|
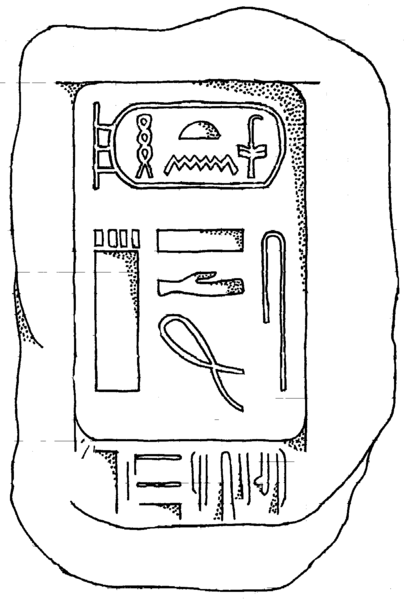
Huni
Huni (original reading unknown) was an ancient Egyptian king and the last pharaoh of the Third Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom period. Following the Turin king list, he is commonly credited with a reign of 24 years, ending c. 2613 BC. Huni's chronological position as the last king of the third dynasty is seen as fairly certain, but there is still some uncertainty on the succession order of rulers at the end of the 3rd dynasty. It is also unclear under which Hellenized name the ancient historian Manetho could have listed him in his historical writing ''Aegyptiacae''. Most possibly he is to be identified with the Hellenized name Aches, as Winfried Barta proposes. Many Egyptologists believe that Huni was the father and direct predecessor of king Sneferu, but this is questioned by other scholars. Huni is seen by scholars as a confusing figure in Egyptian history, because he was long remembered in Egyptian traditions, but very few documents, objects or monuments f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
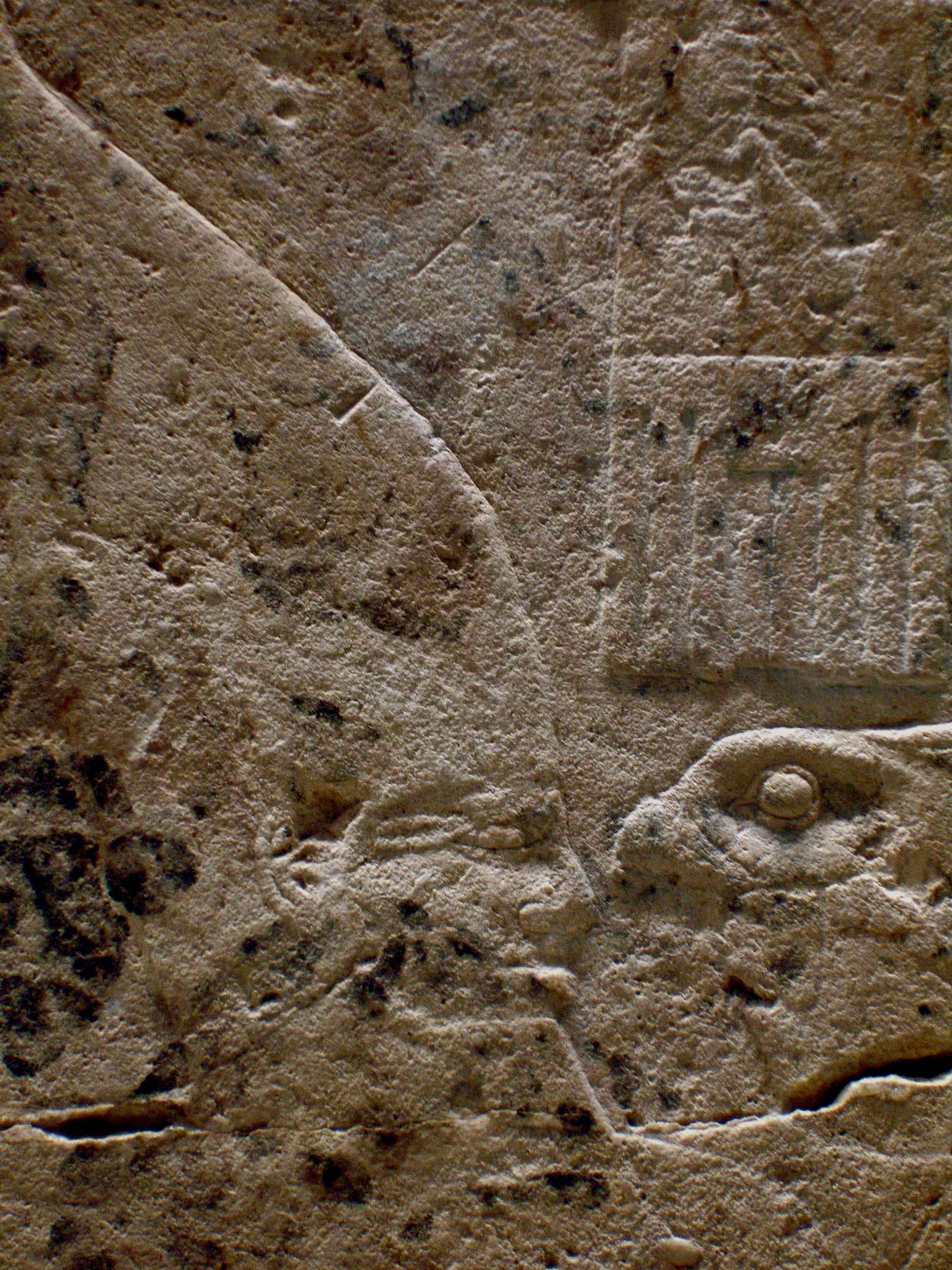
Huni Slab
Huni (original reading unknown) was an ancient Egyptian king and the last pharaoh of the Third Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom period. Following the Turin king list, he is commonly credited with a reign of 24 years, ending c. 2613 BC. Huni's chronological position as the last king of the third dynasty is seen as fairly certain, but there is still some uncertainty on the succession order of rulers at the end of the 3rd dynasty. It is also unclear under which Hellenized name the ancient historian Manetho could have listed him in his historical writing ''Aegyptiacae''. Most possibly he is to be identified with the Hellenized name Aches, as Winfried Barta proposes. Many Egyptologists believe that Huni was the father and direct predecessor of king Sneferu, but this is questioned by other scholars. Huni is seen by scholars as a confusing figure in Egyptian history, because he was long remembered in Egyptian traditions, but very few documents, objects or monuments fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Dynasty Of Egypt
The Third Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty III) is the first dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Other dynasties of the Old Kingdom include the Fourth, Fifth and Sixth. The capital during the period of the Old Kingdom was at Memphis. Overview After the turbulent last years of the Second Dynasty, which might have included civil war, Egypt came under the rule of Djoser, marking the beginning of the Third Dynasty.Dodson, Hilton, ''The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt'', 2004 Both the Turin King List and the Abydos King List record five kings,Toby A.H. Wilkinson, ''Early Dynastic Egypt'', Routledge, 2001 while the Saqqara Tablet only records four, and Manetho records nine,Aidan Dodson: ''The Layer Pyramid of Zawiyet el-Aryan: Its Layout and Context.'' In: ''Journal of the American Research Center in Egypt (JARCE)'', No. 37 (2000). American Research Center (Hg.), Eisenbrauns, Winona Lake/Bristol 2000, , pp. 81–90. many of whom did not exist or are simply the same king unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khaba
Khaba (also read as Hor-Khaba) was a pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, active during the Third Dynasty of Egypt, 3rd Dynasty of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom period. The exact time during which Khaba ruled is unknown but may have been around 2670 BC,Thomas Schneider: ''Lexikon der Pharaonen''. Albatros, Düsseldorf 2002, , p. 97. and almost definitely towards the end of the dynasty. King Khaba is considered to be difficult to assess as a figure of ancient Egypt. His name is archaeologically well-attested by stone bowls and mud seal impressions. Khaba's reign is securely dated to the Third Dynasty. Because of the contradictions within Ramesside king lists and the lack of contemporary, festive inscriptions, his exact chronological position within the dynasty remains disputed. These problems originate in part from contradictory king lists, which were all compiled long after Khaba's death, especially during the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt, Ramesside era (which is separated from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qahedjet
Qahedjet (also Hor-Qahedjet) could be the Horus name of an ancient Egyptian king (pharaoh), who may have ruled during the 3rd Dynasty or could be a voluntarily archaistic representation of Thutmose III.Jean-Pierre Pätznick: ''L'Horus Qahedjet: souverain de la 3eme dynasty ?'', Proceedings of the Ninth Congress of Egyptologists, Orientalia Lovaniensa Analecta, Ch. 2.1, p. 1455Online/ref> Since the only artifact attesting to the ruler and his name is a small stela made of polished limestone of uncertain origin and authenticity,Chr. Ziegler: ''Catalogue des steles, peintures et reliefs egyptiens de l'Ancien Empire et de la Premiere Periode Intermediaire, Musee du Louvre'', Paris 1990, pp. 54-57 Egyptologists are discussing the chronological position and historical figure of Qahedjet. The stela Description The stela of king Qahedjet is 50.5 cm high, 31.0 cm wide and 3.0 cm thick and made of finely polished limestone. It was bought in 1967 by the Louvre at Paris, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sneferu
Sneferu ( snfr-wj "He has perfected me", from ''Ḥr-nb-mꜣꜥt-snfr-wj'' "Horus, Lord of Maat, has perfected me", also read Snefru or Snofru), well known under his Hellenized name Soris ( grc-koi, Σῶρις by Manetho), was the founding pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt during the Old Kingdom. Estimates of his reign vary, with for instance ''The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt'' suggesting a reign from around 2613 to 2589 BC, a reign of 24 years, while Rolf Krauss suggests a 30-year reign, and Rainer Stadelmann a 48-year reign. He built at least three pyramids that survive to this day and introduced major innovations in the design and construction of pyramids. Reign length The 24-year Turin Canon figure for Sneferu's reign is considered today to be an underestimate since this king's highest-known date is an inscription discovered at the Red Pyramid of Dahshur and mentioning Sneferu's 24th cattle count, corresponding to at least 24 full years. Sneferu, however, was kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metjen
Metjen (also read as Methen) was an ancient Egyptian high official at the transition time from 3rd Dynasty to 4th Dynasty. He is famous for his tomb inscription, which provide that he worked and lived under the kings (pharaohs) Huni and Sneferu. Identity Family According to his own tomb inscriptions, Metjen was a son of the high official Inpu-em-Ankh, a judge at the royal court of justice and a royal scribe. Metjen's mother was a high priestess named ''Neb-senet''. Metjen also had children, which he indirectly mentions, but their names are not handed down.Toby A. H. Wilkinson: ''Early Dynastic Egypt''. Routledge, London/New York 2001, , p. 93, 112, 125 & 147.Wolfgang Helck: ''Untersuchungen zur Thinitenzeit'' (= ''Ägyptologische Abhandlungen'', Vol. 45). Harrassowitz, Wiesbaden 1987, , p. 268–274. Titles As a high-ranking official, Metjen bore several elite titularies: * ''Confidant of the king'' (Egyptian: ''Rekh-neswt''). A title that allowed Metjen to receive audi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djefatnebti
Djefatnebti (also Djefatnebty) was an ancient Egyptian queen consort. She lived at the end of the Third Dynasty of Egypt, 3rd Dynasty and may have been a wife of the last king of that dynasty, Huni.Francesco RaffaeleRoyal Women (queens, princesses) in early Egypt (Dynasty 0–3)/ref> Identity Djefatnebti’s name appears in one single, black ink inscription on an earthen beer jar, which was excavated at the eastern corner of Elephantine. Altogether three inscriptions were found. The first one mentions the "year of the followers of Horus" and the foundation of a building which name is lost due to damage. The second one mentions the "year of the 2nd time of the followers of Horus" and an "11th time of counting-the-fields at Heliopolis (Ancient Egypt), Heliopolis". The third one contains the notation "The king of Upper- and Lower Egypt appears", a "3rd time of battling the robbers" and the death of Djefatnebti. Since the "counting of the fields" was performed as a tax collection ever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saqqara Tablet
The Saqqara Tablet, now in the Egyptian Museum, is an ancient stone engraving surviving from the Ramesside Period of Egypt which features a list of pharaohs. It was found in 1861 in Saqqara, in the tomb of Tjuneroy (or Tjenry), an official ("chief lector priest" and "Overseer of Works on All Royal Monuments") of the pharaoh Ramesses II. The inscription lists fifty-eight kings, from Anedjib and Qa'a ( First Dynasty) to Ramesses II (Nineteenth Dynasty), in reverse chronological order, omitting "rulers from the Second Intermediate Period, the Hyksos, and those rulers... who had been close to the heretic Akhenaten". The names (each surrounded by a border known as a cartouche), of which only forty-seven survive, are badly damaged. As with other Egyptian king lists, the Saqqara Tablet omits certain kings and entire dynasties. The list counts backward from Ramesses II to the mid-point of the First Dynasty, except for the Eleventh and Twelfth Dynasties, which are reversed. A well known p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turin King List
The Turin King List, also known as the Turin Royal Canon, is an ancient Egyptian hieratic papyrus thought to date from the reign of Pharaoh Ramesses II, now in the Museo Egizio (Egyptian Museum) in Turin. The papyrus is the most extensive list available of kings compiled by the ancient Egyptians, and is the basis for most chronology before the reign of Ramesses II. Creation and use The papyrus is believed to date from the reign of Ramesses II, during the middle of the New Kingdom, or the 19th Dynasty. The beginning and ending of the list are now lost; there is no introduction, and the list does not continue after the 19th Dynasty. The composition may thus have occurred at any subsequent time, from the reign of Ramesses II to as late as the 20th Dynasty. The papyrus lists the names of rulers, the lengths of reigns in years, with months and days for some kings. In some cases they are grouped together by family, which corresponds approximately to the dynasties of Manetho's book. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meresankh I
Meresankh I ("She loves life") was an ancient Egyptian kingʻs wife and the mother of King Sneferu.Dodson, Aidan and Hilton, Dyan. ''The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt''. Thames & Hudson. 2004. She may have been a wife of King Huni, the last king of the 3rd Dynasty.Meresankh Iʻs name appears on a fragment of the Palermo Stone and an estate of Meresankh may be named in the tomb of Pehernefer in Saqqara. She is named alongside her son Sneferu in graffiti in the pyramid temple at Meidum. This graffiti dates to the reign of Tuthmosis III of the 18th Dynasty. The text recites a ''hetep di nesu'' (offerings) text for the ''ka'' of King Sneferu Sneferu ( snfr-wj "He has perfected me", from ''Ḥr-nb-mꜣꜥt-snfr-wj'' "Horus, Lord of Maat, has perfected me", also read Snefru or Snofru), well known under his Hellenized name Soris ( grc-koi, Σῶρις by Manetho), was the founding phar ... and Queen Meresankh.Alexander J. Peden: ''The graffiti of pharaonic Egypt: scope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hetepheres I
Hetepheres I was a queen of Egypt during the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt (c. 2600 BC) who was a wife of one king, the mother of the next king, the grandmother of two more kings, and the figure who tied together two dynasties. Biography Hetepheres I may have been a wife of King Sneferu, and was the mother of King Khufu. It is possible that Hetepheres had been a minor wife of Sneferu and only rose in prominence after her son ascended the throne. She was the grandmother of two kings, Djedefre and Khafre, and of queen Hetepheres II. Her titles include: King's Mother (''Mut-nisut, mwt- nswt''), Mother of the King of the Two Lands (''Mut-nisut-biti, mwt- nswt- bjtj''), Attendant of Horus (''Khet-heru, ḫt-hrw''), and God's Daughter of his body (''Zat-netjer-net-khetef,'' '' zꜣt- nṯr- nt- ẖt .f'').Grajetzki, ''Ancient Egyptian Queens – a hieroglyphic dictionary'', London, 2011. The marriage of Hetepheres I to Snefru solidified his rise to the throne. Because she carrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abusir
Abusir ( ar, ابو صير ; Egyptian ''pr wsjr'' cop, ⲃⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲓ ' "the House or Temple of Osiris"; grc, Βούσιρις) is the name given to an Egyptian archaeological locality – specifically, an extensive necropolis of the Old Kingdom period, together with later additions – in the vicinity of the modern capital Cairo. The name is also that of a neighbouring village in the Nile Valley, whence the site takes its name. Abusir is located several kilometres north of Saqqara and, like it, served as one of the main elite cemeteries for the ancient Egyptian capital city of Memphis. Several other villages in northern and southern Egypt are named Abusir or Busiri. Abusir is one relatively small segment of the extensive "pyramid field" that extends from north of Giza to below Saqqara. The locality of Abusir took its turn as the focus of the prestigious western burial rites operating out of the then-capital of Memphis during the Old Kingdom 5th Dynasty. As an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |