|
Hydnora Abyssinica
''Hydnora'' is a group of parasitic plants described as a genus in 1775. It is native to Africa, Madagascar, and the Arabian Peninsula. Hydnora pollinates through brood-site mimicry. This is a method of pollination in which the plant emits a smell that is attractive to insects, so that the plant can trap the insect and allow to take pollen so that it can pollinate other Hydnora. Taxonomy The following species are listed within the genus ''Hydnora'': # ''Hydnora abyssinica'' A.Br. - Oman, Yemen, Saudi Arabia; S + C + SE + E Africa from Eritrea + Sudan to Namibia + KwaZulu-Natal # ''Hydnora africana'' Thunb. - Angola, Namibia, Cape Province #''Hydnora arabica'' Bolin & Musselman - Oman & Yemen # ''Hydnora esculenta'' Jum. & H.Perrier - Madagascar # ''Hydnora sinandevu'' Beentje & Q.Luke - Kenya, Tanzania # ''Hydnora triceps'' Drège & E.Mey. - Northern Cape Province, Namibia # ''Hydnora visseri'' Bolin, E.Maass, & Musselman - Northern Cape Province, Namibia Etymology The genus name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thunb
Carl Peter Thunberg, also known as Karl Peter von Thunberg, Carl Pehr Thunberg, or Carl Per Thunberg (11 November 1743 – 8 August 1828), was a Swedish naturalist and an "apostle" of Carl Linnaeus. After studying under Linnaeus at Uppsala University, he spent seven years travelling in southern Africa and Asia, collecting and describing many plants and animals new to European science, and observing local cultures. He has been called "the father of South African botany", "pioneer of Occidental Medicine in Japan", and the "Japanese Linnaeus". Early life Thunberg was born and grew up in Jönköping, Sweden. At the age of 18, he entered Uppsala University where he was taught by Carl Linnaeus, regarded as the "father of modern taxonomy". Thunberg graduated in 1767 after 6 years of studying. To deepen his knowledge in botany, medicine and natural history, he was encouraged by Linnaeus in 1770 to travel to Paris and Amsterdam. In Amsterdam and Leiden Thunberg met the Dutch botanis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydnora Esculenta
''Hydnora'' is a group of parasitic plants described as a genus in 1775. It is native to Africa, Madagascar, and the Arabian Peninsula. Hydnora pollinates through brood-site mimicry. This is a method of pollination in which the plant emits a smell that is attractive to insects, so that the plant can trap the insect and allow to take pollen so that it can pollinate other Hydnora. Taxonomy The following species are listed within the genus ''Hydnora'': # ''Hydnora abyssinica'' A.Br. - Oman, Yemen, Saudi Arabia; S + C + SE + E Africa from Eritrea + Sudan to Namibia + KwaZulu-Natal # ''Hydnora africana'' Thunb. - Angola, Namibia, Cape Province #''Hydnora arabica'' Bolin & Musselman - Oman & Yemen # ''Hydnora esculenta'' Jum. & H.Perrier - Madagascar Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of Eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
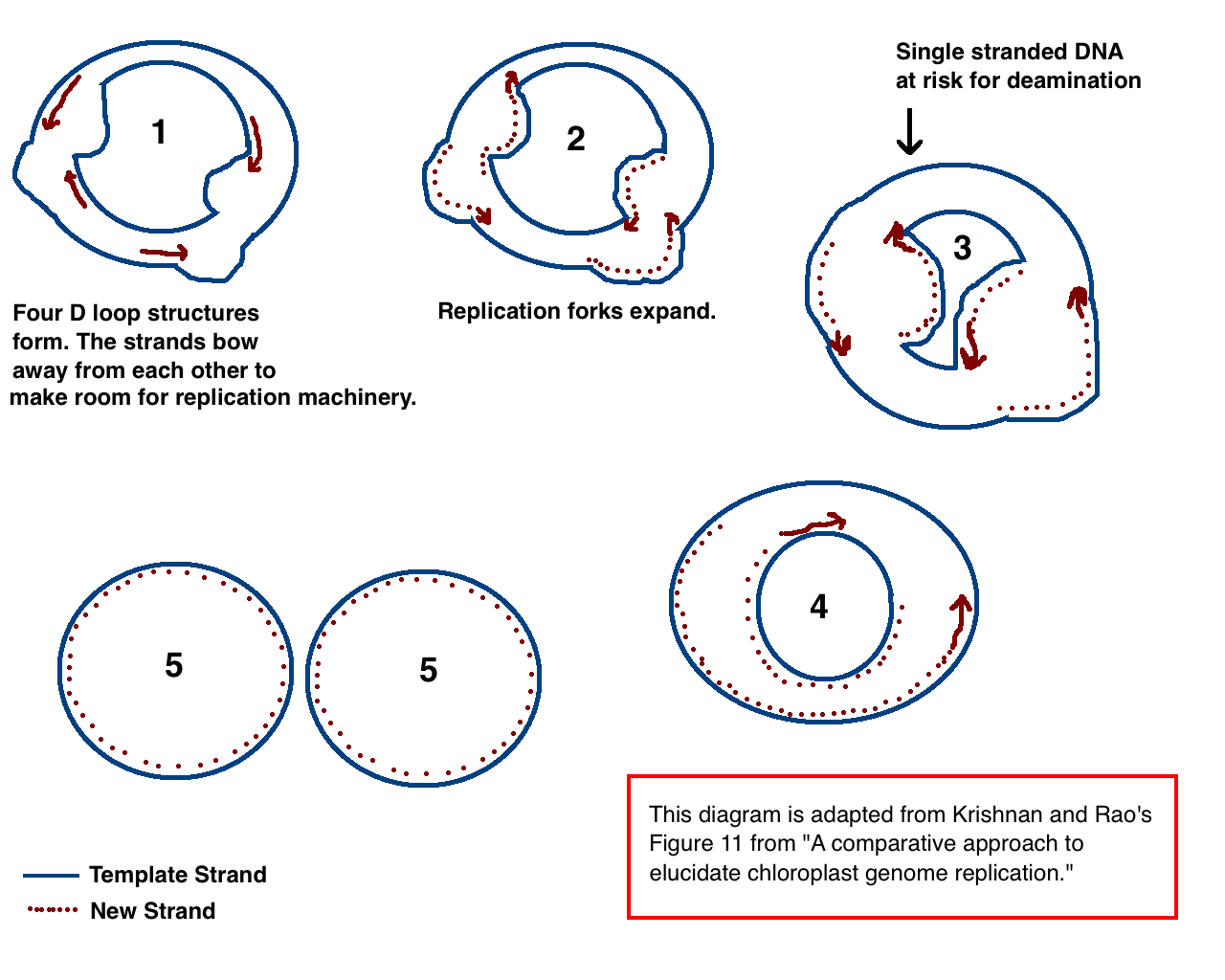
Chloroplast Genome
Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) is the DNA located in chloroplasts, which are photosynthetic organelles located within the cells of some eukaryotic organisms. Chloroplasts, like other types of plastid, contain a genome separate from that in the cell Cell nucleus, nucleus. The existence of chloroplast DNA was identified biochemically in 1959, and confirmed by electron microscopy in 1962. The discoveries that the chloroplast contains ribosomes and performs protein synthesis revealed that the chloroplast is genetically semi-autonomous. The first complete chloroplast genome sequences were published in 1986, ''Nicotiana tabacum'' (tobacco) by Sugiura and colleagues and ''Marchantia polymorpha'' (liverwort) by Ozeki et al. Since then, List of sequenced plastomes, a great number of chloroplast DNAs from various species have been DNA sequencing, sequenced. Molecular structure Chloroplast DNAs are circular, and are typically 120,000–170,000 base pairs long. They can have a contour length of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowering Plants
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. They include all forbs (flowering plants without a woody stem), grasses and grass-like plants, a vast majority of broad-leaved trees, shrubs and vines, and most aquatic plants. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ἀγγεῖον / ('container, vessel') and σπέρμα / ('seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed within a fruit. They are by far the most diverse group of land plants with 64 orders, 416 families, approximately 13,000 known genera and 300,000 known species. Angiosperms were formerly called Magnoliophyta (). Angiosperms are distinguished from the other seed-producing plants, the gymnosperms, by having flowers, xylem consisting of vessel elements instead of tracheids, endosperm within their seeds, and fruits that completely envelop the seeds. The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from the common ancestor of all livi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowering Plant
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants that produce their seeds enclosed within a fruit. They are by far the most diverse group of land plants with 64 orders, 416 families, approximately 13,000 known genera and 300,000 known species. Angiosperms were formerly called Magnoliophyta (). Like gymnosperms, angiosperms are seed-producing plants. They are distinguished from gymnosperms by characteristics including flowers, endosperm within their seeds, and the production of fruits that contain the seeds. The ancestors of flowering plants diverged from the common ancestor of all living gymnosperms before the end of the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. The closest fossil relatives of flowering plants are uncertain and contentious. The earliest angiosperm fossils ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastid Genome
Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) is the DNA located in chloroplasts, which are photosynthetic organelles located within the cells of some eukaryotic organisms. Chloroplasts, like other types of plastid, contain a genome separate from that in the cell nucleus. The existence of chloroplast DNA was identified biochemically in 1959, and confirmed by electron microscopy in 1962. The discoveries that the chloroplast contains ribosomes and performs protein synthesis revealed that the chloroplast is genetically semi-autonomous. The first complete chloroplast genome sequences were published in 1986, ''Nicotiana tabacum'' (tobacco) by Sugiura and colleagues and ''Marchantia polymorpha'' (liverwort) by Ozeki et al. Since then, a great number of chloroplast DNAs from various species have been sequenced. Molecular structure Chloroplast DNAs are circular, and are typically 120,000–170,000 base pairs long. They can have a contour length of around 30–60 micrometers, and have a mass of about 80–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastome Map Of Hydnora Visseri
Chloroplast DNA (cpDNA) is the DNA located in chloroplasts, which are photosynthetic organelles located within the cells of some eukaryotic organisms. Chloroplasts, like other types of plastid, contain a genome separate from that in the cell nucleus. The existence of chloroplast DNA was identified biochemically in 1959, and confirmed by electron microscopy in 1962. The discoveries that the chloroplast contains ribosomes and performs protein synthesis revealed that the chloroplast is genetically semi-autonomous. The first complete chloroplast genome sequences were published in 1986, ''Nicotiana tabacum'' (tobacco) by Sugiura and colleagues and ''Marchantia polymorpha'' (liverwort) by Ozeki et al. Since then, a great number of chloroplast DNAs from various species have been sequenced. Molecular structure Chloroplast DNAs are circular, and are typically 120,000–170,000 base pairs long. They can have a contour length of around 30–60 micrometers, and have a mass of about 80� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truffle
A truffle is the fruiting body of a subterranean ascomycete fungus, predominantly one of the many species of the genus ''Tuber''. In addition to ''Tuber'', many other genera of fungi are classified as truffles including ''Geopora'', ''Peziza'', ''Choiromyces'', ''Leucangium'', and over a hundred others. These genera belong to the class Pezizomycetes and the Pezizales order. Several truffle-like basidiomycetes are excluded from Pezizales, including ''Rhizopogon'' and ''Glomus''. Truffles are ectomycorrhizal fungi, so they are usually found in close association with tree roots. Spore dispersal is accomplished through fungivores, animals that eat fungi. These fungi have significant ecological roles in nutrient cycling and drought tolerance. Some truffle species are highly prized as food. French gastronome Jean Anthelme Brillat-Savarin called truffles "the diamond of the kitchen". Edible truffles are used in Italian, French and numerous other national . Truffles are cultivat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic period (), and the Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Epic and Classical periods of the language. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regarded as a separate historical stage, although its earliest form closely resembles Attic Greek and its latest form approaches Medieval Greek. There were several regional dialects of Ancient Greek, of which Attic Greek developed into Koine. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydnora Visseri
''Hydnora visseri'', the Visser's hydnora, is a subterranean holoparasitic plant, lacking leaves and roots, and is described from southwestern Namibia and northwestern South Africa and has the longest tepal lobes of all ''Hydnora'' species. The genus ''Hydnora'' is composed entirely of holoparasitic plants that attach to the root of their hosts and are restricted to Africa and southwestern Asia. Description ''Hydnora visseri'', as a holoparasitic plant, lacks chlorophyll and depends entirely on its hosts, '' Euphorbia gregaria'' or ''E. gummifera'', for all water and nutrition. ''H. visseri'' lacks leaves and roots. The vegetative body of the plant is a brown warty rhizome that spreads laterally through the soil. The bumps on the rhizome of ''Hydnora'' spp. can differentiate into haustoria (specialized organs for parasitizing the host plant), flower buds, or bifurcations of the rhizome. The rhizomes when broken are reddish to pink and contain high levels of tannins. The only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Cape Province
The Northern Cape is the largest and most sparsely populated province of South Africa. It was created in 1994 when the Cape Province was split up. Its capital is Kimberley, South Africa, Kimberley. It includes the Kalahari Gemsbok National Park, part of the Kgalagadi Transfrontier Park and an Transboundary Protected Area, international park shared with Botswana. It also includes the Augrabies Falls and the diamond mining regions in Kimberley and Alexander Bay, Northern Cape, Alexander Bay. The Namaqualand region in the west is famous for its Dimorphotheca sinuata, Namaqualand daisies. The southern towns of De Aar and Colesberg found within the Great Karoo are major transport nodes between Johannesburg, Cape Town and Port Elizabeth. Kuruman can be found in the north-east and is known as a Mission (station), mission station. It is also well known for its artesian spring and Eye of Kuruman. The Orange River flows through the province of Northern Cape, forming the borders with the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydnora Triceps
''Hydnora triceps'' is a holoparasitic flowering plant native to Africa that grows on the roots of '' Euphorbia dregeana''. Completely lacking in chlorophyll, it depends on its host for water and nutrients. The plant structure is composed of only specialized stems, buds, and haustoria, lacking any leaf-like structures entirely. It spends its life underground and only emerges to flower. Taxonomy German botanist Johann Franz Drège described ''Hydnora triceps'' in 1830 after collecting it from the Northwestern Cape. It was then thought extinct for many years until rediscovered by botanist Johann Visser in 1988. It is one of four species of parasitic underground plants in the genus '' Hydnora''. Distribution ''Hydnora triceps'' is found only in the northwestern Cape and southern Namibia. Additionally, since it is entirely dependent on '' Euphorbia dregeana'', which also seems to be its exclusive host, it is only found in association with this plant. About 10% of all the ''Euphorbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |