-type, M-type, and S-type. These were named after and are generally identified with carbonaceous, metallic, and silicaceous compositions, respectively. The size of asteroids varies greatly; the largest, Ceres, is almost across and qualifies as a dwarf planet. The total mass of all the asteroids combined is only 3% that of Earth's Moon. The majority of main belt asteroids follow slightly elliptical, stable orbits, revolving in the same direction as the Earth and taking from three to six years to comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C/2017 U7
C/2017 U7 (PanSTARRS) is a hyperbolic comet (previously classified as A/2017 U7, a hyperbolic asteroid), first observed on 29 October 2017 by astronomers of the Pan-STARRS facility at Haleakala Observatory, Hawaii, United States when the object was from the Sun. Despite being discovered only 10 days after interstellar asteroid 1I/'Oumuamua, it was not announced until March 2018 (along with C/2018 C2 (Lemmon), which was believed to be another hyperbolic asteroid at the time) as its orbit is not strongly hyperbolic beyond most Oort Cloud comets. Based on the absolute magnitude of 10.6, it may measure tens of kilometers in diameter. As of August 2018, there is only 1 hyperbolic asteroid known, ʻOumuamua, but hundreds of hyperbolic comets are known. Orbit Although C/2017 U7's orbit is no longer bound to the Solar System, unlike ʻOumuamua, it is probably not an interstellar object. It had an inbound orbital period of roughly 800000 years. Its point of origin is inclined only 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minor Planet Electronic Circular
The Minor Planet Center (MPC) is the official body for observing and reporting on minor planets under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Founded in 1947, it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. Function The Minor Planet Center is the official worldwide organization in charge of collecting observational data for minor planets (such as asteroids), calculating their orbits and publishing this information via the '' Minor Planet Circulars''. Under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU), it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, which is part of the Center for Astrophysics along with the Harvard College Observatory. The MPC runs a number of free online services for observers to assist them in observing minor planets and comets. The complete catalogue of minor planet orbits (sometimes referred to as the "Minor Planet Catalogue") may also be freely downloaded. In addition to astrometric data, the MPC collect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperbolic Comet
This is a list of parabolic and hyperbolic comets in the Solar System. Many of these comets may come from the Oort cloud, or perhaps even have interstellar origin. The Oort Cloud is not gravitationally attracted enough to the Sun to form into a fairly thin disk, like the inner Solar System. Thus, comets originating from the Oort Cloud can come from roughly any orientation (inclination to the ecliptic), and many even have a retrograde orbit. By definition, a hyperbolic orbit means that the comet will only travel through the Solar System once, with the Sun acting as a gravitational slingshot, sending the comet hurtling out of the Solar System entirely unless its eccentricity is otherwise changed. Comets orbiting in this way still originate from the Solar System, however. Typically comets in the Oort Cloud are thought to have roughly circular orbits around the Sun, but their orbital velocity is so slow that they may easily be perturbed by passing stars and the galactic tide. Astr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocomet
An exocomet, or extrasolar comet, is a comet outside the Solar System, which includes rogue comets and comets that orbit stars other than the Sun. The first exocomets were detected in 1987 around Beta Pictoris, a very young A-type main-sequence star. There are now (as of February 2019) a total of 27 stars around which exocomets have been observed or suspected. The majority of discovered exocometary systems (Beta Pictoris, HR 10, 51 Ophiuchi, HR 2174, HD 85905, 49 Ceti, 5 Vulpeculae, 2 Andromedae, HD 21620, Rho Virginis, HD 145964, HD 172555, Lambda Geminorum, HD 58647, Phi Geminorum, Delta Corvi, HD 109573, Phi Leonis, 35 Aquilae, HD 24966, HD 38056, HD 79469 and HD 225200) are around very young A-type stars. The relatively old shell star Phi Leonis shows evidence of exocomets in the spectrum and comet-like activity was detected around the old F2V-type star Eta Corvi. In 2018 transiting exocomets were discovered around F-type stars, using data from the Kepler space te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoch (astronomy)
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodies) can be used to generate an ephemeris, a table of values giving the posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Jupiter is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky after the Moon and Venus, and it has been observed since Pre-history, prehistoric times. It was named after the Jupiter (mythology), Roman god Jupiter, the king of the gods. Jupiter is primarily composed of hydrogen, but helium constitutes one-quarter of its mass and one-tenth of its volume. It probably has a rocky core of heavier elements, but, like the other giant planets in the Solar System, it lacks a well-defined solid surface. The ongoing contraction of Jupiter's interior generates more heat than it receives from the Sun. Because of its rapid rotation, the planet' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyra
Lyra (; Latin for lyre, from Greek ''λύρα'') is a small constellation. It is one of the 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the modern 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence is sometimes referred to as Vultur Cadens or Aquila Cadens ("Falling Vulture" or "Falling Eagle"), respectively. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is nearly overhead in temperate northern latitudes shortly after midnight at the start of summer. From the equator to about the 40th parallel south it is visible low in the northern sky during the same (thus winter) months. Vega, Lyra's brightest star, is one of the brightest stars in the night sky, and forms a corner of the famed Summer Triangle asterism. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of binary stars known as Beta Lyrae variables. These binary st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
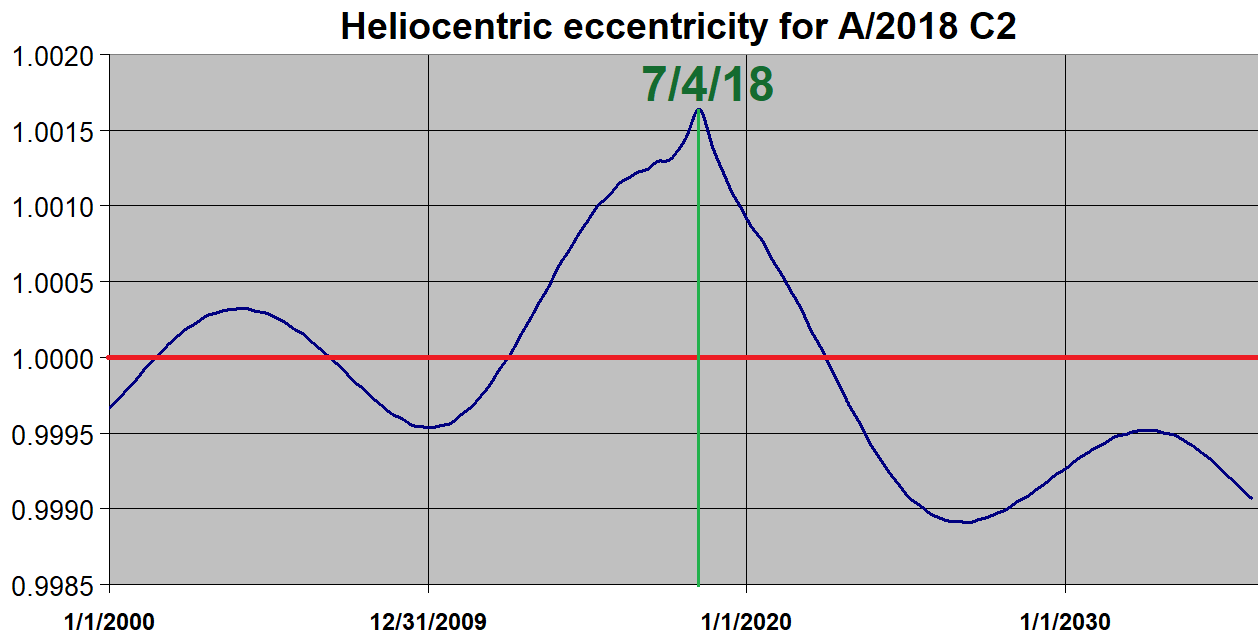
C/2018 C2 (Lemmon)
C/2018 C2 (Lemmon) is a hyperbolic comet (previously classified as A/2018 C2, a hyperbolic asteroid). It was first observed on 5 February 2018 by the Mount Lemmon Survey conducted at the Mount Lemmon Observatory near Tucson, Arizona, in the United States. The discovery was announced on 4 March 2018 along with another hyperbolic object, A/2017 U7. Based on the absolute magnitude of 15.1, it may measure several kilometers in diameter. On 22 March 2018 it was determined to be a hyperbolic comet. Orbit While near perihelion, A/2018 C2's heliocentric orbit is not bound to the Solar System, unlike ʻOumuamua, it is not an interstellar object. The heliocentric eccentricity drops below 1 starting with an epoch of January 2023, when it is 13.8 AU from the Sun, making the orbit bound to the Sun before it leaves the planetary region of the Solar System. The more stable barycentric orbit of A/2018 C2, shows that it is only a very distant small Solar System body, approaching as far as 50,0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JPL Small-Body Database
The JPL Small-Body Database (SBDB) is an astronomy database about small Solar System bodies. It is maintained by Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and NASA and provides data for all known asteroids and several comets, including orbital parameters and diagrams, physical diagrams, close approach details, radar astrometry, discovery circumstances, alternate designations and lists of publications related to the small body. The database is updated daily when new observations are available. In April 2021 the JPL Small-Body Database Browser started using planetary ephemeris ( DE441) and small-body perturber SB441-N16. Most objects such as asteroids get a two-body solution (Sun+object) recomputed twice a year. Comets generally have their two-body orbits computed at a time near the perihelion passage (closest approach to the Sun) as to have the two-body orbit more reasonably accurate for both before and after perihelion. For most asteroids, the epoch used to define an orbit is updated twice a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |