|
Hyperbaric Chamber
A diving chamber is a vessel for human occupation, which may have an entrance that can be sealed to hold an internal pressure significantly higher than ambient pressure, a pressurised gas system to control the internal pressure, and a supply of breathing gas for the occupants. There are two main functions for diving chambers: * as a simple form of submersible vessel to transport divers underwater and to provide a temporary base and retrieval system in the depths; * as a land, ship or offshore platform-based hyperbaric chamber or system, to artificially reproduce the hyperbaric conditions under the sea. Internal pressures above normal atmospheric pressure are provided for diving-related applications such as saturation diving and diver decompression, and non-diving medical applications such as hyperbaric medicine. Basic types of diving chambers There are two basic types of submersible diving chambers, differentiated by the way in which the pressure in the diving chamber is pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutral Buoyancy Lab
The Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory (NBL) is an astronaut training facility and neutral buoyancy pool operated by NASA and located at the Sonny Carter Training Facility, near the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. The NBL's main feature is a large indoor pool of water, in which astronauts may perform simulated EVA tasks in preparation for upcoming missions. Trainees wear suits designed to provide neutral buoyancy to simulate the microgravity that astronauts would experience during spaceflight. History In the late 1980s NASA began to consider replacing its previous neutral-buoyancy training facility, the Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF). The WETF, located at Johnson Space Center, had been successfully used to train astronauts for numerous missions, but its pool was too small to hold useful mock-ups of space station components of the sorts intended for the mooted Space Station ''Freedom'', or its successor, the International Space Station. This new pool was going ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Supplied Diving
Surface-supplied diving is diving using equipment supplied with breathing gas using a diver's umbilical from the surface, either from the shore or from a diving support vessel, sometimes indirectly via a diving bell. This is different from scuba diving, where the diver's breathing equipment is completely self-contained and there is no link to the surface. The primary advantages of conventional surface supplied diving are lower risk of drowning and considerably larger breathing gas supply than scuba, allowing longer working periods and safer decompression. Disadvantages are the absolute limitation on diver mobility imposed by the length of the umbilical, encumbrance by the umbilical, and high logistical and equipment costs compared with scuba. The disadvantages restrict use of this mode of diving to applications where the diver operates within a small area, which is common in commercial diving work. The copper helmeted free-flow standard diving dress is the version which made com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarines
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely operated vehicles and robots, as well as medium-sized or smaller vessels, such as the midget submarine and the wet sub. Submarines are referred to as ''boats'' rather than ''ships'' irrespective of their size. Although experimental submarines had been built earlier, submarine design took off during the 19th century, and they were adopted by several navies. They were first widely used during World War I (1914–1918), and are now used in many navies, large and small. Military uses include attacking enemy surface ships (merchant and military) or other submarines, and for aircraft carrier protection, blockade running, nuclear deterrence, reconnaissance, conventional land attack (for example, using a cruise missile), and covert insertion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submersibles
A submersible is a small watercraft designed to operate underwater. The term "submersible" is often used to differentiate from other underwater vessels known as submarines, in that a submarine is a fully self-sufficient craft, capable of independent cruising with its own power supply and air renewal system, whereas a submersible is usually supported by a nearby surface vessel, platform, shore team or sometimes a larger submarine. In common usage by the general public, however, the word "submarine" may be used to describe a craft that is by the technical definition actually a submersible. There are many types of submersibles, including both crewed and uncrewed craft, otherwise known as remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) or unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs). Submersibles have many uses worldwide, such as oceanography, underwater archaeology, ocean exploration, adventure, equipment maintenance and recovery, and underwater videography. History The first underwater vessel was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underwater Habitat
Underwater habitats are underwater structures in which people can live for extended periods and carry out most of the basic human functions of a 24-hour day, such as working, resting, eating, attending to personal hygiene, and sleeping. In this context, 'habitat' is generally used in a narrow sense to mean the interior and immediate exterior of the structure and its fixtures, but not its surrounding marine environment. Most early underwater habitats lacked regenerative systems for air, water, food, electricity, and other resources. However, some underwater habitats allow for these resources to be delivered using pipes, or generated within the habitat, rather than manually delivered. An underwater habitat has to meet the needs of human physiology and provide suitable environmental conditions, and the one which is most critical is breathing air of suitable quality. Others concern the physical environment (pressure, temperature, light, humidity), the chemical environment (drink ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
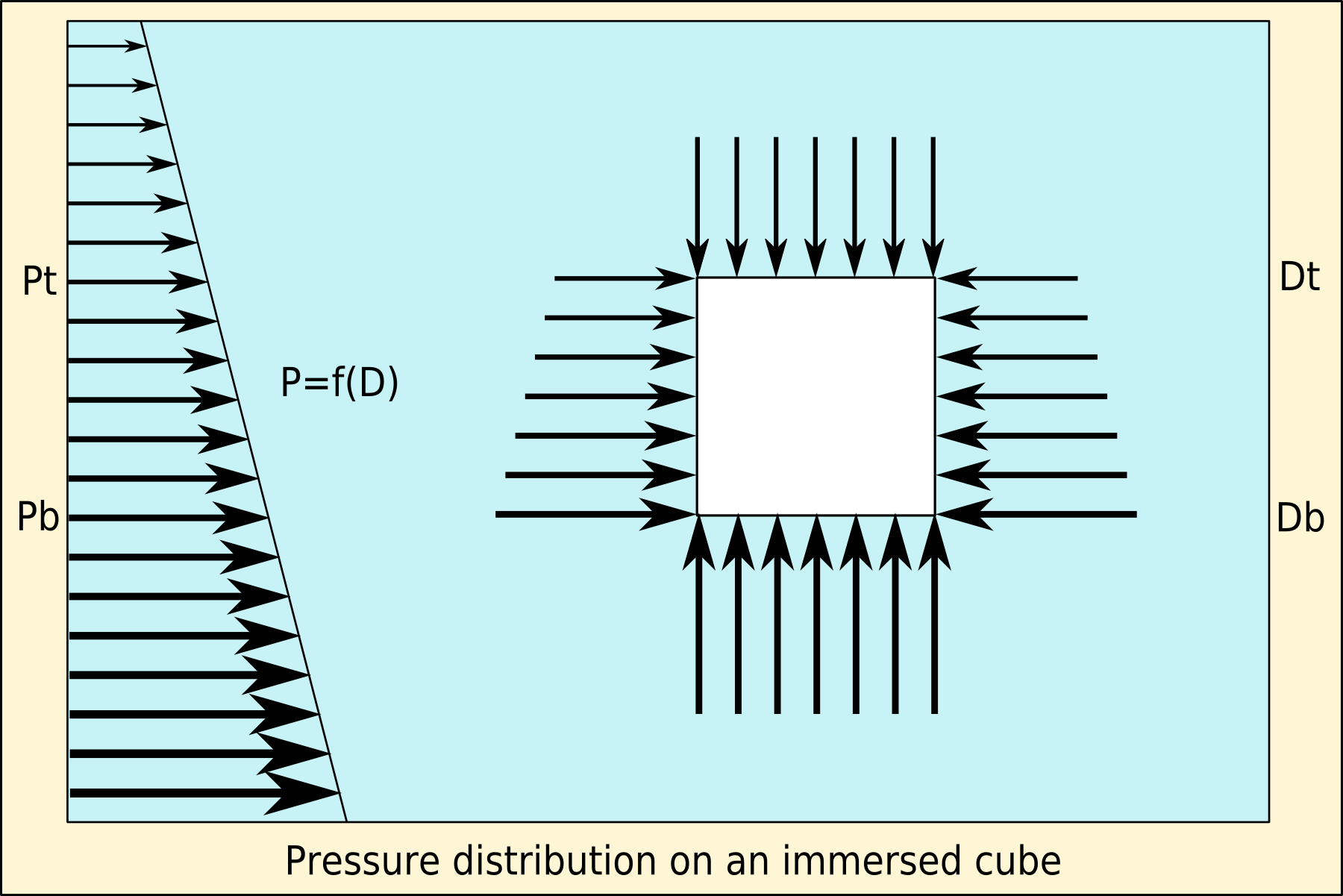
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umbilical Cable
An umbilical cable or umbilical is a cable and/or hose that supplies required consumables to an apparatus, like a rocket, or to a person, such as a diver or astronaut. It is named by analogy with an umbilical cord. An umbilical can, for example, supply air and power to a pressure suit or hydraulic power, electrical power and fiber optics to subsea equipment and divers. Spaceflight applications Rockets Umbilicals connect a missile or space vehicle to ground support equipment on the launch pad before launch. Cables carry electrical power, communications, and telemetry, and pipes or hoses carry liquid propellants, cryogenic fluids, and pressurizing and purge gases. These are automatically disconnected shortly before or at launch. Umbilical connections are also used between rocket stages, and between the rocket and its spacecraft payload; these umbilicals are disconnected as stages are disconnected and discarded. Space suits Early space suits used in Project Gemini in 1965 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wire Rope
Steel wire rope (right hand lang lay) Wire rope is several strands of metal wire twisted into a helix forming a composite ''rope'', in a pattern known as ''laid rope''. Larger diameter wire rope consists of multiple strands of such laid rope in a pattern known as ''cable laid''. In stricter senses, the term ''wire rope'' refers to a diameter larger than , with smaller gauges designated cable or cords. Initially wrought iron wires were used, but today steel is the main material used for wire ropes. Historically, wire rope evolved from wrought iron chains, which had a record of mechanical failure. While flaws in chain links or solid steel bars can lead to catastrophic failure, flaws in the wires making up a steel cable are less critical as the other wires easily take up the load. While friction between the individual wires and strands causes wear over the life of the rope, it also helps to compensate for minor failures in the short run. Wire ropes were developed starting with min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diving Support Vessel
A diving support vessel is a ship that is used as a floating base for professional diving projects. Basic requirements are the ability to keep station accurately and reliably throughout a diving operation, often in close proximity to drilling or production platforms, for positioning to degrade slowly enough in deteriorating conditions to recover divers without excessive risk, and to carry the necessary support equipment for the mode of diving to be used. Recent offshore diving support vessels tend to be dynamically positioned (DP) and double as remotely operated underwater vehicle (ROV) support vessels, and also be capable of supporting seismic survey operations and cable-laying operations. DP makes a wider range of operations possible, but the platform presents some inherent hazards, particularly the thrusters, making launch and recovery by diving bell widespread. They may use a moonpool to shelter the position where the bell or ROV enters and exits the water, and the launch an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underwater Habitat
Underwater habitats are underwater structures in which people can live for extended periods and carry out most of the basic human functions of a 24-hour day, such as working, resting, eating, attending to personal hygiene, and sleeping. In this context, 'habitat' is generally used in a narrow sense to mean the interior and immediate exterior of the structure and its fixtures, but not its surrounding marine environment. Most early underwater habitats lacked regenerative systems for air, water, food, electricity, and other resources. However, some underwater habitats allow for these resources to be delivered using pipes, or generated within the habitat, rather than manually delivered. An underwater habitat has to meet the needs of human physiology and provide suitable environmental conditions, and the one which is most critical is breathing air of suitable quality. Others concern the physical environment (pressure, temperature, light, humidity), the chemical environment (drink ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely operated vehicles and Autonomous underwater vehicle, robots, as well as medium-sized or smaller vessels, such as the midget submarine and the wet sub. Submarines are referred to as ''boats'' rather than ''ships'' irrespective of their size. Although experimental submarines had been built earlier, submarine design took off during the 19th century, and they were adopted by several navies. They were first widely used during World War I (1914–1918), and are now used in many navy, navies, large and small. Military uses include attacking enemy surface ships (merchant and military) or other submarines, and for aircraft carrier protection, Blockade runner, blockade running, Ballistic missile submarine, nuclear deterrence, reconnaissance, conventio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airlock
An airlock, air-lock or air lock, often abbreviated to just lock, is a compartment with doors which can be sealed against pressure which permits the passage of people and objects between environments of differing pressure or atmospheric composition while minimizing the change of pressure in the adjoining spaces and mixing of environments. The lock consists of a relatively small chamber with two airtight doors in series which do not open simultaneously. An airlock may be used for passage between environments of different gases or different pressures, or both, to minimize pressure loss or prevent the gases from mixing. An airlock may also be used underwater to allow passage between an air environment in a pressure vessel and the water environment outside, in which case the airlock can contain air or water. This is called a floodable airlock or an underwater airlock, and is used to prevent water from entering a submersible vessel or an underwater habitat. Air-locks are used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)


