|
Hydrocholeretic
Hydrocholeretics are substances that increase the volume of secretion of bile from the liver without increasing the amount of solids secreted. Some substances can result in decreased solid production, possibly due to circulatory effects. Cyclobutyrol is a compound commonly used as a hydrocholeretic. Its effects in rats include a dose-dependent increase in bile flow, sodium, potassium, chloride and bicarbonate outputs and reduced bile acid concentrations. See also * Cholekinetic * Choleretic Choleretics are substances that increase the volume of secretion of bile from the liver as well as the amount of solids secreted. See also * Cholekinetic * Hydrocholeretic Hydrocholeretics are substances that increase the volume of secretion of bi ... References Bile acids {{gastrointestinal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholekinetic
A cholekinetic drug is a pharmaceutical drug which increases the contractile power of the bile duct. See also * Choleretic * Hydrocholeretic Hydrocholeretics are substances that increase the volume of secretion of bile from the liver without increasing the amount of solids secreted. Some substances can result in decreased solid production, possibly due to circulatory effects. Cyclobuty ... Drugs {{gastrointestinal-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choleretic
Choleretics are substances that increase the volume of secretion of bile from the liver as well as the amount of solids secreted. See also * Cholekinetic * Hydrocholeretic Hydrocholeretics are substances that increase the volume of secretion of bile from the liver without increasing the amount of solids secreted. Some substances can result in decreased solid production, possibly due to circulatory effects. Cyclobuty ... References {{gastrointestinal-drug-stub Bile acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
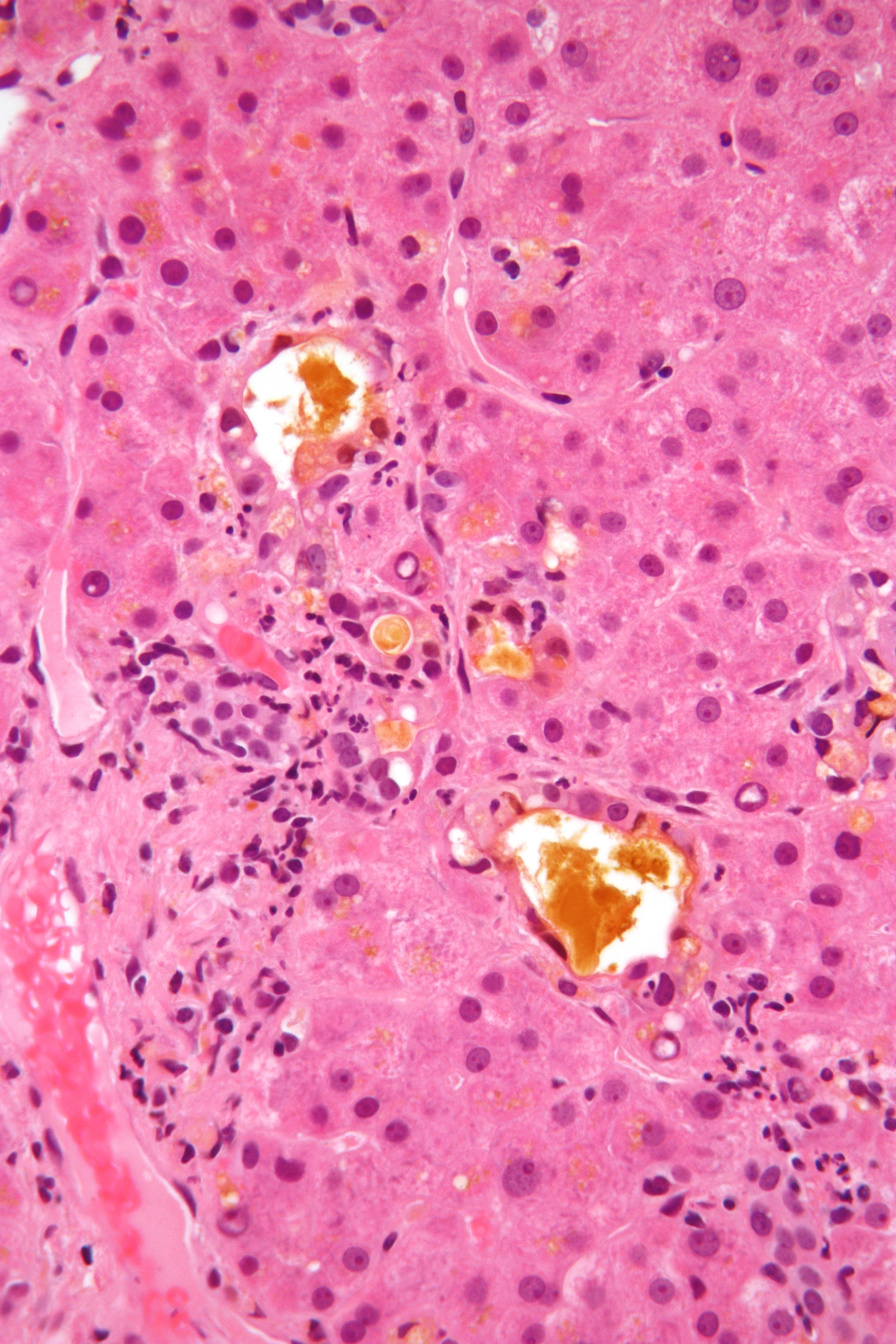
Bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver (liver bile) and stored and concentrated in the gallbladder. After eating, this stored bile is discharged into the duodenum. The composition of hepatic bile is (97–98)% water, 0.7% bile salts, 0.2% bilirubin, 0.51% fats (cholesterol, fatty acids, and lecithin), and 200 meq/L inorganic salts. The two main pigments of bile are bilirubin, which is yellow, and its oxidised form biliverdin, which is green. When mixed, they are responsible for the brown color of feces. About 400 to 800 millilitres of bile is produced per day in adult human beings. Function Bile or gall acts to some extent as a surfactant, helping to emulsify the lipids in food. Bile salt anions are hydrophilic on one side and hydrophobic on the other side; consequently, they tend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclobutyrol
Cyclobutyrol is a drug used in bile therapy. Cyclobutyrol (CB) is a choleretic Choleretics are substances that increase the volume of secretion of bile from the liver The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the sy ... agent which also inhibits biliary lipids secretion. References * Beta hydroxy acids Cyclohexanols {{gastrointestinal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |