|
Hummel Bird
The Hummel Bird is an experimental/amateur built aircraft designed by Morry Hummel and produced by Hummel Aviation of Byran, Ohio, United States. It is a single-seat, single-engine, all-metal airplane typically powered by a 1/2 VW engine in the 32 hp-45 hp range although other engines have been used successfully. It is built from plans, but many of the components are available pre-made from Hummel Aviation. Examples have been built for less than $4,000 with extensive "scrounging", but with all new material and a pre-built engine, a more likely figure would be $8,000–$10,000. Development The Hummel Bird is a derivative of an earlier design known as the Parker Teenie Two. Originally designed by Calvin Parker, the design was featured in ''Popular Mechanics'' May 1971. Plans for the Teenie Two were originally offered for sale in 1969 and are still offered today with more than 12,000 sets sold. The next generation of the design was called the Watson GW-1 Windwagon. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homebuilt Aircraft
Homebuilt aircraft, also known as amateur-built aircraft or kit planes, are constructed by persons for whom this is not a professional activity. These aircraft may be constructed from "scratch", from plans, or from assembly kits.Armstrong, Kenneth: ''Choosing Your Homebuilt - the one you will finish and fly! Second Edition'', pp. 39–52. Butterfield Press, 1993. Peter M Bowers: ''Guide to Homebuilts - Ninth Edition''. TAB Books, Blue Ridge Summit PA, 1984. Overview In the United States, Brazil, Australia, New Zealand and South Africa, homebuilt aircraft may be licensed Experimental under FAA or similar local regulations. With some limitations, the builder(s) of the aircraft must have done it for their own education and recreation rather than for profit. In the U.S., the primary builder can also apply for a repairman's certificate for that airframe. The repairman's certificate allows the holder to perform and sign off on most of the maintenance, repairs, and inspections themsel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Stabilizer
A tailplane, also known as a horizontal stabiliser, is a small lifting surface located on the tail (empennage) behind the main lifting surfaces of a fixed-wing aircraft as well as other non-fixed-wing aircraft such as helicopters and gyroplanes. Not all fixed-wing aircraft have tailplanes. Canards, tailless and flying wing aircraft have no separate tailplane, while in V-tail aircraft the vertical stabiliser, rudder, and the tail-plane and elevator are combined to form two diagonal surfaces in a V layout. The function of the tailplane is to provide stability and control. In particular, the tailplane helps adjust for changes in position of the centre of pressure or centre of gravity caused by changes in speed and attitude, fuel consumption, or dropping cargo or payload. Tailplane types The tailplane comprises the tail-mounted fixed horizontal stabiliser and movable elevator. Besides its planform, it is characterised by: *Number of tailplanes - from 0 ( tailless or canard) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clark Y
Clark Y is the name of a particular airfoil profile, widely used in general purpose aircraft designs, and much studied in aerodynamics over the years. The profile was designed in 1922 by Virginius E. Clark using thickness distribution of the German-developed Goettingen 398 airfoil.Piccirillo, Albert, "The Clark Y Airfoil - A Historical Retrospective," SAE/AIAA paper 2000-01-5517, presented at the World Aviation Congress & Exposition, October 10, 2000, San Diego, California. The airfoil has a thickness of 11.7 percent and is flat on the lower surface aft of 30 percent of chord. The flat bottom simplifies angle measurements on propellers, and makes for easy construction of wings. For many applications the Clark Y has been an adequate airfoil section; it gives reasonable overall performance in respect of its lift-to-drag ratio, and has gentle and relatively benign stall characteristics. But the flat lower surface is not optimal from an aerodynamic perspective, and it is rarely used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyrocopter
An autogyro (from Ancient Greek, Greek and , "self-turning"), also known as a ''gyroplane'', is a type of rotorcraft that uses an unpowered rotor in free autorotation to develop lift (force), lift. Forward thrust is provided independently, by an engine-driven propeller. While similar to a helicopter rotor in appearance, the autogyro's rotor must have air flowing across the rotor disc to generate rotation, and the air flows upwards through the rotor disc rather than down. The autogyro was invented by Spanish engineer Juan de la Cierva in an attempt to create an aircraft that could fly safely at low speeds. He first flew one on 9 January 1923, at Cuatro Vientos Airport, Cuatro Vientos Airfield in Madrid. The aircraft resembled the fixed-wing aircraft of the day, with a front-mounted engine and propeller. Cierva's autogyro is considered the predecessor of the modern helicopter. The success of the autogyro garnered the interest of industrialists and under license from Cierva in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
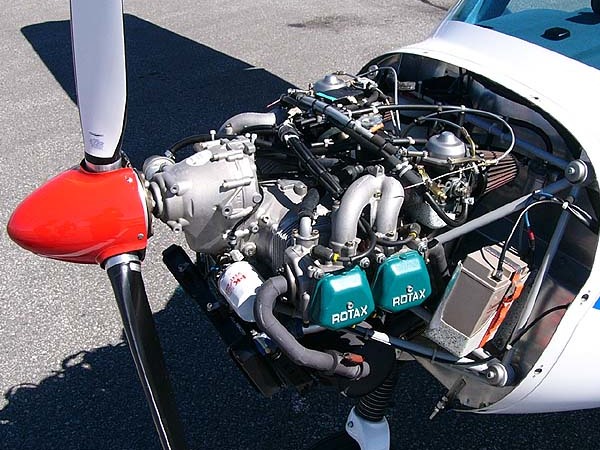
Rotax
Rotax is the brand name for a range of internal combustion engines developed and manufactured by the Austrian company BRP-Rotax GmbH & Co KG (until 2016 BRP-Powertrain GmbH & Co. KG), in turn owned by the Canadian Bombardier Recreational Products. Rotax four-stroke and advanced two-stroke engines are used in a wide variety of small land, sea and airborne vehicles. Bombardier Recreational Products (BRP) use them in their own range of such vehicles. In the light aircraft class, in 1998 Rotax outsold all other aero engine manufacturers combined.Gunston, W.; "''World Encyclopaedia of Aero Engines''", 4th Edition, Patrick Stephens Ltd, 1998, Page 170. History The company was founded in 1920 in Dresden, Germany, as ROTAX-WERK AG. In 1930, it was taken over by Fichtel & Sachs and transferred its operations to Schweinfurt, Germany. Operations were moved to Wels, Austria, in 1943 and finally to Gunskirchen, Austria, in 1947. In 1959, the majority of Rotax shares were taken over by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1/2 VW Engine
The Volkswagen air-cooled engine is an air-cooled, gasoline-fuelled, boxer engine with four horizontally opposed cast-iron cylinders, cast aluminum alloy cylinder heads and pistons, magnesium-alloy crankcase, and forged steel crankshaft and connecting rods. There are two distinct families/variations of the aircooled engine namely Type 1 and Type 4. The Type 3 engine is a variation of the Type 1 engine with pancake cooling arrangement. Variations of the engine were produced by Volkswagen plants worldwide from 1936 until 2006 for use in Volkswagen's own vehicles, notably the Type 1 (Beetle), Type 2 (bus, transporter), Type 3, and Type 4. Additionally, the engines were widely used in industrial, light aircraft and kit car applications. Type 1: 1.0–1.6 litres 1200 The 1.2-litre engine is called ''Typ 122'' and has a displacement of .''Die Betriebsanleitung für den Volkswagen-Industriemotor Typ 122, Typ 126A.'' Volkswagen AG. Wolfsburg. March 1985. Page 29 As industrial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basic Ultralight Aeroplane
The Canadian Aviation Regulations define two types of ultralight aircraft: basic ultra-light aeroplane (BULA), and advanced ultra-light aeroplane (AULA). Definition Regulation of ultra-light aircraft in Canada is covered by the Canadian Aviation Regulations. An earlier definition of "ultra-light aeroplane", effective October 10, 1996, meant: * a single-seat aeroplane that has a launch weight of 165 kg (364 pounds) or less, and a wing area, expressed in square metres, of not less than the launch weight in kilograms minus 15, divided by 10, and in no case less than , * a two-seat instructional aeroplane that has a launch weight of 195 kg (430 pounds) or less, and a wing area, expressed in square metres, of not less than 10 m2 and a wing loading of not more than 25 kg/m2 (5.12 lb/ft2), the wing loading being calculated using the launch weight plus the occupant weight of 80 kg (176 pounds) per person, or * an advanced ultra-light aeroplane; On June 1, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultralight Aircraft (United States)
Ultralight aircraft in the United States are much smaller and lighter than ultralight aircraft as defined by all other countries. In the United States, ultralights are described as "ultralight vehicles" and not as aircraft. They are not required to be registered, nor is the pilot required to have a pilot's certificate. United States definition of "ultralight" Regulation of ultralight aircraft in the United States is covered by the Code of Federal Regulations, Title 14 (Federal Aviation Regulations), Part 103, or ''14 CFR Part 103'', which defines an "ultralight" as a vehicle that: * has only one seat * Is used only for recreational or sport flying * Does not have a U.S. or foreign airworthiness certificate * If unpowered, weighs less than 155 pounds * If powered: ** Weighs less than 254 pounds (115 kg) empty weight, excluding floats and safety devices ** Has a maximum fuel capacity of 5 U.S. gallons (19 L) ** Does not exceed 55 knots (102 km/h; 63 mph) c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conventional Landing Gear
Conventional landing gear, or tailwheel-type landing gear, is an aircraft undercarriage consisting of two main wheels forward of the center of gravity and a small wheel or skid to support the tail.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 133. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. From the Ground Up, 27th edition, page 11 The term taildragger is also used, although some argue it should apply only to those aircraft with a tailskid rather than a wheel. The term "conventional" persists for historical reasons, but all modern jet aircraft and most modern propeller aircraft use tricycle gear. History In early aircraft, a tailskid made of metal or wood was used to support the tail on the ground. In most modern aircraft with conventional landing gear, a small articulated wheel assembly is attached to the rearmost part of the airframe in place of the skid. This wheel may be steered by the pilot through a connection to the rudder pedals, allowing the rudd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricycle Landing Gear
Tricycle gear is a type of aircraft undercarriage, or ''landing gear'', arranged in a tricycle fashion. The tricycle arrangement has a single nose wheel in the front, and two or more main wheels slightly aft of the center of gravity. Tricycle gear aircraft are the easiest for takeoff, landing and taxiing, and consequently the configuration is the most widely used on aircraft.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 524. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. Aviation Publishers Co. Limited, ''From the Ground Up'', page 11 (27th revised edition) History Several early aircraft had primitive tricycle gear, notably very early Antoinette planes and the Curtiss Pushers of the pre-World War I Pioneer Era of aviation. Waldo Waterman's 1929 tailless '' Whatsit'' was one of the first to have a steerable nose wheel. In 1956, Cessna introduced sprung-steel tricycle landing gear on the Cessna 172. Their marketing department described this as "Land-O-Matic" t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rib (aircraft)
In an aircraft, ribs are forming elements of the structure of a wing, especially in traditional construction. By analogy with the anatomical definition of " rib", the ribs attach to the main spar, and by being repeated at frequent intervals, form a skeletal shape for the wing. Usually ribs incorporate the airfoil shape of the wing, and the skin adopts this shape when stretched over the ribs. Type of ribs There are several types of ribs. Form-ribs, plate-type ribs, truss ribs, closed-ribs, forged ribs and milled ribs, where form-ribs are used for light to medium loading and milled ribs offer the greatest strength. * Form-ribs are made from a sheet of metal bent into shape, such as a U-profile. This profile is placed on the skin, just like a stringer, but then in the other direction. * Plate-type ribs consist of sheet-metal, which has upturned edges and (often has) weight-saving holes cut into it. * Truss ribs are built up out of profiles that are joined together. These joints requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spar (aviation)
In a fixed-wing aircraft, the spar is often the main structural member of the wing, running spanwise at right angles (or thereabouts depending on wing sweep) to the fuselage. The spar carries flight loads and the weight of the wings while on the ground. Other structural and forming members such as ribs may be attached to the spar or spars, with stressed skin construction also sharing the loads where it is used. There may be more than one spar in a wing or none at all. Where a single spar carries most of the force, it is known as the main spar. Spars are also used in other aircraft aerofoil surfaces such as the tailplane and fin and serve a similar function, although the loads transmitted may be different from those of a wing spar. Spar loads The wing spar provides the majority of the weight support and dynamic load integrity of cantilever monoplanes, often coupled with the strength of the wing 'D' box itself. Together, these two structural components collectively provide the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |