|
Hungarian Historical Society
The Hungarian Historical Society ( hu, Magyar Történelmi Társulat) is a learned society in Hungary, established in 1867. Its main responsibilities are the cultivation of the History of Hungary, dissemination of scientific findings, supporting research and development and representing the history of Hungary domestically and around the world. Aims The historical society's aims are: *Cultivating and promoting Hungarian historiography and history, organizing archival research and publishing national historical sources according to the unpolitical spirituality. *Spreading the recent study results of the Hungarian and – as far as possible – Universal History to reach the widest audience. *Its traditional aims are to become a large, informal "guild" to defend and represent the interests of the Hungarian historians, the educators of the history of Hungary and those people who are interested in history. Motto : "Emlékezzünk régiekről!″ (Remember the Old Ones) History The H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Society
A historical society (sometimes also preservation society) is an organization dedicated to preserving, collecting, researching, and interpreting historical information or items. Originally, these societies were created as a way to help future generations understand their heritage. Historical societies vary in specialization, with focuses ranging from specific geographical areas such as countries or towns, universities, railways, ethnic and religious groups, to genealogy, pioneer history, and the preservation of antiques or historic buildings. Often, many of these organizations ensure that historic architecture is preserved/restored and period houses are maintained for tours open to the public. History It is said that historical societies originated in Western Europe during the 16th and 17th centuries. These early organizations were usually formed as societies for “lovers of Antiquity.” The oldest historical society in the United States is what is now called the Massachus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imre Mikó
Count Imre Mikó de Hidvég (4 September 1805 – 16 September 1876) was a Hungarian statesman, politician, economist, historian and patron from Transylvania, who served as Minister of Public Works and Transport between 1867 and 1870. He was one of the liberal-oriented, prominent figures of the politics of Transylvania in the 19th century. He functioned as Governor of Transylvania twice (1848 and 1860–1861). He worked tirelessly for the rise of his home in economic, cultural and scientific areas, earning the honorary title of "Széchenyi of Transylvania". Biography He started his political career as an official of the Gubernium (the Government of Transylvania) in 1826, and reached the position of Treasurer in 1847, at the same time he became a leading figure of the liberal opposition in Transylvania. He was appointed interim, then actual Governor during the Hungarian Revolution of 1848. He presided the Székely National Assembly in Agyagfalva (today: ''Lutița, Romania''), wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Women's History
Women's history is the study of the role that women have played in history and the methods required to do so. It includes the study of the history of the growth of woman's rights throughout recorded history, personal achievement over a period of time, the examination of individual and groups of women of historical significance, and the effect that historical events have had on women. Inherent in the study of women's history is the belief that more traditional recordings of history have minimized or ignored the contributions of women to different fields and the effect that historical events had on women as a whole; in this respect, women's history is often a form of historical revisionism, seeking to challenge or expand the traditional historical consensus. The main centers of scholarship have been the United States and Britain, where second-wave feminist historians, influenced by the new approaches promoted by social history, led the way. As activists in women's liberation, discus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental History
Environmental history is the study of human interaction with the natural world over time, emphasising the active role nature plays in influencing human affairs and vice versa. Environmental history first emerged in the United States out of the environmental movement of the 1960s and 1970s, and much of its impetus still stems from present-day global environmental concerns. The field was founded on conservation issues but has broadened in scope to include more general social and scientific history and may deal with cities, population or sustainable development. As all history occurs in the natural world, environmental history tends to focus on particular time-scales, geographic regions, or key themes. It is also a strongly multidisciplinary subject that draws widely on both the humanities and natural science. The subject matter of environmental history can be divided into three main components. The first, nature itself and its change over time, includes the physical impact of hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church History
__NOTOC__ Church history or ecclesiastical history as an academic discipline studies the history of Christianity and the way the Christian Church has developed since its inception. Henry Melvill Gwatkin defined church history as "the spiritual side of the history of civilized people ever since our Master's coming". A. M. Renwick, however, defines it as an account of the Church's success and failure in carrying out Christ's Great Commission.A. M. Renwick and Allan Harman, A. M. Harman, ''The Story of the Church'' (3rd ed.), p. 8. Renwick suggests a fourfold division of church history into Mission (Christianity), missionary activity, Ecclesiastical polity, church organization, Christian theology, doctrine and "the effect on human life". Church history is often, but not always, studied from a Christian perspective. Writers from different Christian traditions will often highlight people and events particularly relevant to their own denominational history. Catholic and Orthodox writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doctorandus
Doctorandus (drs., ; ) is a Dutch academic title according to the pre-Bachelor–Master system. The female form is doctoranda (dra., though this abbreviation is no longer used). The title is acquired by passing the ''doctoraalexamen'', the exam which usually concludes university study. Some students will continue to do research under the supervision of a professor, which eventually allows them to obtain the title of doctor. In Dutch, the words ''doctoraal'' and ''doctoraat'' have different meanings, the first referring to the doctorandus, the second word referring to the doctorate phase or title. The word 'doctorandus' is based on the traditional principle that this degree is a prerequisite and intermediate step for obtaining a doctorate title. However, in the twentieth century the doctorandi have become considered to be graduates and when they can choose a scientific career, they do so usually as a paid '' promovendus'' and not as research students. An exception are medical studen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information History
Information history may refer to the history of each of the categories listed below (or to combinations of them). It should be recognized that the understanding of, for example, libraries as information systems only goes back to about 1950. The application of the term ''information'' for earlier systems or societies is a retronym. The word and concept "information" The Latin roots and Greek origins of the word "information" is presented by Capurro & Hjørland (2003). References on "formation or molding of the mind or character, training, instruction, teaching" date from the 14th century in both English (according to Oxford English Dictionary) and other European languages. In the transition from Middle Ages to Modernity the use of the concept of information reflected a fundamental turn in epistemological basis – from "giving a (substantial) form to matter" to "communicating something to someone". Peters (1988, pp. 12–13) concludes: :Information was readily deployed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
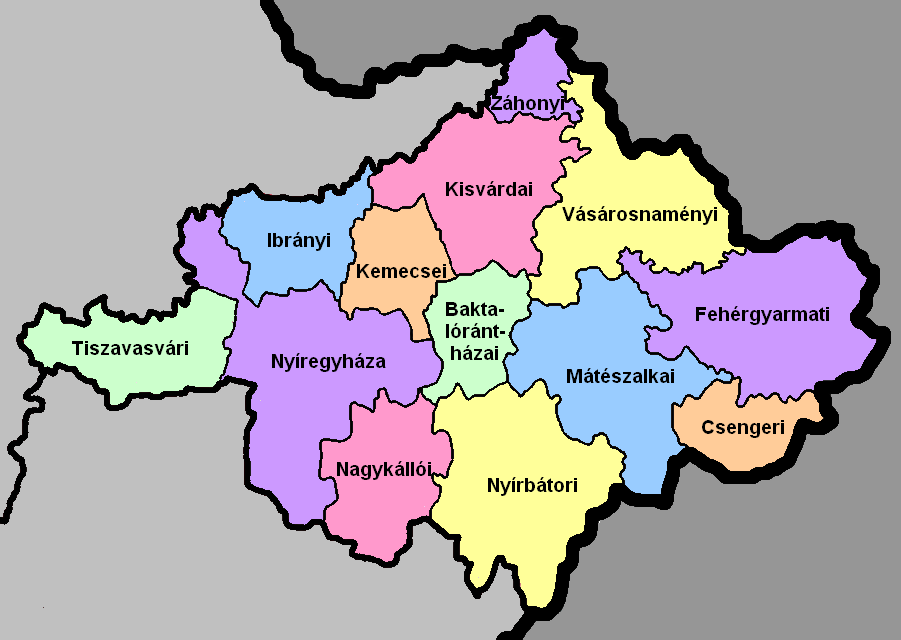
Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County
Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg ( hu, Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg megye, ) is an administrative county (Hungarian: ''megye'') in north-eastern Hungary, bordering Slovakia (Košice Region), Ukraine (Zakarpattia Oblast), and Romania ( Bihor and Satu Mare counties). It shares borders with the Hungarian counties Hajdú-Bihar and Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén. The capital of Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg county is Nyíregyháza. Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg County was organised after World War II from the previous counties Szatmár-Ugocsa-Bereg and Szabolcs. Before 1991, it was called Szabolcs-Szatmár County. Geography Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg is located in the north-eastern tip of Hungary. It borders Ukraine (Zakarpattia Oblast), Slovakia (Košice Region), and Romania ( Bihor and Satu Mare counties), and has good connections both by road and rail. Within Hungary, the county is bordered by Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén County and the Tisza River to the north-west and Hajdú-Bihar County to the south-west. The ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Transdanubia
Western Transdanubia ( hu, Nyugat-Dunántúl) is a statistical ( NUTS 2) region of Hungary. It is part of the Transdanubia (NUTS 1) region. Western Transdanubia includes the counties of Zala, Vas, and Győr-Moson-Sopron. See also *List of regions of Hungary There are seven statistical regions of Hungary created in 1999 by the Law 1999/XCII amending Law 1996/XXI. Regions are groupings of the 19 counties and the capital city. *''Northern Hungary'' includes the counties Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén, Hev ... References {{coord, 47, 41, 3, N, 17, 38, 6, E, source:itwiki_type:adm1st, display=title NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heves County
Heves county ( hu, Heves megye, ) lies in northern Hungary, between the right bank of the river Tisza and the Mátra and Bükk mountains. It shares borders with the Hungarian counties Pest, Nógrád, Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén and Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok. Eger is the county seat. Tourist sights * Lake Tisza * Bükk National Park * Bélapátfalva, abbey * Castle and City of Eger * Erdőtelek Arboretum * Feldebrő, 11th century Romanesque church * Gyöngyös, Mátra Museum * Hatvan, Grassalkovich mansion * Kisnána castle * Noszvaj, De la Motte mansion * Parád * Sirok castle * Szilvásvárad, Szalajka Valley * Szarvaskő, castle ruins Geography Heves county is a geographically diverse area; its northern part is mountainous (the Mátra and Bükk are the two highest mountain ranges in Hungary), while at south it includes a part of the Great Hungarian Plain. From south it is bordered by Lake Tisza, the largest artificial lake in Hungary. The average temperature is between 8 and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
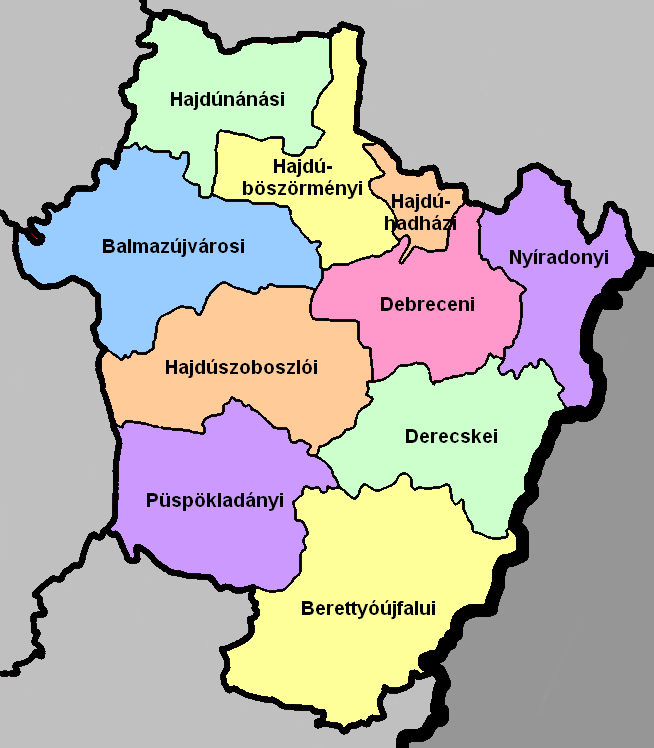
Hajdú-Bihar County
Hajdú-Bihar ( hu, Hajdú-Bihar megye, ) is an administrative county (comitatus or megye) in eastern Hungary, on the border with Romania. It shares borders with the Hungarian counties Szabolcs-Szatmár-Bereg, Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén, Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok and Békés. The capital of Hajdú-Bihar county is Debrecen. Together with Bihor County in Romania it constitutes the Biharia Euroregion. Geography The area of the county does not form a geographical unit; it shares several features with the neighbouring areas: from northeast the sand hills of the Nyírség spread over the county borders. The western part is the Hortobágy National Park ("Puszta"), a large flat area of the country. The county of Hajdú-Bihar occupies the eastern part of Hungary. Most of its territory is completely flat and is part of the Pannonian Plain region (called the Grand Plain in the country). The highest point hardly rises over 170.5 metres in the north. It seems that the county slopes to the south be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Great Plain
The Southern Great Plain ( hu, Dél-Alföld) is a statistical ( NUTS 2) region of Hungary. It is part of Great Plain and North (NUTS 1) region. The Southern Great Plain includes three counties: * Bács-Kiskun * Békés * Csongrád-Csanád See also *List of regions of Hungary There are seven statistical regions of Hungary created in 1999 by the Law 1999/XCII amending Law 1996/XXI. Regions are groupings of the 19 counties and the capital city. *''Northern Hungary'' includes the counties Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén, Hev ... References NUTS 2 statistical regions of the European Union * {{Hungary-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |