|
Hubert Grenfell
Hubert Henry Grenfell, (12 June 1845 – 13 September 1906), was a British naval officer, and expert in naval gunnery. Life He was born at Rugby, Warwickshire, Rugby on 12 June 1845, the son of Algernon Grenfell, a cleric and schoolmaster, and his wife Maria Guerin Price, sister of Bonamy Price. Joining the navy as a cadet on 13 December 1859, when fourteen, Grenfell passed out first from the ''HMS Britannia (1820), Britannia'', and gained as sub-lieutenant the Beaumont Testimonial in 1865. He qualified as gunnery lieutenant in 1867, and was appointed first lieutenant on HMS Queen Charlotte (1810), HMS ''Excellent'', on 22 September 1869. While holding this appointment, Grenfell worked out with the naval engineer Edward Newman pioneering hydraulic machinery, hydraulic mountings for heavy naval ordnance. He also published in ''Engineering'' and service journals. On 31 December 1876 he was made commander, and on 1 May 1877 was appointed, on account of his linguistic attainments, sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rugby, Warwickshire
Rugby is a market town in eastern Warwickshire, England, close to the River Avon. In the 2021 census its population was 78,125, making it the second-largest town in Warwickshire. It is the main settlement within the larger Borough of Rugby which has a population of 114,400 (2021). Rugby is situated on the eastern edge of Warwickshire, near to the borders with Leicestershire and Northamptonshire. Rugby is the most easterly town within the West Midlands region, with the nearby county borders also marking the regional boundary with the East Midlands. It is north of London, east-southeast of Birmingham, east of Coventry, north-west of Northampton, and south-southwest of Leicester. Rugby became a market town in 1255, but remained a small and fairly unimportant town until the 19th century. In 1567 Rugby School was founded as a grammar school for local boys, but by the 18th century it had gained a national reputation as a public school. The school is the birthplace of Rugby foo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incandescent Electric Lamp
An electric light, lamp, or light bulb is an electrical component that produces light. It is the most common form of artificial lighting. Lamps usually have a base made of ceramic, metal, glass, or plastic, which secures the lamp in the socket of a light fixture, which is often called a "lamp" as well. The electrical connection to the socket may be made with a screw-thread base, two metal pins, two metal caps or a bayonet cap. The three main categories of electric lights are incandescent lamps, which produce light by a filament heated white-hot by electric current, gas-discharge lamps, which produce light by means of an electric arc through a gas, such as fluorescent lamps, and LED lamps, which produce light by a flow of electrons across a band gap in a semiconductor. Before electric lighting became common in the early 20th century, people used candles, gas lights, oil lamps, and fires. Vasily Vladimirovich Petrov developed the first persistent electric arc in 1802, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century Royal Navy Personnel
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the large S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
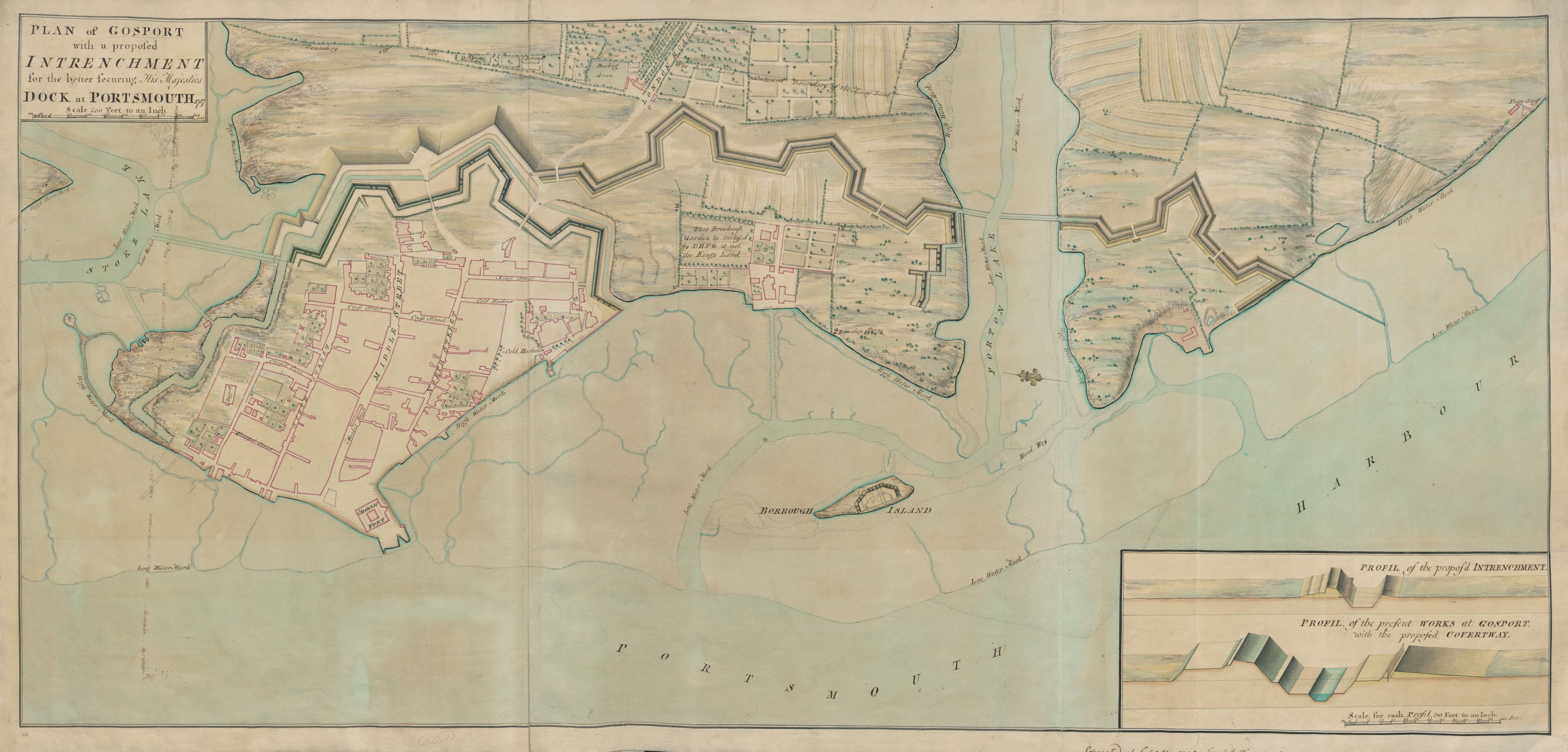
Gosport
Gosport ( ) is a town and non-metropolitan borough on the south coast of Hampshire, South East England. At the 2011 Census, its population was 82,662. Gosport is situated on a peninsula on the western side of Portsmouth Harbour, opposite the city of Portsmouth, to which it is linked by the Gosport Ferry. Gosport lies south-east of Fareham, to which it is linked by a Bus Rapid Transit route and the A32. Until the last quarter of the 20th century, Gosport was a major naval town associated with the defence and supply infrastructure of His Majesty's Naval Base (HMNB) Portsmouth. As such over the years extensive fortifications were created. Gosport is still home to and a Naval Armament Supply Facility, as well as a Helicopter Repair base. The Town area of the Borough, including Newtown, consists of the town centre, Stoke Road shopping area, Walpole Park, Royal Clarence Yard and three modern marinas: Royal Clarence, Gosport Marina and Haslar Marina. As part of the ''Renaissa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Von Schütz
The gens Julia (''gēns Iūlia'', ) was one of the most prominent patrician families in ancient Rome. Members of the gens attained the highest dignities of the state in the earliest times of the Republic. The first of the family to obtain the consulship was Gaius Julius Iulus in 489 BC. The gens is perhaps best known, however, for Gaius Julius Caesar, the dictator and grand uncle of the emperor Augustus, through whom the name was passed to the so-called Julio-Claudian dynasty of the first century AD. The Julius became very common in imperial times, as the descendants of persons enrolled as citizens under the early emperors began to make their mark in history.''Dictionary of Greek and Roman Biography and Mythology'', vol. II, pp. 642, 643. Origin The Julii were of Alban origin, mentioned as one of the leading Alban houses, which Tullus Hostilius removed to Rome upon the destruction of Alba Longa. The Julii also existed at an early period at Bovillae, evidenced by a ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Gruson
Hermann August Jacques Gruson (March 13, 1821, in Magdeburg – January 30, 1895) was a German engineer, inventor and industrial entrepreneur. Life Hermann Gruson was a descendant of a Huguenot immigrant family, and son of Prime Minister Lieutenant Louis Abraham Gruson in Magdeburg citadel. He attended the Domgymnasium Magdeburg, but then switched to the industrial and trade school, which he graduated in 1839, and did his military service as a one-year volunteer in a pioneer unit. He then attended the University of Berlin. He concentrated mainly on scientific and mathematical subjects and also attended lectures of his uncle Johann Philipp Gruson. Gruson then worked for five years in the engineering works of August Borsig, who was friends with his father, and learned machining. Borsig was able to place Gruson in a job with the Berlin-Hamburg railway, which he held between 1843 and 1851. In November 1847, Gruson rescued a boy who was drowning, and was awarded a medal for saving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institution Of Naval Architects
The Royal Institution of Naval Architects (also known as RINA) is an international organisation representing naval architects. It is an elite international professional institution based in London. Its members are involved worldwide at all levels in the design, construction, repair and operation of ships, boats and marine structures. Members are elected by the council and are presented with the titles AssocRINA (Associate), AMRINA (Associate Member), MRINA (Member) and FRINA (Fellow) depending on their membership type. These title are usually suffixed after the name of the member. The Patron of the Institution is Queen Elizabeth II. History The Royal Institution of Naval Architects was founded in Britain in 1860 as The Institution of Naval Architects and incorporated by Royal Charter in 1910 and 1960 to "advance the art and science of ship design". Founding members included John Scott Russell, Edward Reed, Rev Joseph Woolley, Nathaniel Barnaby, Frederick Kynaston Barnes and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armstrong Whitworth
Sir W G Armstrong Whitworth & Co Ltd was a major British manufacturing company of the early years of the 20th century. With headquarters in Elswick, Newcastle upon Tyne, Armstrong Whitworth built armaments, ships, locomotives, automobiles and aircraft. The company was founded by William Armstrong in 1847, becoming Armstrong Mitchell and then Armstrong Whitworth through mergers. In 1927, it merged with Vickers Limited to form Vickers-Armstrongs, with its automobile and aircraft interests purchased by J D Siddeley. History In 1847, the engineer William George Armstrong founded the Elswick works at Newcastle, to produce hydraulic machinery, cranes and bridges, soon to be followed by artillery, notably the Armstrong breech-loading gun, with which the British Army was re-equipped after the Crimean War. In 1882, it merged with the shipbuilding firm of Charles Mitchell to form Armstrong Mitchell & Company and at the time its works extended for over a mile (about 2 km) along th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonamy Price
Bonamy Price (22 May 18078 January 1888) was a British political economist. Biography Price was born at Saint Peter Port, Guernsey, where he lived until age 14, when he left Guernsey and entered the tutelage of Reverend Charles Bradley in High Wycombe. He entered at Worcester College, Oxford, in 1825, where he received double first in classics in 1829. During his time at Worcester College, he was occasionally studied under Thomas Arnold, at Laleham; who went on to become head master of Rugby School, and offered Price a role as assistant master of mathematics at the school, where he remained from 1830 until 1850. Price married Lydia Rose, daughter of Joseph Rose who was the vicar at Rothley, on 18 December 1934. In 1868 Price was elected Drummond Professor of Political Economy at Oxford, and was thrice re-elected to the post, which he held till his death. U.S. Senator from Missouri Carl Schurz quoted extensively from one of Price's treatises during his Senate speech of 14 J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alverstoke, Hampshire
Alverstoke is a small settlement which forms part of the borough of Gosport, on the south coast of Hampshire, England. It stretches east–west from Fort Blockhouse, Haslar to Browndown Battery, and is centred east of the shore of Stokes Bay and near the head of a creek which extends a mile westward from Portsmouth Harbour. Residents of Alverstoke have at times in the 20th century been called 'The Alverstocracy' by some residents of Gosport, in a tongue-in-cheek fashion, due to higher house prices and a perceived higher social status of the area. History The name 'Alverstoke' is most likely to be derived from a corruption of the name Alwara – an Anglo-Saxon Lady of the Manor – and Stoke, a settlement on the area of Alverstoke. Alverstoke is mentioned in the Domesday Book as Alwarestock. Official Crown and Manorial records for the village refer to "The liberty of Alverstoke with Gosport", although the name has clearly evolved over the years: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen Provinces and territories of Canada, provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", "Birthplace of Confederation" and "Cradle of Confederation". Its capital and largest city is Charlottetown. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Part of the traditional lands of the Miꞌkmaq, it was colonized by the French in 1604 as part of the colony of Acadia. The island was ceded to the British at the conclusion of the French and Indian War in 1763 and became part of the colony of Nova Scotia, and in 1769 the island became its own British colony. Prince Edward Island hosted the Charlottetown Conference in 1864 to discuss a Maritime Union, union of the Maritime provinces; however, the conference became the first in a series of meetings which led to Canadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.jpg)

