|
Howrah–Gaya–Delhi Line
The Howrah–Gaya–Delhi is a railway line connecting and Delhi cutting across Indo-Gangetic Plain and a comparatively small stretch of the line crossing over the Chota Nagpur Plateau. It covers a distance of across, West Bengal, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Delhi. The Grand Chord is a part of this line and as such is referred to by many as Howrah–Delhi line (via Grand Chord). Sections The long trunk line, amongst the long and busy trunk lines connecting the metros, has been treated in more detail in smaller sections: # Howrah–Bardhaman chord #Bardhaman–Asansol section #Asansol–Gaya section #Gaya–Mughalsarai section #Mughalsarai–Kanpur section #Kanpur–Delhi section History Construction of a line from Howrah to Sahibganj, for the proposed Howrah–Delhi link, started in 1851. The first Howrah–Delhi line via what later became the Sahibganj loop was opened in 1866. With the completion of the Raniganj-Kiul section, the shorter Howrah–Delhi main line via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fourth-most populous and thirteenth-largest state by area in India, as well as the eighth-most populous country subdivision of the world. As a part of the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent, it borders Bangladesh in the east, and Nepal and Bhutan in the north. It also borders the Indian states of Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, Sikkim and Assam. The state capital is Kolkata, the third-largest metropolis, and seventh largest city by population in India. West Bengal includes the Darjeeling Himalayan hill region, the Ganges delta, the Rarh region, the coastal Sundarbans and the Bay of Bengal. The state's main ethnic group are the Bengalis, with the Bengali Hindus forming the demographic majority. The area's early history featured a succession ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howrah–Bardhaman Chord
The Howrah–Bardhaman chord is a broad-gauge rail line connecting Howrah and Bardhaman. The railway line operates in Howrah, Hooghly and Purba Bardhaman districts in the state of West Bengal. It is part of the Howrah–Gaya–Delhi line, Howrah–Allahabad–Mumbai line and the Kolkata Suburban Railway system. History The Howrah–Bardhaman chord, a shorter link to Bardhaman from Howrah than the Howrah–Bardhaman main line, was constructed in 1917. In 1932, the Calcutta chord line was built over the then Willingdon Bridge (now Vivekananda Setu) joining Dum Dum with Dankuni. Dhaniakhali station on the Howrah–Bardhaman chord line was added in December 2003. Electrification Howrah–Bardhaman chord was electrified in 1964–66. Overview India's first air-conditioned double-decker train, running between Howrah and Dhanbad was introduced in 2011. The train will run at a permissible speed of 110 km per hour on the Howrah–Bardhaman chord line. Earlier, nine rak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughalsarai Junction Railway Station
Mughalsarai Junction, officially known as Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Junction, (station code: DDU, formerly MGS) is a railway station in the town of Mughalsarai in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The station contains the largest railway marshaling yard in Asia. Mughalsarai yard cater to around 450–500 trains in a month. All trains including premium category east bound Rajdhani trains and Duronto trains halt (makes it unique in entire Indian Railway Network; which distinguishes it from other major railway stations like Prayagraj junction, Bhopal junction, Agra Cantt, Gwalior junction, Kharagpur, Nagpur etc.) at this station. Major installations in Mughalsarai include electric locomotive shed holding 147 locomotives, diesel locomotive shed holding 53 locomotives, wagon ROH shed and a 169-bed divisional hospital. History The East Indian Railway Company started connecting Delhi and Howrah from the mid nineteenth century. This was the second biggest railway station after Gadd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allahabad Junction Railway Station
Prayagraj Junction (station code: PRYJ), is a railway station on the Howrah–Delhi main line, Prayagraj–Mau–Gorakhpur main line and Howrah–Prayagraj–Mumbai line. It is the headquarters of the North Central Railway zone. It is located in Prayagraj in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It serves Prayagraj and the surrounding areas. History The East Indian Railway Company initiated efforts to develop a railway line from Howrah to Delhi in the mid nineteenth century. Even when the line to Mughalsarai was being constructed and only the lines near Howrah were put in operation, the first train ran from Allahabad to Kanpur in 1859. For the first through train from Howrah to Delhi in 1864, coaches were ferried on boats across the Yamuna at Allahabad. With the completion of the Old Naini Bridge across the Yamuna through trains started running in 1865–66. The opening of the Curzon Bridge, across the Ganges, in 1902, linked Allahabad to regions north of or beyond the Ganges. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
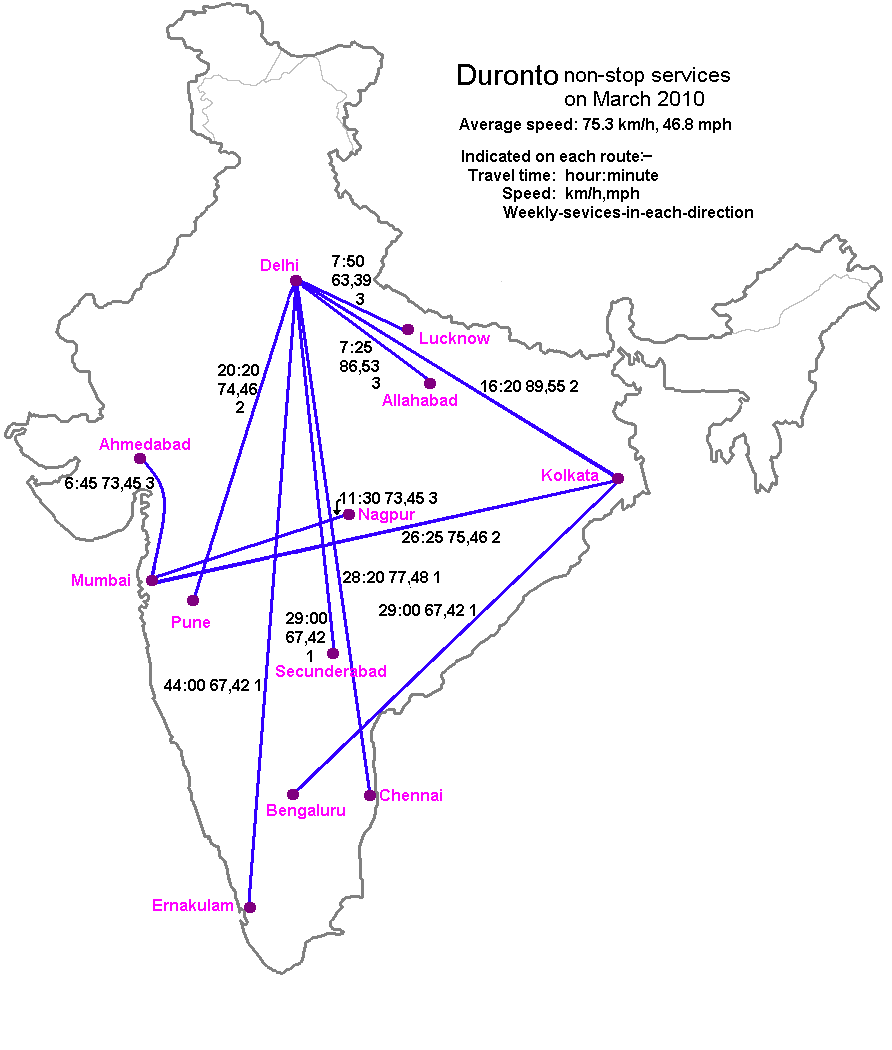
Duronto Express
Duronto Express is a category of long-distance non-stop source to destination trains run by the Indian Railways. Initially these trains did not have any ticketing stops between the origin and the destination, but since January 2016 it is possible to book tickets from those technical stops. "Duronto" means "Speedster" in Bengali. These trains' coaches have characteristic yellow-green livery which contains a bi-meaning signature which are a field full of flower and a river flowing over it, 2nd meaning is a boy is running on the fields which signifies the meaning of Duronto. Duronto Express services connect the several metros and major state capitals of India. As of now, there are currently 24 pairs that are working . History The Government of India's Ministry of Railways has been trying to introduce high-speed rail in India. In 2007, the ministry chose the 500-kilometre stretch between Delhi and Amritsar for a pre-feasibility study. On 19 January 2009, Railway Minister, Mamata B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rajdhani Express
Rajdhani may refer to: * ''Rajdhani'' (film), 1956 Indian film * ''Rajadhani'' (1994 film), Indian Malayalam-language film * ''Rajadhani'' (2011 film), Indian Kannada-language film * Rajdhani, Kotli, a village in Pakistan * Rajdhani, Gorakhpur, a village in India * Rajdhani Express, premium passenger train service in India * Rajadhani Express Blue Line Express ( Sinhala: රාජධානි එක්ස්ප්රස් ''Rajadhani Ekspras'') is a train service provider in Sri Lanka, a part of Blue Line Company. Blue Line Express provides premium services on several routes i ..., a railway service provider in Sri Lanka See also * Rajadhani (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governor General
Governor-general (plural ''governors-general''), or governor general (plural ''governors general''), is the title of an office-holder. In the context of governors-general and former British colonies, governors-general are appointed as viceroy to represent the monarch of a personal union in any sovereign state over which the monarch does not normally reign in person. Governors-general have also previously been appointed in respect of major colonial states or other territories held by either a monarchy or republic, such as Japan in Korea and France in Indochina. Current uses In modern usage, in the context of governor-generals and former British colonies, the term ''governor-general'' originated in those British colonies that became self-governing within the British Empire. Before World War I, the title was used only in federated colonies in which its constituents had had ''governors'' prior to federating, namely Canada, Australia, and the Union of South Africa. In these cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning "king". He has also been styled the king's lieutenant. A viceroy's territory may be called a viceroyalty, though this term is not always applied. The adjective form is ''viceregal'', less often ''viceroyal''. The term ''vicereine'' is sometimes used to indicate a female viceroy ''suo jure'', although ''viceroy'' can serve as a gender-neutral term. Vicereine is more commonly used to indicate a viceroy's wife. The term has occasionally been applied to the governors-general of the Commonwealth realms, who are ''viceregal'' representatives of the monarch. ''Viceroy'' is a form of royal appointment rather than noble rank. An individual viceroy often also held a noble title, however, such as Bernardo de Gálvez, 1st Viscount of Galveston, who was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gilbert Elliot-Murray-Kynynmound, 4th Earl Of Minto
Gilbert John Elliot-Murray-Kynynmound, 4th Earl of Minto, (; 9 July 18451 March 1914), known as Viscount Melgund by courtesy from 1859 to 1891, was a British peer and politician who served as Governor General of Canada, the eighth since Canadian Confederation, and as Viceroy and Governor-General of India, the country's 17th. Early life and career Minto was born in London, the son of William Elliot-Murray-Kynynmound, 3rd Earl of Minto, and Emma, daughter of General Sir Thomas Hislop, 1st Baronet. After the death of his grandfather in 1859 he became known by the courtesy title of Viscount Melgund. After completing his education at Eton College and Trinity College, Cambridge, he was commissioned a Lieutenant in the Scots Guards in 1867, but left in 1870. He joined the 1st Roxburghshire Mounted Rifle Volunteer Corps as a captain in 1872. In 1874, in the capacity of a newspaper correspondent, he witnessed the operations of the Carlists in Spain; he took service with the Turkish ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahibganj Loop
The Sahibganj loop is a railway line connecting Khana Junction and Kiul Junction. Originally a part of the Howrah–Delhi main line, it was opened to traffic in 1866. With the construction of a shorter railway line for a part of the route, the stretch was assigned a separate identity. History Railway transportation was introduced in India within 30 years of its maiden run in England. The East Indian Railway Company which was formed on 1 June 1845, completed its survey for a railway line from Kolkata, then called Calcutta, to Delhi via Mirzapur in 1846. The company initially became defunct on refusal of government guarantee, which was given in 1849. Thereafter, an agreement was signed between East Indian Railway Company and the East India Company, for the construction and operation of an "experimental" line between Kolkata and Rajmahal, which would later be extended to Delhi via Mirzapur. Construction began in 1851. On 15 August 1854, the first passenger train in the eastern s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanpur–Delhi Section
The Kanpur–Delhi section is a railway line connecting and Delhi. This section includes Agra Chord and Etah link. The main line is part of Howrah–Delhi main line and Howrah–Gaya–Delhi line. The Agra–Delhi chord is part of Delhi–Mumbai line and Delhi–Chennai line. History The East Indian Railway Company initiated efforts to develop a railway line from Howrah to Delhi in the mid nineteenth century. Even when the line to Mughalsarai was being constructed and only the lines near Howrah were put in operation, the first train ran from Allahabad to Kanpur in 1859 and the Kanpur–Etawah section was opened to traffic in the 1860s. For the first through train from Howrah to Delhi in 1864, coaches were ferried on boats across the Yamuna at Allahabad. With the completion of the Old Naini Bridge across the Yamuna through trains started running in 1865–66. The -wide metre-gauge Delhi–Bandikui and Bandikui–Agra lines of Rajputana State Railway were opened in 1874. The l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughalsarai–Kanpur Section
The Mughalsarai–Kanpur section, officially Pandit Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Nagar–Kanpur section, is a railway line connecting and . This track is part of the Howrah–Delhi main line and Howrah–Gaya–Delhi line. The main line is under the jurisdiction of North Central Railway. Mughalsarai is under the jurisdiction of East Central Railway. Some branch lines are under the jurisdiction of the North Eastern Railway and Northern Railway. Geography The main line was laid in the Gangetic Plain, south of the Ganges. Between Naini and Allahabad, it crosses the Yamuna and enters the doab region or the inland peninsula between the Ganges and Yamuna, still keeping south of the Ganges. Some branch lines came up on the northern side of the Ganges and got interlinked as bridges came up across the Ganges. Two places on these tracks are major pilgrimage centres – Allahabad on the main line and Varanasi, a little off the main line, on a branch line. Varanasi is connected by rail to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |