|
Huntingdon, Abbotsford
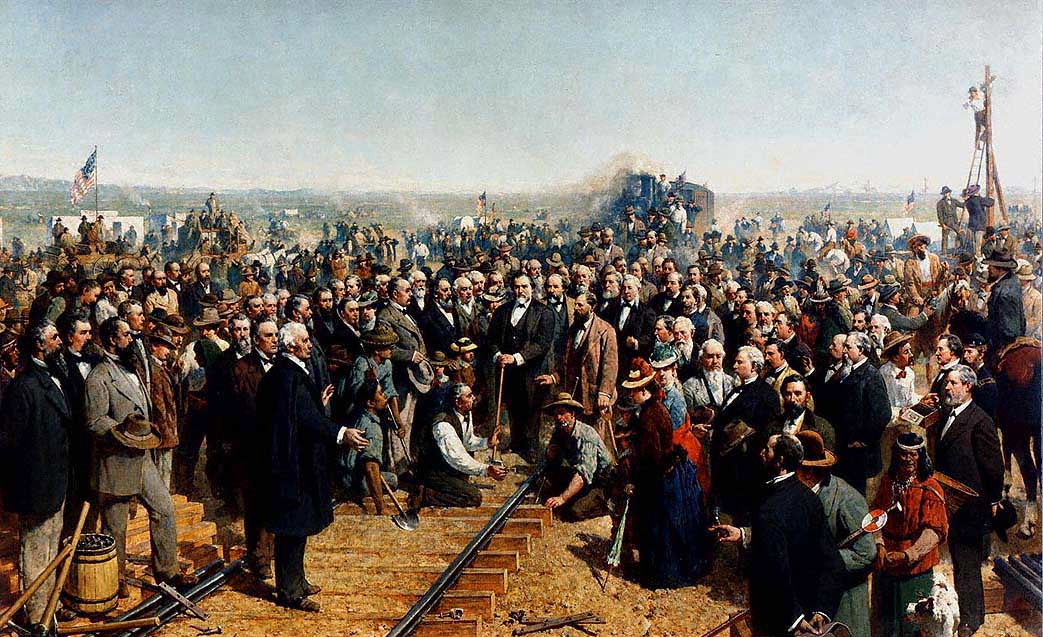
Huntingdon is a community within Abbotsford, British Columbia, Canada. It is located immediately north of the Canada–US border, and is the location of the Sumas-Huntingdon Border Crossing. The main road through the community is Highway 11. The name of the community is also the present name of the border crossing connecting to Sumas, Washington. It is named for Collis P. Huntington, a Union Pacific Railroad railway executive who helped connect the Canadian Pacific Railway line to US Lines. The CPR wanted direct BC connection to Seattle, south, and onto California so it built a bridge at Mission and rail line across Matsqui Prairie to connect with the Seattle, Lake Shore and Eastern Railway. The Northern Pacific Railway, Union Pacific Railroad and Milwaukee Roads built lines to Sumas, with an eye of coming to Vancouver, but never crossed the border in the end. BC Electric Railway and Great Northern did build to Huntingdon and into the eastern Fraser Valley. Member of Parliamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbotsford, British Columbia
Abbotsford is a city located in British Columbia, adjacent to the Canada–United States border, Greater Vancouver and the Fraser River. With an estimated population of 153,524 people it is the largest municipality in the province outside metropolitan Vancouver. Abbotsford-Mission has the third highest proportion of visible minorities among census metropolitan areas in Canada, after the Greater Toronto Area and the Greater Vancouver CMA. It is home to Fraser Valley Trade and Exhibition Centre, Tradex, the University of the Fraser Valley, and Abbotsford International Airport. As of the Canada 2021 Census, 2021 census, it is the largest municipality of the Fraser Valley Regional District and the List of municipalities in British Columbia, fifth-largest municipality of British Columbia. The Abbotsford–Mission metropolitan area of around 195,726 inhabitants as of the 2021 census is the 23rd largest census metropolitan area in Canada. It has also been named by Statistics Canada as C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumas, British Columbia
Sumas was a district municipality in the Fraser Valley region of British Columbia, Canada, located between the then-Village of Abbotsford (W) and Chilliwack (E). It was amalgamated with the Village of Abbotsford in 1972 into the District of Abbotsford. It, prior to amalgamation and after, was a part of the Central Fraser Valley Regional District until the district's abolition in 1995. Notable distinct communities with the municipality were Kilgard and Huntingdon, the latter being the Canadian side of the Sumas Border Crossing Sumas () is a city in Whatcom County, Washington, United States. It had a population of 1,307 as of the 2010 census. Sumas is located adjacent to the Canada–U.S. border and borders the city of Abbotsford, British Columbia. The Sumas-Huntingd ... into the United States. Most of the municipality was farmland - its dominant landform was the rich agricultural land of Sumas Prairie, which was created through the draining of Sumas Lake early in the 20th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ed Fast
Edward D. Fast (born June 18, 1955) is a Canadian politician who has served as the member of Parliament (MP) for Abbotsford since 2006. A member of the Conservative Party of Canada, he was Minister for International Trade and Minister for the Asia–Pacific Gateway from 2011 to 2015 under Prime Minister Stephen Harper. Early life and career Born in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Ed Fast moved to and grew up in Vancouver, British Columbia. After graduating from law school at the University of British Columbia in 1982, Fast co-founded the law firm currently known as Linley Welwood. He was elected in 1985 and served two terms as an Abbotsford School Board Trustee. He was elected to Abbotsford City Council in 1996 and served for three 3-year terms. During that time, he served as Deputy Mayor and as Chair of the Parks, Recreation & Culture Commission. Federal politics In government Fast won the 2006 federal election with 63.27% of the vote as the Member of Parliament for the riding of Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbotsford (electoral District)
Abbotsford is a federal electoral district in British Columbia, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada since 2004. Demographics *Notes: Totals greater than 100% due to multiple origin responses.Demographics based on 2012 Canadian federal electoral redistribution riding boundaries. The riding has the lowest proportion of Catholics in Canada, with just 10.6% of the population adhering to Catholicism., as well as the highest proportion (9.8%) of "Christian, not included elsewhere" (non-Protestant, non-Catholic, non-Orthodox). 12.2% of its population claim Dutch ethnic origin, the highest such figure for any Canadian federal riding. Geography As of the 2012 federal electoral boundaries redistribution, the district includes the southeastern portion of the City of Abbotsford and the Upper Sumas 6 Indian reserve. History The electoral district was created in 2003. 56.1% of the riding was taken from Fraser Valley riding, and 43.9% from Langley—Abbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern Railway Of Canada
Most transportation historians date the history of Canada's railways as beginning on February 25, 1832, with the incorporation of British North America's first steam-powered railway, the Champlain and St. Lawrence Railroad. This line opened for traffic on July 21, 1836, although there are cases of animal-drawn mining tramways in Nova Scotia from the 18th century onward. Thousands of railways followed the C&SL and were given a charter by the federal or provincial governments, although in most cases these charters never resulted in an actual line being constructed. Many of these charters were so-called "paper railways" and were absorbed into other railways, that is they existed on paper with the actual trains bearing the name of another railway or system of railways. For example, Canadian National Railways alone consisted of over some 400 railways (see Canadian National Railways-List of Companies). The reason for these "paper" railways was the ease of getting a charter, this was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BC Electric Railway
The British Columbia Electric Railway (BCER) was an historic railway which operated in southwestern British Columbia, Canada. Originally the parent company for, and later a division of, BC Electric Company (now BC Hydro), the BCER assumed control of existing streetcar and interurban lines in southwestern British Columbia in 1897, and operated the electric railway systems in the region until the last interurban service was discontinued in 1958. During and after the streetcar era, BC Electric also ran bus and trolleybus systems in Greater Vancouver and bus service in Greater Victoria; these systems subsequently became part of BC Transit, and the routes in Greater Vancouver eventually came under the control of TransLink. Trolley buses still run in the City of Vancouver with one line extending into Burnaby. History Streetcar and interurban services were inaugurated in southwestern British Columbia between 1890 and 1891, operated by the following companies: * National Electric Tramwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milwaukee Road
The Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Railroad (CMStP&P), often referred to as the "Milwaukee Road" , was a Class I railroad that operated in the Midwestern United States, Midwest and Pacific Northwest, Northwest of the United States from 1847 until 1986. The company experienced financial difficulty through the 1970s and 1980s, including bankruptcy in 1977 (though it filed for bankruptcy twice in 1925 and 1935, respectively). In 1980, it abandoned its Pacific Extension, which included track in the states of Montana, Idaho, and Washington (state), Washington. The remaining system was merged into the Soo Line Railroad , a subsidiary of Canadian Pacific Railway , on January 1, 1986. Much of its historical trackage remains in use by other railroads. The company brand is commemorated by buildings like the historic Chicago, Milwaukee, St. Paul and Pacific Depot Freight House and Train Shed, Milwaukee Road Depot in Minneapolis and preserved locomotives such as Milwaukee Road 26 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Pacific Railway
The Northern Pacific Railway was a transcontinental railroad that operated across the northern tier of the western United States, from Minnesota to the Pacific Northwest. It was approved by Congress in 1864 and given nearly of land grants, which it used to raise money in Europe for construction. Construction began in 1870 and the main line opened all the way from the Great Lakes to the Pacific when former President Ulysses S. Grant drove in the final "golden spike" in western Montana on September 8, 1883. The railroad had about of track and served a large area, including extensive trackage in the states of Idaho, Minnesota, Montana, North Dakota, Oregon, Washington, and Wisconsin. In addition, the NP had an international branch to Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada. The main activities were shipping wheat and other farm products, cattle, timber, and minerals; bringing in consumer goods, transporting passengers; and selling land. The Northern Pacific was headquartered in Minnesota, fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001. Headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, the railway owns approximately of track in seven provinces of Canada and into the United States, stretching from Montreal to Vancouver, and as far north as Edmonton. Its rail network also serves Minneapolis–St. Paul, Milwaukee, Detroit, Chicago, and Albany, New York, in the United States. The railway was first built between eastern Canada and British Columbia between 1881 and 1885 (connecting with Ottawa Valley and Georgian Bay area lines built earlier), fulfilling a commitment extended to British Columbia when it entered Confederation in 1871; the CPR was Canada's first transcontinental railway. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains, and borders the province of Alberta to the east and the Yukon and Northwest Territories to the north. With an estimated population of 5.3million as of 2022, it is Canada's third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria and its largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver is the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada; the 2021 census recorded 2.6million people in Metro Vancouver. The first known human inhabitants of the area settled in British Columbia at least 10,000 years ago. Such groups include the Coast Salish, Tsilhqotʼin, and Haida peoples, among many others. One of the earliest British settlements in the area was Fort Victoria, established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Pacific Railroad
The Union Pacific Railroad , legally Union Pacific Railroad Company and often called simply Union Pacific, is a freight-hauling railroad that operates 8,300 locomotives over routes in 23 U.S. states west of Chicago and New Orleans. Union Pacific is the second largest railroad in the United States after BNSF, with which it shares a duopoly on transcontinental freight rail lines in the Western, Midwestern and Southern United States. Founded in 1862, the original Union Pacific Rail Road was part of the first transcontinental railroad project, later known as the Overland Route. Over the next century, UP absorbed the Missouri Pacific Railroad, the Chicago and North Western Transportation Company, the Western Pacific Railroad, the Missouri–Kansas–Texas Railroad and the Chicago, Rock Island and Pacific Railroad. In 1996, the Union Pacific merged with Southern Pacific Transportation Company, itself a giant system that was absorbed by the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)