|
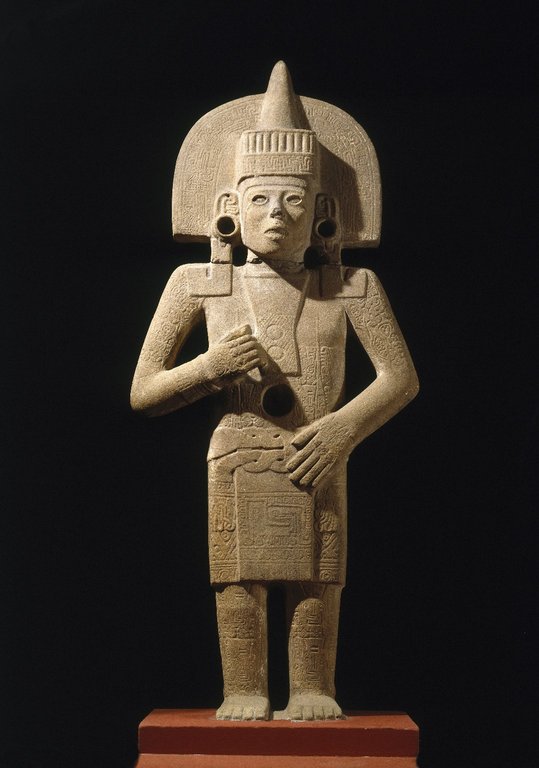
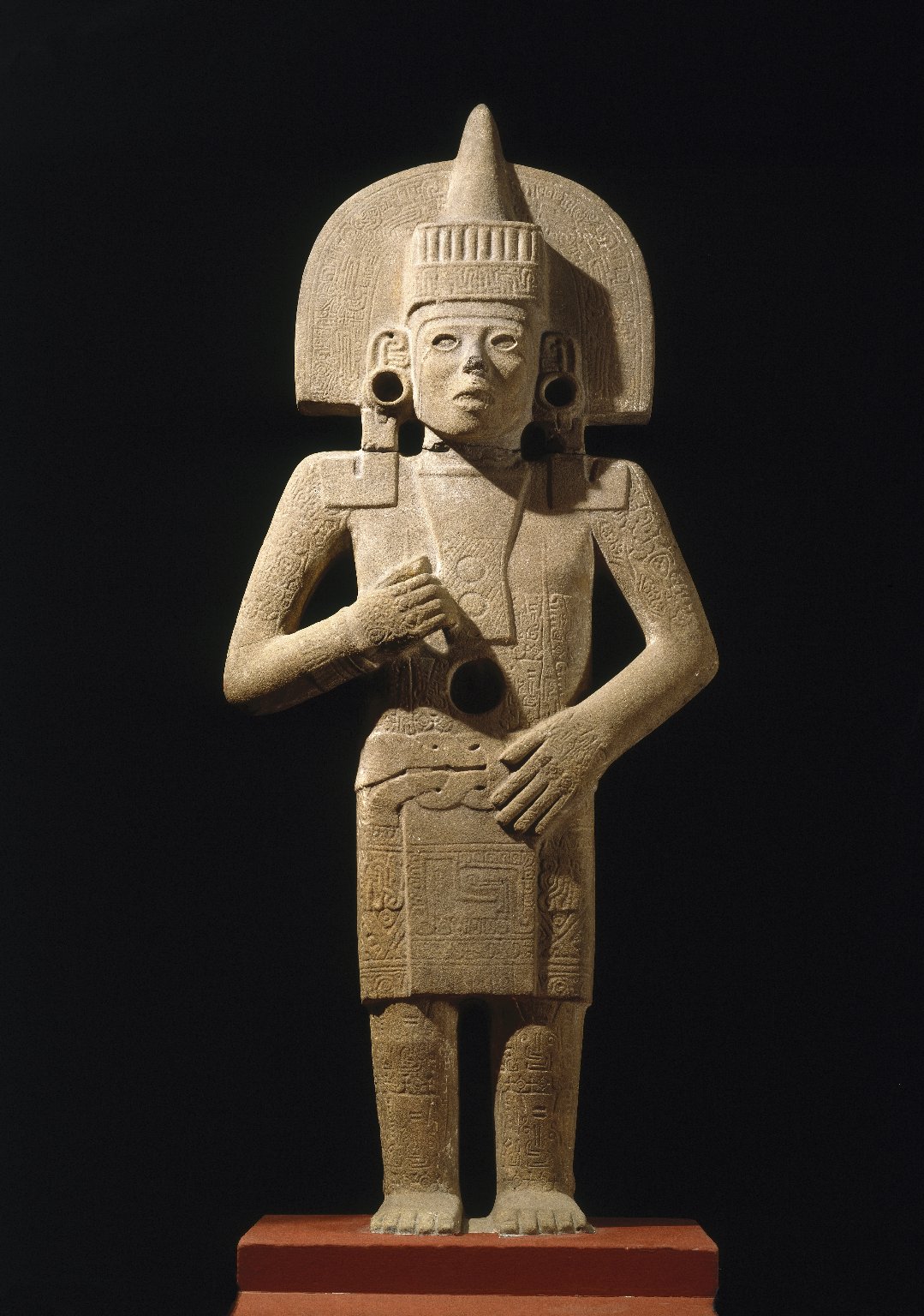
Huastec Civilization
The Huastec civilization (sometimes spelled Huaxtec or Wastek) was a pre-Columbian civilization of Mesoamerica, occupying a territory on the Gulf coast of Mexico that included the northern portion of Veracruz state, and neighbouring regions of the states of Hidalgo, Querétaro, San Luis Potosí, and Tamaulipas.Diehl 2000, pp. 184–185. The Huastec people were an early offshoot of the Maya peoples that migrated northwards. Surviving remains from the Huastec civilization include several large archaeological sites, a well-preserved temple, and a large amount of stone sculpture. By the Late Postclassic (c. AD 1200–1521), the Huastecs had developed metallurgy and were producing copper alloys. The Aztec Empire conquered the Huastec region around the 15th century, and probably demanded tribute payments. Culture The Huastec civilization is poorly studied, although there is a large body of stone sculpture, and a well-preserved Late Postclassic temple at Castillo de Teayo. In the Lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museo De Antropología De Xalapa
The Museo de Antropología de Xalapa ( en, Xalapa Museum of Anthropology) is an anthropological museum in the city of Xalapa, capital of the state of Veracruz in eastern Mexico. The building was designed by the architect Paul Balev at EDSA, 4 E 70th St, New York, N.Y. and opened in 1986. Some of the pieces in the museum date back to the Early Pre-Classic Period from 1300 BC to 900 BC. Mission/Goal The Museum of Anthropology of Xalapa has a tradition of solid institutional management and a forward-looking perspective. Its mission and goals correspond fully to the ideal of a university extension, promoting research, conservation and the dissemination of heritage, and providing a multidisciplinary environment for the development of students and professionals from various fields. History The Museum of Anthropology of Xalapa was born more than fifty years ago as the Anthropological Museum of the Department of Education. ~1937-governorship of Miguel Alemán Valdés ~1943-DG Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castillo De Teayo (Mesoamerican Site)
Castillo de Teayo is a mesoamerican Prehispanic archeological site and Mesoamerican pyramid, located in the La Huasteca region in northern Veracruz, Mexico. The main access to the site is via Federal Highway 130 México-Tuxpan up to the city of Teayo, it belongs to the Huastec culture and it is estimated it was inhabited between the 10th and 12th centuries. In the modern era the contemporary settlement of Castillo de Teayo developed around the ancient pyramid that the settlement and its municipality of Castillo de Teayo were named after. In the Tuxpan Canvas,A series of native maps found in Tihuatlan this place is represented by the Teayotlán glyph. According to one version, the name etymology comes from the Huastec language word teayo o teayoc, which means “on the stone turtle”. Another official version of the name is that it comes from the Nahuatl word Teayok, Te-ayo-k “Turtle on stone”. The site received its current name because there is a temple or archaeological m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Las Flores (archaeological Site)
Las Flores is an archaeological site pertaining to the Huastec civilization in the city of Tampico, Tamaulipas in Mexico. Background According to paleontological and archaeological records, the earliest settlements in Tamaulipas are dated to twelve thousand years before the Christian era, and are identified in the so-called "complex Devil", in allusion to a Canyon of the Sierra of Tamaulipas. Later, at the Tropic of cancer level, are the first manifestations of native civilization, linked to the discovery and domestication of corn and thus to the beginning of agricultural life and the grouping of permanent settlements. As a result, in this period began to appear manifestations of Mesoamerican cultures in this region. Before the arrival of the Spanish invaders, the Tamaulipas territory was occupied by various ethnic groups, one of them were the Wasteks. Américo Vespucio, famous Italian cartographer aftero whom the American continent was named, visited the Tamaulipas territory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balcón De Montezuma
Balcón de Montezuma, also known as "Balcon del Chiue" () is an archaeological site located at the Alta Cumbre ''ejido'', some south of Ciudad Victoria, in the state of Tamaulipas, México. It is situated about one kilometer north of Highway 101, towards San Luis Potosí. This Huastec site is located some north-west from the Las Flores Huastec archaeological site. Background According to paleontological and archaeological records, the earliest settlements in Tamaulipas are dated to twelve thousand years before the Christian era, and are identified in the so-called "complex Devil", in allusion to a Canyon of the Sierra of Tamaulipas. Later, at the Tropic of cancer level, are the first manifestations of native civilization, linked to the discovery and domestication of corn and thus to the beginning of agricultural life and the grouping of permanent settlements. As a result, in this period began to appear manifestations of Mesoamerican cultures in this region. Before the arrival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Sabinito
El Sabinito is a Pre-Columbian ruin associated with the Huastec civilization. Located in the Mexican state of Tamaulipas, El Sabinito is approximately 25 kilometers southwest and 96 kilometers east of the modern-day cities Soto la Marina and Ciudad Victoria. Alongside the Balcon de Montezuma, El Sabinito marks the northernmost boundary of Mesoamerican civilization. History and description El Sabinito was discovered in 1987 by Aureliano Medina in a region of Tamaulipas characterized by its virgin, tropical jungles and suffocating humidity. Today, this region lies within the municipality of Soto la Marina and north of the Sierra de Tamaulipas. Compared to other Huastec ruins in Tamaulipas, such as the Balcon de Montezuma and the Pyramid of Tammapul, El Sabinito was the most urbanized and culturally significant. The Huastecs of Tamaulipas originally belonged to the Mayan culture but migrated northward to the present-day state around 1300 BCE. Upon their arrival, the immigrant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Religion
The Aztec religion is a monistic pantheism in which the Nahua concept of was construed as the supreme god , as well as a diverse pantheon of lesser gods and manifestations of nature. The popular religion tended to embrace the mythological and polytheistic aspects, and the Aztec Empire's state religion sponsored both the monism of the upper classes and the popular heterodoxies. The Aztec Empire officially recognized the most popular cults such that the deity was represented in the central temple precinct of the capital . The imperial cult was specifically that of the distinctive warlike patron god of the Mexica . Subjugated peoples were allowed to retain their own religious traditions in conquered provinces so long as they added the imperial god to their local pantheons, while the Empire would often incorporate practices from its new territories into the mainstream religion. In common with many other indigenous Mesoamerican civilizations, the Aztecs put great ritual emphasis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ehecatl
Ehecatl ( nci-IPA, Ehēcatl, eʔˈeːkatɬ, ) is a pre-Columbian deity associated with the wind, who features in Aztec mythology and the mythologies of other cultures from the central Mexico region of Mesoamerica. He is most usually interpreted as the aspect of the Feathered Serpent deity (Quetzalcoatl in Aztec and other Nahua cultures) as a god of wind, and is therefore also known as Ehecatl-Quetzalcoatl. Ehecatl also figures prominently as one of the creator gods and culture heroes in the mythical creation accounts documented for pre-Columbian central Mexican cultures.Miller and Taube (1993, pp. 70,84) Since the wind blows in all directions, Ehecatl was associated with all the cardinal direction The four cardinal directions, or cardinal points, are the four main compass directions: north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials N, E, S, and W respectively. Relative to north, the directions east, south, and west are at ...s. His temple was built as a cylin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classic Maya Collapse
In archaeology, the classic Maya collapse is the decline of the Classic Maya civilization and the abandonment of Maya cities in the southern Maya lowlands of Mesoamerica between the 7th and 9th centuries. At Ceibal, the Preclassic Maya experienced a similar collapse in the 2nd century. The Classic Period of Mesoamerican chronology is generally defined as the period from 250 to 900 CE, the last century of which is referred to as the Terminal Classic. The Classic Maya collapse is one of the greatest unsolved mysteries in archaeology. Urban centers of the southern lowlands, among them Palenque, Copán, Tikal, and Calakmul, went into decline during the 8th and 9th centuries and were abandoned shortly thereafter. Archaeologically, this decline is indicated by the cessation of monumental inscriptions and the reduction of large-scale architectural construction at the primary urban centers of the Classic Period. Although termed a collapse, it did not mark the end of the Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Script
Maya script, also known as Maya glyphs, is historically the native writing system of the Maya civilization of Mesoamerica and is the only Mesoamerican writing system that has been substantially deciphered. The earliest inscriptions found which are identifiably Maya date to the 3rd century BCE in San Bartolo, Guatemala. Maya writing was in continuous use throughout Mesoamerica until the Spanish conquest of the Maya in the 16th and 17th centuries. Maya writing used logograms complemented with a set of syllabic glyphs, somewhat similar in function to modern Japanese writing. Maya writing was called "hieroglyphics" or hieroglyphs by early European explorers of the 18th and 19th centuries who found its general appearance reminiscent of Egyptian hieroglyphs, although the two systems are unrelated. Though modern Mayan languages are almost entirely written using the Latin alphabet rather than Maya script, there have been recent developments encouraging a revival of the Maya glyph sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, architecture, mathematics, calendar, and astronomical system. The Maya civilization developed in the Maya Region, an area that today comprises southeastern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize, and the western portions of Honduras and El Salvador. It includes the northern lowlands of the Yucatán Peninsula and the highlands of the Sierra Madre, the Mexican state of Chiapas, southern Guatemala, El Salvador, and the southern lowlands of the Pacific littoral plain. Today, their descendants, known collectively as the Maya, number well over 6 million individuals, speak more than twenty-eight surviving Mayan languages, and reside in nearly the same area as their ancestors. The Archaic period, before 2000 BC, saw the first developments in agricul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayan Languages
The Mayan languagesIn linguistics, it is conventional to use ''Mayan'' when referring to the languages, or an aspect of a language. In other academic fields, ''Maya'' is the preferred usage, serving as both a singular and plural noun, and as the adjectival form. form a language family spoken in Mesoamerica, both in the south of Mexico and northern Central America. Mayan languages are spoken by at least 6 million Maya people, primarily in Guatemala, Mexico, Belize, El Salvador and Honduras. In 1996, Guatemala formally recognized 21 Mayan languages by name,Achiʼ is counted as a variant of Kʼicheʼ by the Guatemalan government. and Mexico recognizes eight within its territory. The Mayan language family is one of the best-documented and most studied in the Americas. Modern Mayan languages descend from the Proto-Mayan language, thought to have been spoken at least 5,000 years ago; it has been partially reconstructed using the comparative method. The proto-Mayan language diver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huastec Language
The Huastec (or Wasteko or Huasteco) language of Mexico is spoken by the Huastecos living in rural areas of San Luis Potosí and northern Veracruz. Though relatively isolated from them, it is related to the Mayan languages spoken further south and east in Mexico and Central America. According to the 2005 population census, there are about 200,000 speakers of Huasteco in Mexico (some 120,000 in San Luis Potosí and some 80,000 in Veracruz). The language and its speakers are also called Teenek, and this name has gained currency in Mexican national and international usage in recent years. The now-extinct Chicomuceltec language, spoken in Chiapas and Guatemala, was most closely related to Wasteko. The first linguistic description of the Huasteco language accessible to Europeans was written by Andrés de Olmos, who also wrote the first grammatical descriptions of Nahuatl and Totonac. Wasteko-language programming is carried by the CDI's radio station XEANT-AM, based in Tancanhuit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |