|
Hydraulic Brakes
A hydraulic brake is an arrangement of braking mechanism which uses brake fluid, typically containing glycol ethers or diethylene glycol, to transfer pressure from the controlling mechanism to the braking mechanism. History During 1904, Frederick George Heath (Heath Hydraulic Brake Co., Ltd.), Redditch, England devised and fitted a hydraulic (water/glycerine) brake system to a cycle using a handlebar lever and piston. He obtained patent GB190403651A for “Improvements in hydraulic actuated brakes for cycles and motors”, as well as subsequently for improved flexible rubber hydraulic pipes. In 1908, Ernest Walter Weight of Bristol, England devised and fitted a four-wheel hydraulic (oil) braking system to a motor car. He patented it in Great Britain (GB190800241A) in December 1908, later in Europe and the USA and then exhibited it at the 1909 London Motor Show. His brother, William Herbert Weight improved the patent (GB190921122A) and both were assigned to the Weight Patent Aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
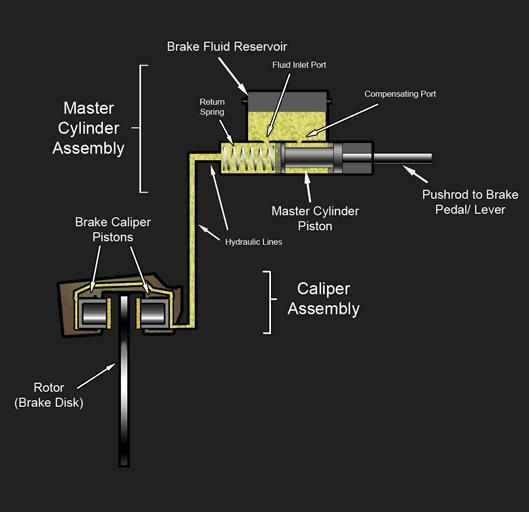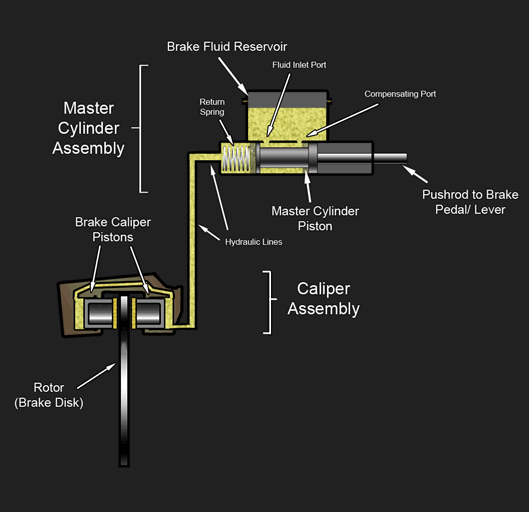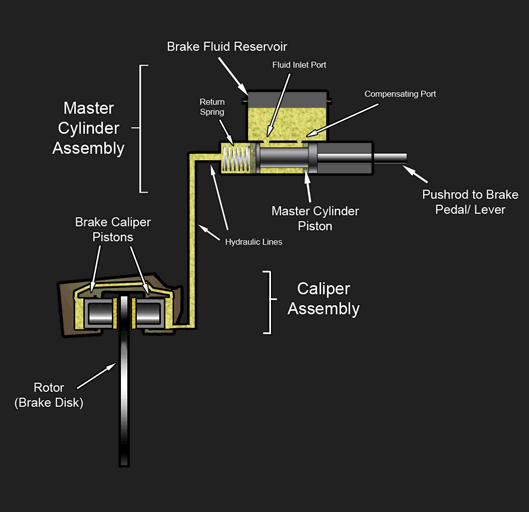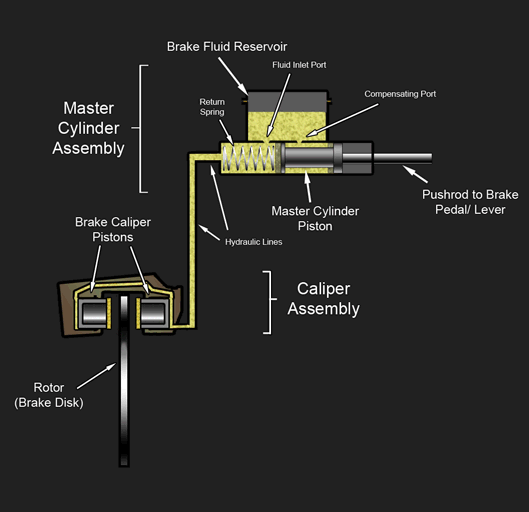
Hydraulic Disc Brake Diagram
Hydraulics (from Greek: Υδραυλική) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concerns gases. Fluid mechanics provides the theoretical foundation for hydraulics, which focuses on the applied engineering using the properties of fluids. In its fluid power applications, hydraulics is used for the generation, control, and transmission of power by the use of pressurized liquids. Hydraulic topics range through some parts of science and most of engineering modules, and cover concepts such as pipe flow, dam design, fluidics and fluid control circuitry. The principles of hydraulics are in use naturally in the human body within the vascular system and erectile tissue. Free surface hydraulics is the branch of hydraulics dealing with free surface flow, such as occurring in rivers, canals, lakes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
O-rings
An O-ring, also known as a packing or a toric joint, is a mechanical gasket in the shape of a torus; it is a loop of elastomer with a round cross-section, designed to be seated in a groove and compressed during assembly between two or more parts, forming a seal at the interface. The O-ring may be used in static applications or in dynamic applications where there is relative motion between the parts and the O-ring. Dynamic examples include rotating pump shafts and hydraulic cylinder pistons. Static applications of O-rings may include fluid or gas sealing applications in which: (1) the O-ring is compressed resulting in zero clearance, (2) the O-ring material is vulcanized solid such that it is impermeable to the fluid or gas, and (3) the O-ring material is resistant to degradation by the fluid or gas. The wide range of potential liquids and gases that need to be sealed has necessitated the development of a wide range of materials. O-rings are one of the most common seals used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newton (unit)
The newton (symbol: N) is the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI). It is defined as 1 kg⋅m/s, the force which gives a mass of 1 kilogram an acceleration of 1 metre per second per second. It is named after Isaac Newton in recognition of his work on classical mechanics, specifically Newton's second law of motion. Definition A newton is defined as 1 kg⋅m/s (it is a derived unit which is defined in terms of the SI base units). One newton is therefore the force needed to accelerate one kilogram of mass at the rate of one metre per second squared in the direction of the applied force. The units "metre per second squared" can be understood as measuring a rate of change in velocity per unit of time, i.e. an increase in velocity by 1 metre per second every second. In 1946, Conférence Générale des Poids et Mesures (CGPM) Resolution 2 standardized the unit of force in the MKS system of units to be the amount needed to accelerate 1 kilogram of mass at the rat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disc Brake
A disc brake is a type of brake that uses the calipers to squeeze pairs of pads against a disc or a "rotor" to create friction. This action slows the rotation of a shaft, such as a vehicle axle, either to reduce its rotational speed or to hold it stationary. The energy of motion is converted into waste heat which must be dispersed. Hydraulically actuated disc brakes are the most commonly used form of brake for motor vehicles, but the principles of a disc brake are applicable to almost any rotating shaft. The components include the disc, master cylinder, and caliper (which contains a cylinder and two brake pads) on both sides of the disc. Design The development of disc-type brakes began in England in the 1890s. In 1902, the Lanchester Motor Company designed brakes that looked and operated in a similar way to a modern disc-brake system even though the disc was thin and a cable activated the brake pad. Other designs were not practical or widely available in cars for anothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brake Shoes
A brake shoe is the part of a braking system which carries the brake lining in the drum brakes used on automobiles, or the brake block in train brakes and bicycle brakes. A device that is put on a track to slow down railroad cars is also called brake shoe. Automobile drum brake The brake shoe carries the brake lining, which is riveted or glued to the shoe. When the brake is applied, the shoe moves and presses the lining against the inside of the drum. The friction between lining and drum provides the braking effort. Energy is dissipated as heat. Modern cars have disc brakes all round, or discs at the front and drums at the rear. An advantage of discs is that they can dissipate heat more quickly than drums so there is less risk of overheating. The reason for retaining drums at the rear is that a drum is more effective than a disc as a parking brake. Railway tread brake The brake shoe carries the brake block. The block was originally made of wood, then usage of cast ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel Cylinder
A wheel cylinder is a component of a hydraulic drum brake system. It is located in each wheel and is usually positioned at the top of the wheel, above the shoes. Its function is to exert force onto the shoes so as to bring them into contact with the drum and stop the vehicle with friction Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: *Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of .... The wheel cylinders are usually connected to the shoes with small bird-beak shaped rods. Wheel cylinders were first invented by Bendix in 1958. It is very similar to a slave cylinder and functions in much the same way, internally consisting of only a simple plunger. On older vehicles, these may begin to leak and hinder the performance of the brakes. They are, however, normally inexpensive and relatively easy to replace. The wheel cylinder con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sintered Glass
Fritted glass is finely porous glass through which gas or liquid may pass. It is made by sintering together glass particles into a solid but porous body. This porous glass body can also be called a frit. Applications in laboratory glassware include use in fritted glass filter items, scrubbers, or spargers. Other laboratory applications of fritted glass include packing in chromatography columns and resin beds for special chemical synthesis. In a fritted glass filter, a disc or pane of fritted glass is used to filter out solid particles, precipitate, or residue from a fluid, similar to a piece of filter paper. The fluid can go through the pores in the fritted glass, but the frit will often stop a solid from going through. A fritted filter is often part of a glassware item, so fritted glass funnels and fritted glass crucibles are available. Laboratory scale sparger In chemistry, sparging, also known as gas flushing in metallurgy, is a technique in which a gas is bubble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kevlar
Kevlar (para-aramid) is a strong, heat-resistant synthetic fiber, related to other aramids such as Nomex and Technora. Developed by Stephanie Kwolek at DuPont in 1965, the high-strength material was first used commercially in the early 1970s as a replacement for steel in racing tires. It is typically spun into ropes or fabric sheets that can be used as such, or as an ingredient in composite material components. Kevlar has many applications, ranging from bicycle tires and racing sails to bulletproof vests, all due to its high tensile strength-to-weight ratio; by this measure it is five times stronger than steel. It is also used to make modern marching drumheads that withstand high impact; and for mooring lines and other underwater applications. A similar fiber called Twaron with the same chemical structure was developed by Akzo in the 1970s; commercial production started in 1986, and Twaron is now manufactured by Teijin. History Poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide (K2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of the body. The concept originated with the studies by Archimedes of the usage of levers, which is reflected in his famous quote: "''Give me a lever and a place to stand and I will move the Earth''". Just as a linear force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist to an object around a specific axis. Torque is defined as the product of the magnitude of the perpendicular component of the force and the distance of the line of action of a force from the point around which it is being determined. The law of conservation of energy can also be used to understand torque. The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Project Video Camera
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macroscopic single crystals are usually identifiable by their geometrical shape, consisting of flat faces with specific, characteristic orientations. The scientific study of crystals and crystal formation is known as crystallography. The process of crystal formation via mechanisms of crystal growth is called crystallization or solidification. The word ''crystal'' derives from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning both "ice" and "rock crystal", from (), "icy cold, frost". Examples of large crystals include snowflakes, diamonds, and table salt. Most inorganic solids are not crystals but polycrystals, i.e. many microscopic crystals fused together into a single solid. Polycrystals include most metals, rocks, ceramics, and ice. A third category of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycol Ethers
Glycol ethers are a class of chemical compounds consisting of alkyl ethers that are based on glycols such as ethylene glycol or propylene glycol. They are commonly used as solvents in paints and cleaners. They have good solvent properties while having higher boiling points than the lower-molecular-weight ethers and alcohols. The name "Cellosolve" was registered in 1924 as a United States trademark by Carbide & Carbon Chemicals Corporation (a division of Union Carbide Corporation) for "Solvents for Gums, Resins, Cellulose Esters, and the Like". "Ethyl Cellosolve" or simply "Cellosolve" consists mainly of ethylene glycol monoethyl ether and was introduced as a lower-cost solvenet alternative to ethyl lactate. "Butyl Cellosolve" (ethylene glycol monobutyl ether) was introduced in 1928, and "Methyl Cellosolve" ( ethylene glycol monomethyl ether) in 1929. Glycol ethers are designated "E-series" for or "P-series" for those made from ethylene oxide or propylene oxide, respectively. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drum Brake
A drum brake is a brake that uses friction caused by a set of shoes or pads that press outward against a rotating cylinder-shaped part called a brake drum. The term ''drum brake'' usually means a brake in which shoes press on the inner surface of the drum. When shoes press on the outside of the drum, it is usually called a ''clasp brake''. Where the drum is pinched between two shoes, similar to a conventional disc brake, it is sometimes called a ''pinch drum brake'', though such brakes are relatively rare. A related type called a band brake uses a flexible belt or "band" wrapping around the outside of a drum. History The modern automobile drum brake was first used in a car made by Maybach in 1900, although the principle was only later patented in 1902 by Louis Renault. He used woven asbestos lining for the drum brake lining, as no alternative dissipated heat like the asbestos lining, though Maybach had used a less sophisticated drum brake. In the first drum brakes, levers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |