|
Hybridization Probe
In molecular biology, a hybridization probe (HP) is a fragment of DNA or RNA of usually 15–10000 nucleotide long which can be radioactively or fluorescently labeled. HP can be used to detect the presence of nucleotide sequences in analyzed RNA or DNA that are complementary to the sequence in the probe. The labeled probe is first denatured (by heating or under alkaline conditions such as exposure to sodium hydroxide) into single stranded DNA (ssDNA) and then hybridized to the target ssDNA ( Southern blotting) or RNA (northern blotting) immobilized on a membrane or in situ. To detect hybridization of the probe to its target sequence, the probe is tagged (or "labeled") with a molecular marker of either radioactive or (more recently) fluorescent molecules. Commonly used markers are 32P (a radioactive isotope of phosphorus incorporated into the phosphodiester bond in the probe DNA), digoxigenin, a non-radioactive, antibody-based marker, biotin or fluorescein. DNA sequences o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physical structure of biological macromolecules is known as molecular biology. Molecular biology was first described as an approach focused on the underpinnings of biological phenomena - uncovering the structures of biological molecules as well as their interactions, and how these interactions explain observations of classical biology. In 1945 the term molecular biology was used by physicist William Astbury. In 1953 Francis Crick, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and colleagues, working at Medical Research Council unit, Cavendish laboratory, Cambridge (now the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology), made a double helix model of DNA which changed the entire research scenario. They proposed the DNA structure based on previous research done by Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digoxigenin
Digoxigenin (DIG) is a steroid found exclusively in the flowers and leaves of the plants ''Digitalis purpurea'', ''Digitalis orientalis'' and ''Digitalis lanata'' (foxgloves), where it is attached to sugars, to form the glycosides (e.g. Lanatoside C). Use in biotechnology Digoxigenin is a hapten, a small molecule with high antigenicity, that is used in many molecular biology applications similarly to other popular haptens such as 2,4-Dinitrophenol, biotin, and fluorescein. Typically, digoxigenin is introduced chemically (conjugation) into biomolecules (proteins, nucleic acids) to be detected in further assays. Kd of the digoxigenin-antibody interaction has been estimated at ~12 nM (compare to Kd~0.1pM for the biotin-streptavidin interaction). DIG-binding proteins. Tinberg et al. designed artificial proteins that bind DIG. Their best binder, DIG10.3, was a 141 amino acid protein that bound DIG with a dissociation constant (Kd) of 541 (+/- 193) pM. Anti-digoxigenin antibo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and plants, as opposed to a tissue extract or dead organism. This is not to be confused with experiments done ''in vitro'' ("within the glass"), i.e., in a laboratory environment using test tubes, Petri dishes, etc. Examples of investigations ''in vivo'' include: the pathogenesis of disease by comparing the effects of bacterial infection with the effects of purified bacterial toxins; the development of non-antibiotics, antiviral drugs, and new drugs generally; and new surgical procedures. Consequently, animal testing and clinical trials are major elements of ''in vivo'' research. ''In vivo'' testing is often employed over ''in vitro'' because it is better suited for observing the overall effects of an experiment on a living subject. In dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word ''cloning'' refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine. In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) to a large enough amount to study in detail. PCR was invented in 1983 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation; Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
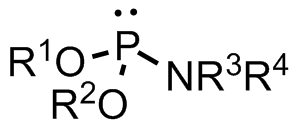
Phosphoramidite
A phosphoramidite (RO)2PNR2 is a monoamide of a phosphite diester. The key feature of phosphoramidites is their markedly high reactivity towards nucleophiles catalyzed by weak acids ''e.c''., triethylammonium chloride or 1''H''-tetrazole. In these reactions, the incoming nucleophile replaces the NR2 moiety. Applications Nucleoside phosphoramidites Phosphoramidites derived from protected nucleosides are referred to as nucleoside phosphoramidites and are widely used in chemical synthesis of DNA, RNA, and other nucleic acids and their analogs. As ligands Certain phosphoramidites are also used as monodentate chiral ligands in asymmetric synthesis. A large group of such ligands is derived from the chiral diol BINOL and can be synthesised by reaction of BINOL with phosphorus trichloride to the chlorophosphite and then reaction with simple secondary amines. This type of ligand was first used in 1996 in an asymmetric copper-catalysed addition of dialkylzincs to enones. See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligonucleotide Synthesis
Oligonucleotide synthesis is the chemical synthesis of relatively short fragments of nucleic acids with defined chemical structure (sequence). The technique is extremely useful in current laboratory practice because it provides a rapid and inexpensive access to custom-made oligonucleotides of the desired sequence. Whereas enzymes synthesize DNA and RNA only in a 5' to 3' direction, chemical oligonucleotide synthesis does not have this limitation, although it is most often carried out in the opposite, 3' to 5' direction. Currently, the process is implemented as solid-phase synthesis using phosphoramidite method and phosphoramidite building blocks derived from protected 2'-deoxynucleosides ( dA, dC, dG, and T), ribonucleosides ( A, C, G, and U), or chemically modified nucleosides, e.g. LNA or BNA. To obtain the desired oligonucleotide, the building blocks are sequentially coupled to the growing oligonucleotide chain in the order required by the sequence of the product (see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acid Methods
Nucleic acid methods are the techniques used to study nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. Purification *DNA extraction *Phenol–chloroform extraction *Minicolumn purification *RNA extraction * Boom method * Synchronous coefficient of drag alteration (SCODA) DNA purification Quantification *Abundance in weight: spectroscopic nucleic acid quantitation *Absolute abundance in number: real-time polymerase chain reaction (quantitative PCR) *High-throughput relative abundance: DNA microarray *High-throughput absolute abundance: serial analysis of gene expression (SAGE) *Size: gel electrophoresis Synthesis *''De novo'': oligonucleotide synthesis *Amplification: polymerase chain reaction (PCR) Kinetics * Multi-parametric surface plasmon resonance *Dual-polarization interferometry * Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) Gene function *RNA interference Other *Bisulfite sequencing * DNA sequencing *Expression cloning *Fluorescence in situ hybridization *Lab-on-a-chip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complementary DNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA synthesized from a single-stranded RNA (e.g., messenger RNA (mRNA) or microRNA (miRNA)) template in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. cDNA is often used to express a specific protein in a cell that does not normally express that protein (i.e., heterologous expression), or to sequence or quantify mRNA molecules using DNA based methods (qPCR, RNA-seq). cDNA that codes for a specific protein can be transferred to a recipient cell for expression, often bacterial or yeast expression systems. cDNA is also generated to analyze transcriptomic profiles in bulk tissue, single cells, or single nuclei in assays such as microarrays, qPCR, and RNA-seq. cDNA is also produced naturally by retroviruses (such as HIV-1, HIV-2, simian immunodeficiency virus, etc.) and then integrated into the host's genome, where it creates a provirus. The term ''cDNA'' is also used, typically in a bioinformatics context, to refer to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microarray
A microarray is a multiplex lab-on-a-chip. Its purpose is to simultaneously detect the expression of thousands of genes from a sample (e.g. from a tissue). It is a two-dimensional array on a solid substrate—usually a glass slide or silicon thin-film cell—that assays (tests) large amounts of biological material using high-throughput screening miniaturized, multiplexed and parallel processing and detection methods. The concept and methodology of microarrays was first introduced and illustrated in antibody microarrays (also referred to as antibody matrix) by Tse Wen Chang in 1983 in a scientific publication and a series of patents. The "gene chip" industry started to grow significantly after the 1995 ''Science Magazine'' article by the Ron Davis and Pat Brown labs at Stanford University. With the establishment of companies, such as Affymetrix, Agilent, Applied Microarrays, Arrayjet, Illumina, and others, the technology of DNA microarrays has become the most sophisticated and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscope Slide
A microscope slide is a thin flat piece of glass, typically 75 by 26 mm (3 by 1 inches) and about 1 mm thick, used to hold objects for examination under a microscope. Typically the object is mounted (secured) on the slide, and then both are inserted together in the microscope for viewing. This arrangement allows several slide-mounted objects to be quickly inserted and removed from the microscope, labeled, transported, and stored in appropriate slide cases or folders etc. Microscope slides are often used together with a cover slip or cover glass, a smaller and thinner sheet of glass that is placed over the specimen. Slides are held in place on the microscope's stage by slide clips, slide clamps or a cross-table which is used to achieve precise, remote movement of the slide upon the microscope's stage (such as in an automated/computer operated system, or where touching the slide with fingers is inappropriate either due to the risk of contamination or lack of precision ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Microarray
A DNA microarray (also commonly known as DNA chip or biochip) is a collection of microscopic DNA spots attached to a solid surface. Scientists use DNA microarrays to measure the expression levels of large numbers of genes simultaneously or to genotype multiple regions of a genome. Each DNA spot contains picomoles (10−12 moles) of a specific DNA sequence, known as '' probes'' (or ''reporters'' or '' oligos''). These can be a short section of a gene or other DNA element that are used to hybridize a cDNA or cRNA (also called anti-sense RNA) sample (called ''target'') under high-stringency conditions. Probe-target hybridization is usually detected and quantified by detection of fluorophore-, silver-, or chemiluminescence-labeled targets to determine relative abundance of nucleic acid sequences in the target. The original nucleic acid arrays were macro arrays approximately 9 cm × 12 cm and the first computerized image based analysis was published in 1981. It was inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |