|
Hurricane Hernan (2002)
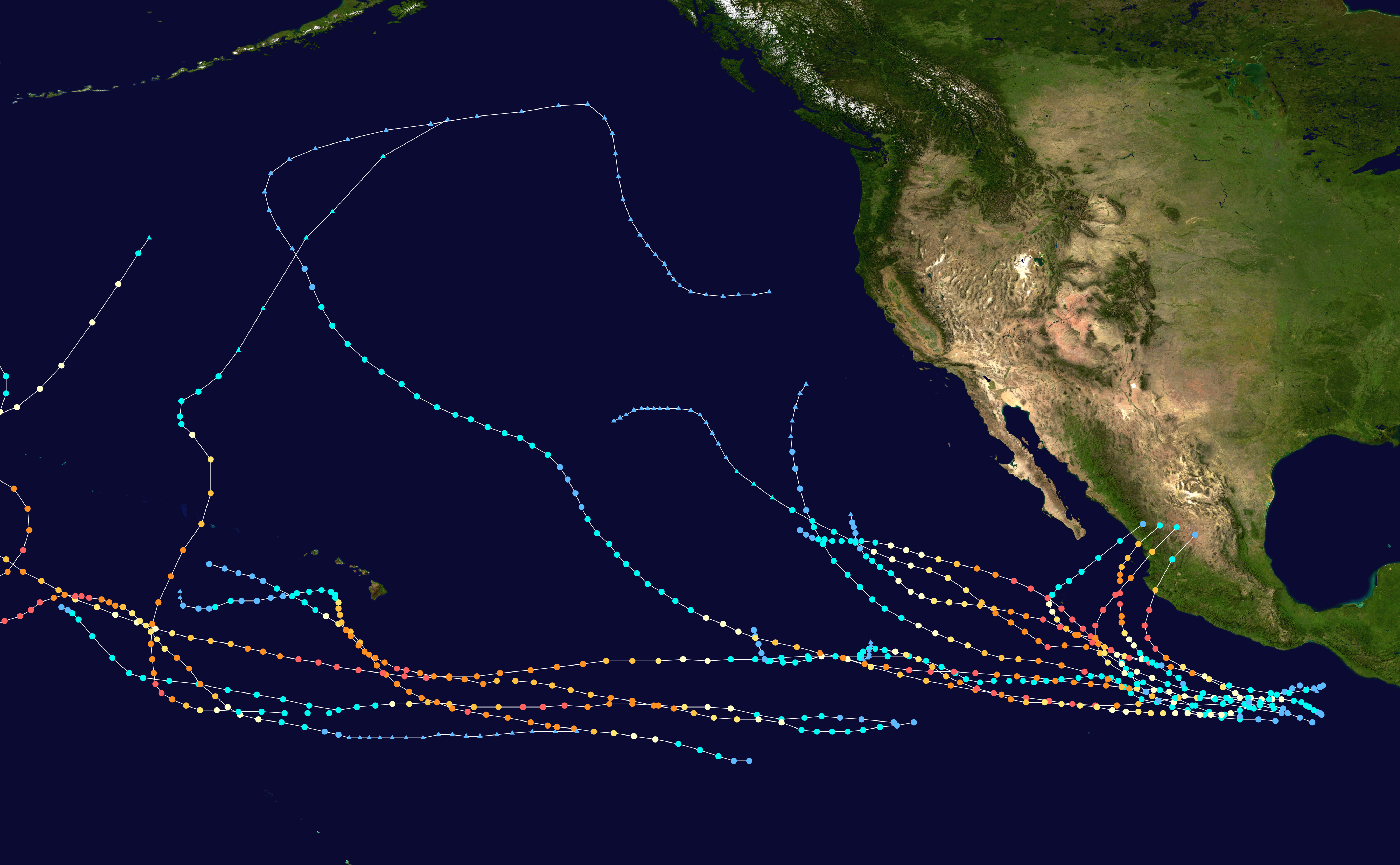
Hurricane Hernan was the second of three Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale, Category 5 hurricanes during the 2002 Pacific hurricane season. The twelfth tropical cyclone, tenth named storm and sixth hurricane of the season, Hernan originated from a tropical wave that formed in the Atlantic Ocean and crossed to the Pacific Ocean. The wave spawned a low-pressure area which organized into a tropical depression on August 30, a tropical storm on August 31 and a hurricane later that day. Hernan rapidly intensified and reached peak intensity as a Category 5 storm on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale. Proceeding northwest, it maintained this strength for eight hours, but on September 2 it entered cooler waters and began to weaken. By September 6 it had degenerated into a remnant area of Low-pressure area, low pressure. Hernan was the second most intense hurricane of the season, and it maintained Category 5 status for the second-longest time of the season, behind Hurricane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revillagigedo Islands
The Revillagigedo Islands ( es, Islas Revillagigedo, ) or Revillagigedo Archipelago are a group of four volcanic islands in the Pacific Ocean, known for their unique ecosystem. They lie approximately from Socorro Island south and southwest of Cabo San Lucas, the southern tip of the Baja California Peninsula, and west of Manzanillo, Colima, Manzanillo. Historically linked to the Mexican state of Colima, to which they were granted in 1861 to establish a penal colony, the islands are under Mexican federal property and jurisdiction. In July 2016, the Revillagigedo Archipelago was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site, and in November 2017 they were declared to be a marine reserve and a List of national parks of Mexico, national park of Mexico. Some of the volcanoes are active, with the last eruption of Volcán Bárcena in 1953, and Socorro (volcano), Socorro in 1993. Travelling to the islands from their nearest land point takes approximately 26 to 30 hours, as they are typicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal wind shear. Vertical wind shear is a change in wind speed or direction with a change in altitude. Horizontal wind shear is a change in wind speed with a change in lateral position for a given altitude. Wind shear is a microscale meteorological phenomenon occurring over a very small distance, but it can be associated with mesoscale or synoptic scale weather features such as squall lines and cold fronts. It is commonly observed near microbursts and downbursts caused by thunderstorms, fronts, areas of locally higher low-level winds referred to as low-level jets, near mountains, radiation inversions that occur due to clear skies and calm winds, buildings, wind turbines, and sailboats. Wind shear has significant effects on the control of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Category 5 Pacific Hurricanes
Category 5 hurricanes are tropical cyclones that reach Category 5 intensity on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale. They are by definition the strongest hurricanes that can form on planet Earth. They are rare in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and generally form only once every several years. In general, Category 5s form in clusters in single years. Landfalls by such storms are rare due to the generally westerly path of tropical cyclones in the Northern Hemisphere. The term "hurricane" is used for tropical cyclones in the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and east of the International Date Line. A Category 5 Pacific hurricane is therefore a tropical cyclone in the north Pacific Ocean that reached Category 5 intensity east of the International Date Line. Identical phenomena in the north Pacific Ocean west of the dateline are called "typhoons" or "super typhoons". Category 5 super typhoons generally happen several times per season, so cyclones of that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of California Hurricanes
A California hurricane is a tropical cyclone that affects the state of California. Usually, only the remnants of tropical cyclones affect California. Since 1900, only two still-tropical storms have hit California, one by direct landfall from offshore, another after making landfall in Mexico. No tropical cyclone has ever made landfall in California at hurricane intensity in recorded history. Since 1850, only eight tropical cyclones have brought gale-force winds to the Southwestern United States. They are: The 1858 San Diego hurricane that was reconstructed as just missing landfall in 1858, the 1939 Long Beach tropical storm that made landfall near San Pedro in 1939, the remnants of Tropical Storm Jennifer-Katherine in 1963, the remnants of Hurricane Emily in 1965, the remnants of Hurricane Joanne in 1972, the remnants of Hurricane Kathleen in 1976, and Hurricane Nora in 1997 after it was downgraded to a tropical storm, and Hurricane Kay, which made landfall in the Baja Californ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Category 5 Pacific Hurricanes
Category 5 hurricanes are tropical cyclones that reach Category 5 intensity on the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale. They are by definition the strongest hurricanes that can form on planet Earth. They are rare in the northeastern Pacific Ocean and generally form only once every several years. In general, Category 5s form in clusters in single years. Landfalls by such storms are rare due to the generally westerly path of tropical cyclones in the Northern Hemisphere. The term "hurricane" is used for tropical cyclones in the Pacific Ocean, north of the equator and east of the International Date Line. A Category 5 Pacific hurricane is therefore a tropical cyclone in the north Pacific Ocean that reached Category 5 intensity east of the International Date Line. Identical phenomena in the north Pacific Ocean west of the dateline are called "typhoons" or "super typhoons". Category 5 super typhoons generally happen several times per season, so cyclones of that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Hernan (other)
The name Hernan has been used for seven tropical cyclones in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. * Tropical Storm Hernan (1984) - Minimal tropical storm with no effect on land * Hurricane Hernan (1990) – High-end Category 4 hurricane, didn't affect land * Hurricane Hernan (1996) – Struck Mexico as a Category 1 hurricane, caused unknown amount of damage * Hurricane Hernan (2002) – Category 5 hurricane that caused minor effects in Mexico and California * Hurricane Hernan (2008) – Category 3 hurricane, no land impact * Hurricane Hernan (2014) – Minimal hurricane with no effect on land * Tropical Storm Hernan (2020) – Weak storm that brushed Mexico as a tropical depression, causing flooding and mudslides {{DEFAULTSORT:Hernan Pacific hurricane set index articles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-pressure Area
In meteorology, a low-pressure area, low area or low is a region where the atmospheric pressure is lower than that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure areas are commonly associated with inclement weather (such as cloudy, windy, with possible rain or storms), while high-pressure areas are associated with lighter winds and clear skies. Winds circle anti-clockwise around lows in the northern hemisphere, and clockwise in the southern hemisphere, due to opposing Coriolis force, Coriolis forces. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in the upper levels of the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere (aloft). The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as cyclogenesis. In Meteorology#Dynamic meteorology, meteorology, atmospheric divergence aloft occurs in two kinds of places: * The first is in the area on the east side of upper Trough (meteorology), troughs, which form half of a Rossby wave within the Westerlies (a trough (meteorology), trough with la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyewall Replacement Cycle
In meteorology, eyewall replacement cycles, also called concentric eyewall cycles, naturally occur in intense tropical cyclones, generally with winds greater than , or major hurricanes ( Category 3 or above). When tropical cyclones reach this intensity, and the eyewall contracts or is already sufficiently small, some of the outer rainbands may strengthen and organize into a ring of thunderstorms—a new, outer eyewall—that slowly moves inward and robs the original, inner eyewall of its needed moisture and angular momentum. Since the strongest winds are in a tropical cyclone's eyewall, the storm usually weakens during this phase, as the inner wall is "choked" by the outer wall. Eventually the outer eyewall replaces the inner one completely, and the storm may re-intensify. The discovery of this process was partially responsible for the end of the U.S. government's hurricane modification experiment Project Stormfury. This project set out to seed clouds outside the eyewall, apparen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saffir–Simpson Scale
The Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS) classifies hurricanes—which in the Western Hemisphere are tropical cyclones that exceed the intensities of tropical depressions and tropical storms—into five categories distinguished by the intensities of their sustained winds. This measuring system was formerly known as the Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale, or SSHS. To be classified as a hurricane, a tropical cyclone must have one-minute-average maximum sustained winds at 10 m above the surface of at least 74 mph (64 kn, 119 km/h; Category 1). The highest classification in the scale, Category 5, consists of storms with sustained winds of at least 157 mph (137 kn, 252 km/h). The classifications can provide some indication of the potential damage and flooding a hurricane will cause upon landfall. The Saffir–Simpson hurricane wind scale is based on the highest wind speed averaged over a one-minute interval 10 m above th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye (cyclone)
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the ''eyewall'', a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe weather and highest winds occur. The cyclone's lowest barometric pressure occurs in the eye and can be as much as 15 percent lower than the pressure outside the storm. In strong tropical cyclones, the eye is characterized by light winds and clear skies, surrounded on all sides by a towering, symmetric eyewall. In weaker tropical cyclones, the eye is less well defined and can be covered by the central dense overcast, an area of high, thick clouds that show up brightly on satellite imagery. Weaker or disorganized storms may also feature an eyewall that does not completely encircle the eye or have an eye that features heavy rain. In all storms, however, the eye is the location of the storm's minimum barometric pressure—where the atmospheric pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Hernan (2002) TRMM
The name Hernan has been used for seven tropical cyclones in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. * Tropical Storm Hernan (1984) – minimal tropical storm with no effect on land * Hurricane Hernan (1990) – high-end Category 4 hurricane, didn't affect land * Hurricane Hernan (1996) – struck Mexico as a Category 1 hurricane, caused unknown amount of damage * Hurricane Hernan (2002) – Category 5 hurricane that caused minor effects in Mexico and California * Hurricane Hernan (2008) – Category 3 hurricane, no land impact * Hurricane Hernan (2014) – Category 1 hurricane with no effect on land * Tropical Storm Hernan (2020) Tropical Storm Hernan was a small and disorganized tropical cyclone that brought widespread flooding and destructive mudslides to several states in southwest Mexico in late August 2020. Hernan was the thirteenth tropical cyclone and eighth named ... – minimal tropical storm that brushed western Mexico, causing flooding and mudslides {{DEFAULTSORT:Hernan Paci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outflow (meteorology)
Outflow, in meteorology, is air that flows outwards from a storm system. It is associated with ridging, or anticyclonic flow. In the low levels of the troposphere, outflow radiates from thunderstorms in the form of a wedge of rain-cooled air, which is visible as a thin rope-like cloud on weather satellite imagery or a fine line on weather radar imagery. For observers on the ground, a thunderstorm outflow boundary often approaches in otherwise clear skies as a low, thick cloud that brings with it a gust front. Low-level outflow boundaries can disrupt the center of small tropical cyclones. However, outflow aloft is essential for the strengthening of a tropical cyclone. If this outflow is restricted or undercut, the tropical cyclone weakens. If two tropical cyclones are in close proximity, the upper-level outflow from the upwind system can limit the development of the other system. Thunderstorms For thunderstorms, outflow tends to indicate the development of a system. Large quan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |