|
Hubbard Medal
The Hubbard Medal is awarded by the National Geographic Society for distinction in exploration, discovery, and research. The medal is named for Gardiner Greene Hubbard Gardiner Greene Hubbard (August 25, 1822 – December 11, 1897) was an American lawyer, financier, and community leader. He was a founder and first president of the National Geographic Society; a founder and the first president of the Bell Tel ..., first National Geographic Society president. It is made of gold and is traditionally presented by the President of the United States. Recipients See also * List of geography awards References Geography awards National Geographic Society National Geographic Society medals recipients {{National Geographic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubbard Gold Medal, Anne Morrow Lindbergh
Hubbard may refer to: Places Canada *Hubbard, Saskatchewan *Hubbards, Nova Scotia Canada/United States *Mount Hubbard, a mountain on the Alaska/Yukon border *Hubbard Glacier, a large freshwater glacier in Alaska and Yukon Greenland *Hubbard Glacier (Greenland), a glacier in the Inglefield Gulf United States *Hubbard, Iowa *Hubbard, Minnesota * Hubbard, Missouri *Hubbard, Nebraska *Hubbard, Ohio *Hubbard, Oregon *Hubbard, Texas *Hubbard, Dodge County, Wisconsin *Hubbard, Rusk County, Wisconsin *Hubbard County, Minnesota *Hubbard Lake, Michigan (other) *Hubbard Township, Hubbard County, Minnesota *Hubbard Township, Polk County, Minnesota *Hubbard Township, Trumbull County, Ohio *Hubbard Brook Experimental Forest, an outdoor laboratory for ecological studies in central New Hampshire *Hubbard Creek, Texas *Hubbard Street, in Chicago, Illinois *Lake Ray Hubbard, a freshwater lake in Dallas and Rockwall County, Texas People *Hubbard (surname), a surname *Fern Hubbard Orme (19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeronaut
Aeronautics is the science or art involved with the study, design, and manufacturing of air flight–capable machines, and the techniques of operating aircraft and rockets within the atmosphere. The British Royal Aeronautical Society identifies the aspects of "aeronautical Art, Science and Engineering" and "The profession of Aeronautics (which expression includes Astronautics)." While the term originally referred solely to ''operating'' the aircraft, it has since been expanded to include technology, business, and other aspects related to aircraft. The term "aviation" is sometimes used interchangeably with aeronautics, although "aeronautics" includes lighter-than-air craft such as airships, and includes ballistic vehicles while "aviation" technically does not. A significant part of aeronautical science is a branch of dynamics called aerodynamics, which deals with the motion of air and the way that it interacts with objects in motion, such as an aircraft. History Early ideas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
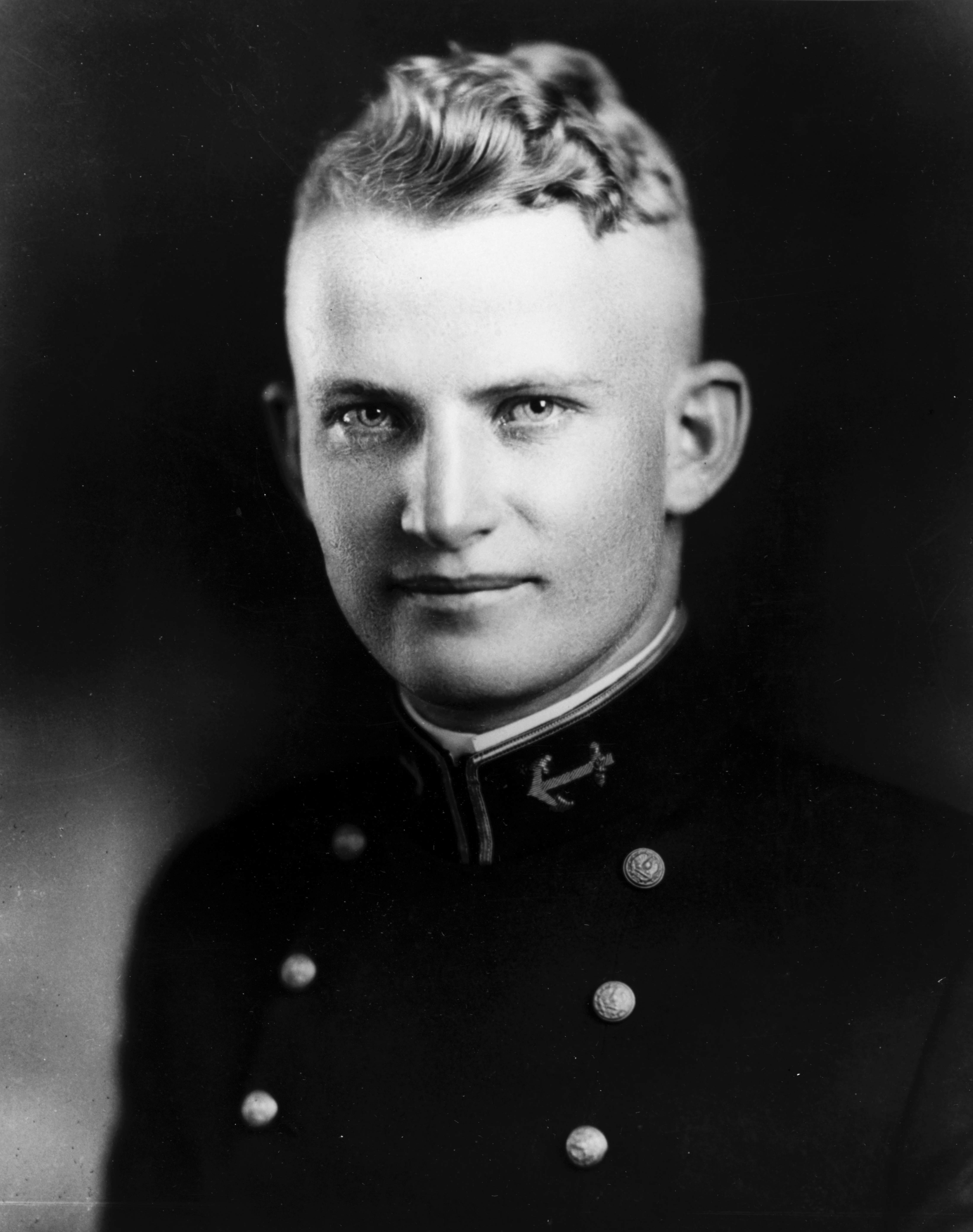
Frank Borman
Frank Frederick Borman II (born March 14, 1928) is a retired United States Air Force (USAF) colonel, aeronautical engineer, test pilot, businessman, and NASA astronaut. He was the commander of Apollo 8, the first mission to fly around the Moon, and together with crewmates Jim Lovell and William Anders, became the first of 24 humans to do so, for which he was awarded the Congressional Space Medal of Honor. , he is the oldest living former American astronaut, eleven days older than Lovell. Four days before he graduated with the West Point Class of 1950, in which he was ranked eighth out of 670, Borman was commissioned in the USAF. He qualified as a fighter pilot and served in the Philippines. He earned a Master of Science degree at Caltech in 1957, and then became an assistant professor of thermodynamics and fluid mechanics at West Point. In 1960, he was selected for Class 60-C at the USAF Experimental Flight Test Pilot School at Edwards Air Force Base in California and qual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman Dyhrenfurth
Norman Gunther Dyhrenfurth ( Breslau, today Wroclaw, May 7, 1918 – Salzburg, September 24, 2017) was a German-Swiss-American mountaineer and filmmaker. He was the leader of the successful American Mount Everest Expedition of 1963, which placed six climbers on the summit. Family and early years Norman Dyhrenfurth was born in Germany, the son of Himalayan explorers Günter Oskar Dyhrenfurth and Hettie Dyhrenfurth. His mother was of half Jewish ancestry. After the Nazis came to power, they emigrated, first to Austria in 1933, then two years later to Switzerland, where they became citizens. In 1936, Dyhrenfurth's parents were awarded a gold medal for alpinism at the 1936 Summer Olympics in Berlin. He emigrated to the United States in 1937. His service in the United States Army enabled him to gain joint U.S.-Swiss citizenship. He was the founder of the Motion Picture Division of the Department of Theater Arts at UCLA, but resigned that position in 1952. In 1954, he was a Fulbright ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropologist
An anthropologist is a person engaged in the practice of anthropology. Anthropology is the study of aspects of humans within past and present societies. Social anthropology, cultural anthropology and philosophical anthropology study the norms and values of societies. Linguistic anthropology studies how language affects social life, while economic anthropology studies human economic behavior. Biological (physical), forensic and medical anthropology study the biological development of humans, the application of biological anthropology in a legal setting and the study of diseases and their impacts on humans over time, respectively. Education Anthropologists usually cover a breadth of topics within anthropology in their undergraduate education and then proceed to specialize in topics of their own choice at the graduate level. In some universities, a qualifying exam serves to test both the breadth and depth of a student's understanding of anthropology; the students who pass are pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Leakey
Mary Douglas Leakey, FBA (née Nicol, 6 February 1913 – 9 December 1996) was a British paleoanthropologist who discovered the first fossilised ''Proconsul A proconsul was an official of ancient Rome who acted on behalf of a consul. A proconsul was typically a former consul. The term is also used in recent history for officials with delegated authority. In the Roman Republic, military command, or ...'' skull, an extinct ape which is now believed to be ancestral to humans. She also discovered the robust ''Zinjanthropus'' skull at Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania, eastern Africa. For much of her career she worked with her husband, Louis Leakey, at Olduvai Gorge, where they uncovered fossils of ancient hominines and the earliest hominins, as well as the stone tools produced by the latter group. Mary Leakey developed a system for Taxonomy (general), classifying the stone tools found at Olduvai. She discovered the Laetoli#Hominin footprints, Laetoli footprints, and at the Laetoli s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Leakey
Louis Seymour Bazett Leakey (7 August 1903 – 1 October 1972) was a Kenyan-British palaeoanthropologist and archaeologist whose work was important in demonstrating that humans evolved in Africa, particularly through discoveries made at Olduvai Gorge with his wife, fellow palaeoanthropologist Mary Leakey. Having established a programme of palaeoanthropological inquiry in eastern Africa, he also motivated many future generations to continue this scholarly work. Several members of the Leakey family became prominent scholars themselves. Another of Leakey's legacies stems from his role in fostering field research of primates in their natural habitats, which he saw as key to understanding human evolution. He personally focused on three female researchers, Jane Goodall, Dian Fossey, and Birutė Galdikas, calling them The Trimates. Each went on to become an important scholar in the field of primatology. Leakey also encouraged and supported many other PhD candidates, most notably from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally reserved for professional space travelers, the term is sometimes applied to anyone who travels into space, including scientists, politicians, journalists, and tourists. "Astronaut" technically applies to all human space travelers regardless of nationality. However, astronauts fielded by Russia or the Soviet Union are typically known instead as cosmonauts (from the Russian "kosmos" (космос), meaning "space", also borrowed from Greek). Comparatively recent developments in crewed spaceflight made by China have led to the rise of the term taikonaut (from the Mandarin "tàikōng" (), meaning "space"), although its use is somewhat informal and its origin is unclear. In China, the People's Liberation Army Astronaut Corps astronauts and their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Glenn
John Herschel Glenn Jr. (July 18, 1921 – December 8, 2016) was an American Marine Corps aviator, engineer, astronaut, businessman, and politician. He was the third American in space, and the first American to orbit the Earth, circling it three times in 1962. Following his retirement from NASA, he served from 1974 to 1999 as a Democratic United States Senator from Ohio; in 1998, he flew into space again at age 77. Before joining NASA, Glenn was a distinguished fighter pilot in World War II, the Chinese Civil War and the Korean War. He shot down three MiG-15s, and was awarded six Distinguished Flying Crosses and eighteen Air Medals. In 1957, he made the first supersonic transcontinental flight across the United States. His on-board camera took the first continuous, panoramic photograph of the United States. He was one of the Mercury Seven, military test pilots selected in 1959 by NASA as the nation's first astronauts. On February 20, 1962, Glenn flew the ''Friendship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George J
George may refer to: People * George (given name) * George (surname) * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Washington, First President of the United States * George W. Bush, 43rd President of the United States * George H. W. Bush, 41st President of the United States * George V, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1910-1936 * George VI, King of Great Britain, Ireland, the British Dominions and Emperor of India from 1936-1952 * Prince George of Wales * George Papagheorghe also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George Harrison, an English musician and singer-songwriter Places South Africa * George, Western Cape ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa * George, Missouri * George, Washington * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Characters * George (Peppa Pig), a 2-year-old pig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arleigh Burke
Arleigh Albert Burke (October 19, 1901 – January 1, 1996) was an admiral of the United States Navy who distinguished himself during World War II and the Korean War, and who served as Chief of Naval Operations during the Eisenhower and Kennedy administrations. , the lead ship of its class of Aegis-equipped guided missile destroyers, was commissioned in Burke's honor in 1991. The honor of naming a vessel after a living figure was only the fourth time it had been bestowed since 1861. Early life and naval career Burke was born in Boulder, Colorado, on October 19, 1901, to Oscar Burke and Clara Mokler. His grandfather, August Björkgren, was a Swedish immigrant to the US and changed his surname to 'Burke', a common Irish surname, to sound more 'American'. Due to the 1918 influenza outbreak, schools were closed in Boulder and he never graduated from high school. Burke won an alternate appointment to the United States Naval Academy given by his local congressman. During his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Allen Siple
Paul Allman Siple (December 18, 1908 – November 25, 1968) was an American Antarctic explorer and geographer who took part in six Antarctic expeditions, including the two Byrd expeditions of 1928–1930 and 1933–1935, representing the Boy Scouts of America as an Eagle Scout. In addition to being an Eagle Scout, Siple was also a Sea Scout. His first and third books covered these adventures. With Charles F. Passel he developed the wind chill factor, and Siple coined the term. Biography Siple was born in Montpelier, Ohio on December 18, 1908, to Clyde Lavonius Siple and Fannie Hope Allman. His family moved to Erie, Pennsylvania, where he graduated from Central High School in 1926. He became an Eagle Scout in 1923 with 59 merit badges. After an extensive nationwide search in 1928, he was the first Eagle Scout selected for an Antarctic expedition, sailing with Richard E. Byrd on his ship the ''City of New York''. Siple appeared in the documentary film ''With Byrd at the South Pole' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)