|
Huonville
Huonville is a town on the Huon River, in the south-east of Tasmania, Australia. It is the seat of the Huon Valley Council area and lies 38 km south of Hobart on the Huon Highway. At the 2016 census, Huonville had a population of 2,714 and at the 2011 census had a population of 1,741. History The first Europeans to set eyes on the Huon River were the crew commanded by Admiral Bruni d'Entrecasteaux. The river was named by him in honour of his second in command, Captain Huon de Kermadec. The name is preserved today in many features: the town, the river, the district and so on. The first European settlers were William and Thomas Walton in 1840. Huonville was not originally intended as the site of a town. Nearby Ranelagh was laid out as the town of Victoria in colonial days. Huonville grew around the bridge crossing the Huon River and hotels at the bridge. It was officially declared a town in 1891. The township has faced significant threats due to climate change in recent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huon Valley Council
Huon Valley Council is a local government body in Tasmania, covering most of the south of the state. Huon Valley is classified as a rural local government area and has a population of 17,219, towns and localities of the region include Cygnet, Dover, Franklin, Geeveston, Southport and the largest principal town, Huonville. History and attributes In 1993 the municipalities of Esperance, Huon and Port Cygnet were amalgamated to form the Huon Valley Council. Remote subantarctic Macquarie Island, which is located some 1400 km southeast of Tasmania proper, was part of Esperance until then, and has been administratively part of the Huon Valley since then. Demographics Huon Valley is classified as rural, agricultural and very large under the Australian Classification of Local Governments. The townships in the south east region of Tasmania that experienced the largest growth over the decade ending June 2011 were Huonville, Franklin (where the population was up by 1,300 people) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cygnet, Tasmania
Cygnet is a town in the Huon Valley, south of Huonville, Tasmania. History The bay on which Cygnet sits was originally named by the Indigenous people who occupied a large territory in South East Tasmania, including Cygnet, Hobart and Bruny Island. Tasmanian leader & elder, Wooraddy, came from Bruny Island. The bay was later named ''Port des Cygnes'' (Port of Swans) by French navigator Bruni D'Entrecasteaux in 1793, because he observed a large number of black swans in the area. The first European settler in the district was William Nichols in 1834. Nichols received a grant for three hundred and twenty acres of land on the north side of Port Cygnet in 1829. After the land had been cleared and accommodation built, Nichols moved his family to this property. At the time the property was only accessible by a walking track from Browns River or up the river by boat. His grandson, John Wilson, established a shipbuilding business at what was now known as Port Cygnet. Until the end of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huon River
The Huon River is a perennial river located in the south-west and south-east regions of Tasmania, Australia. At in length, the Huon River is the fifth-longest in the state, with its course flowing east through the fertile Huon Valley and emptying into the D'Entrecasteaux Channel, before flowing into the Tasman Sea. Location and features The Huon River rises below Junction Hill in the Southwest National Park with much of its upper catchment drawn from the Marsden Range and associated peaks including Mount Anne, Mount Bowes and Mount Wedge. The river flows generally south through the south-eastern portion of Lake Pedder and is impounded at the Scotts Peak Dam. Thereafter, the river flows generally south-east to the Tahune Airwalk. From its source to mouth, the river is joined by 26 tributaries including the Anne, Cracroft, Picton, Weld, Arve, Russell, Little Denison and Mountain rivers. After passing through the rural township of Glen Huon the river flows down rapids to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Division Of Franklin (state)
The electoral division of Franklin is one of the five electorates in the Tasmanian House of Assembly, located in southern Tasmania and includes Bruny Island, Kingston and the eastern shore of the Derwent River. Franklin is named after Sir John Franklin, the Arctic explorer who was Lieutenant-Governor of Van Diemen's Land (1837–43). The division shares its name and boundaries with the federal division of Franklin. Franklin and the other House of Assembly electoral divisions are each represented by five members elected under the Hare-Clark electoral system. History and electoral profile Franklin includes most of the suburbs of Hobart, such as Kingston, Seven Mile Beach and Lauderdale as well as the rural towns of Huonville, Franklin, Cygnet, Margate and Bruny Island. The subantarctic Macquarie Island is also part of the electorate. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hobart
Hobart ( ; Nuennonne/Palawa kani: ''nipaluna'') is the capital and most populous city of the Australian island state of Tasmania. Home to almost half of all Tasmanians, it is the least-populated Australian state capital city, and second-smallest if territories are taken into account, before Darwin, Northern Territory. Hobart is located in Tasmania's south-east on the estuary of the River Derwent, making it the most southern of Australia's capital cities. Its skyline is dominated by the kunanyi/Mount Wellington, and its harbour forms the second-deepest natural port in the world, with much of the city's waterfront consisting of reclaimed land. The metropolitan area is often referred to as Greater Hobart, to differentiate it from the City of Hobart, one of the five local government areas that cover the city. It has a mild maritime climate. The city lies on country which was known by the local Mouheneener people as nipaluna, a name which includes surrounding features such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amy Sherwin
Frances Amy Lillian Sherwin (23 March 1855 – 20 September 1935), the 'Tasmanian Nightingale', was an Australian soprano singer. Biography She was born at Forest Home, Huonville, Tasmania on 23 March 1855. She was taught singing by her mother. On 1 May 1878, she appeared with an Italian opera company at Hobart, Tasmania as Norina in ''Don Pasquale'' and was an immediate success. Proceeding to Melbourne with the company, she sang Lucia in ''Lucia di Lammermoor'' on 3 June 1878 and was received with great enthusiasm. During the next few weeks. she appeared as the title role in Wallace's opera ''Maritana'', Leonora in ''Il Trovatore'', and in other leading parts in Fanny Simonsen's troupe. She moved to the United States in 1879, an in 1880, she created the part of Marguerite of Hector Berlioz's work ''The Damnation of Faust''. She studied under several masters both in the U.S. and in Europe, and appeared at the promenade concerts in London in 1883. In 1885, she sang at Covent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huon Highway
The Huon Highway is an highway in southern Tasmania, Australia. The highway forms part of the A6 and connects Hobart with the southern parts of Tasmania. The original Huon Highway (now known as Huon Road) was a twisty two-lane road skirting around Mount Wellington (Tasmania), Mount Wellington, but that section of the highway was bypassed in stages when the Southern Outlet, Hobart, Southern Outlet was completed in 1968. This provided a more direct, and higher traffic-capacity, route between Hobart and the Huon Valley. A few sections of the old highway remain, all within the Huon Valley, and have been upgraded. See also * Highways in Australia * List of highways in Tasmania References {{Road infrastructure in Tasmania Highways in Tasmania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Michel Huon De Kermadec
Jean-Michel Huon de Kermadec (12 September 1748 – 6 May 1793) was a French Navy officer. He took part in voyages of exploration in the Pacific Ocean under Bruni d'Entrecasteaux, looking for the lost expedition of Jean-François de La Pérouse. Biography Early life Kermadec was born on 12 September 1748 in Bohars, near the city of Brest in France, into a Breton family of old nobility, to Jean-Guillaume Huon de Kermadec and his wife Anne du Mescam. His family had a long naval tradition, as both his father and grand-father were also Navy officers. His brother, Jean-Marie Huon de Kermadec, and uncle, François Pierre Huon de Kermadec, were also Navy officers. Naval career He served in the American War of Independence, and saw action at the Battle of Ushant in 1778 and the following year was serving aboard the ''Diadème'' during the Capture of Grenada and the Siege of Savannah. In 1781, he was made a Knight in the Order of Saint Louis. Joining the ship ''Résolution'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
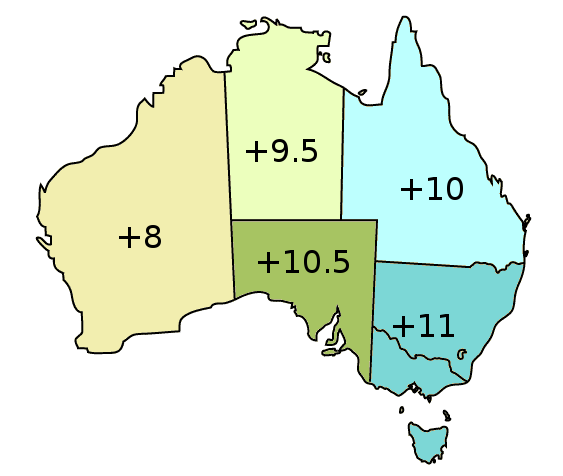
Australian Eastern Standard Time
Australia uses three main time zones: Australian Western Standard Time (AWST; UTC+08:00), Australian Central Standard Time (ACST; UTC+09:30), and Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST; UTC+10:00). Time is regulated by the individual state governments, some of which observe daylight saving time (DST). Australia's external territories observe different time zones. Standard time was introduced in the 1890s when all of the Australian colonies adopted it. Before the switch to standard time zones, each local city or town was free to determine its local time, called local mean time. Now, Western Australia uses Western Standard Time; South Australia and the Northern Territory use Central Standard Time; while New South Wales, Queensland, Tasmania, Victoria, Jervis Bay Territory, and the Australian Capital Territory use Eastern Standard Time. Daylight saving time (+1 hour) is used in jurisdictions in the south and south-east: South Australia, New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, ''Malus sieversii'', is still found today. Apples have been grown for thousands of years in Asia and Europe and were brought to North America by European colonization of the Americas, European colonists. Apples have Religion, religious and mythology, mythological significance in many cultures, including Norse mythology, Norse, Greek mythology, Greek, and Christianity in Europe, European Christian tradition. Apples grown from seed tend to be very different from those of their parents, and the resultant fruit frequently lacks desired characteristics. Generally, apple cultivars are propagated by clonal grafting onto rootstocks. Apple trees grown without rootstocks tend to be larger and much slower to fruit after plantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockle Creek, Tasmania
Cockle Creek is the farthest point south one can drive in Australia. It is located on Recherche Bay on the edge of the Southwest National Park, part of the Tasmanian Wilderness World Heritage Area. There are no shops or other facilities in the settlement, but a campground is located in the National Park with public toilets and a public phone. The National Park Ranger's office is only staffed intermittently. Main activities are camping, fishing, birdwatching and bushwalking. Arts Tasmania with the Tasmania Parks and Wildlife Service offers an artists residency program at Cockle Creek "for an individual or collaboration of practising artists working in any art form to develop their work in response to the natural environment of Tasmania." Bushwalking The area is known for its scenic beauty of deserted white beaches and turquoise waters of Recherche Bay and a variety of short and multi-day bushwalks including the end of the 82 km South Coast Track, recommended for experience ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recherche Bay
Recherche Bay ( ) is an oceanic embayment, part of which is listed on the National Heritage Register, located on the extreme south-eastern corner of Tasmania, Australia. It was a landing place of the d’Entrecasteaux expedition to find missing explorer La Pérouse. It is named in honour of the ''Recherche'', one of the expedition's ships. The Nuenonne name for the bay is ''Leillateah''. French exploration The explorers set up a camp, made a garden and scientific observatory at Recherche Bay in April 1792 for 26 days, and again in January 1793 for 24 days. Both landings were made to seek refuge and replenish supplies although as much time as possible was dedicated to scientific research. The botanists Jacques Labillardière, Claude Riche and Étienne Pierre Ventenat, assisted by gardener botanist Félix Delahaye, collected and catalogued almost 5000 specimens including the blue gum (''Eucalyptus globulus''), which later became Tasmania's floral emblem. The expedition also m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |