|
Horst Bredekamp
Horst Bredekamp (born 29 April 1947, in Kiel) is a German art historian. Life and work Bredekamp studied art history, archeology, philosophy and sociology in Kiel, Munich, Berlin and Marburg. In 1974 he received his doctorate at the Philipps-Universität Marburg with a thesis on art as a medium of social conflicts, especially the "Bilderkämpfe" of late antiquity to the Hussite revolution. He worked first as a volunteer at the Liebieghaus in Frankfurt am Main, from 1976 as assistant in the division of Art History at the University of Hamburg. In 1982 he was appointed Professor of art history at the University of Hamburg, in 1993 he moved to the Humboldt University Berlin. Since 2003 he has been a Permanent Fellow of the Institute for Advanced Study, Berlin, in 2005 the Gadamer-endowed chair. Bredekamp was a fellow at the Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton (1991), Institute for Advanced Study in Berlin (1992), Getty Center, Los Angeles (1995 and 1998) and the Collegi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die Zukunft Der Wissensspeicher - Horst Bredekamp 1 (cropped)
Die, as a verb, refers to death, the cessation of life. Die may also refer to: Games * Die, singular of dice, small throwable objects used for producing random numbers Manufacturing * Die (integrated circuit), a rectangular piece of a semiconductor wafer * Die (manufacturing), a material-shaping device * Die (philately) * Coin die, a metallic piece used to strike a coin * Die casting, a material-shaping process ** Sort (typesetting), a cast die for printing * Die cutting (web), process of using a die to shear webs of low-strength materials * Die, a tool used in paper embossing * Tap and die, cutting tools used to create screw threads in solid substances * Tool and die, the occupation of making dies Arts and media Music * Die (album), ''Die'' (album), the seventh studio album by rapper Necro * Die (musician), Japanese musician, guitarist of the band Dir en grey * DJ Die, British DJ and musician with Reprazent * "DiE", a 2013 single by the Japanese idol group BiS * die!, an inact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanesque Art
Romanesque art is the art of Europe from approximately 1000 AD to the rise of the Gothic Art, Gothic style in the 12th century, or later depending on region. The preceding period is known as the Pre-Romanesque period. The term was invented by 19th-century art historians, especially for Romanesque architecture, which retained many basic features of Roman architecture, Roman architectural style – most notably round-headed arches, but also barrel vaults, apses, and Acanthus (ornament), acanthus-leaf decoration – but had also developed many very different characteristics. In Southern France, Spain, and Italy there was an architectural continuity with the Late Antique, but the Romanesque style was the first style to spread across the whole of Catholic Europe, from Sicily to Scandinavia. Romanesque art was also greatly influenced by Byzantine art, especially in painting, and by the anti-classical energy of the decoration of the Insular art of the British Isles. From these element ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aby Warburg
Aby Moritz Warburg, better known as Aby Warburg, (June 13, 1866 – October 26, 1929) was a German art historian and cultural theorist who founded the Kulturwissenschaftliche Bibliothek Warburg (Library for Cultural Studies), a private library, which was later moved to the Warburg Institute, London. At the heart of his research was the legacy of the classical world, and the transmission of classical representation, in the most varied areas of Western culture through to the Renaissance. Warburg described himself as: "''Amburghese di cuore, ebreo di sangue, d'anima Fiorentino''" ('Hamburger at heart, Jew by blood, Florentine in spirit'). Life Aby Warburg was born in Hamburg into the wealthy Warburg family of German Jewish bankers. His ancestors had come to Germany from Italy in the 17th century and settled in the town of Warburg in Westphalia, taking on the town's name as their family name. In the 18th century the Warburgs moved to Altona near Hamburg. Two brothers Warburg foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Culture
Visual culture is the aspect of culture expressed in visual images. Many academic fields study this subject, including cultural studies, art history, critical theory, philosophy, media studies, Deaf Studies, and anthropology. The field of visual culture studies in the United States corresponds or parallels the ''Bildwissenschaft'' ("image studies") in Germany. Both fields are not entirely new, as they can be considered reformulations of issues of photography and film theory that had been raised from the 1920s and 1930s by authors like Béla Balázs, László Moholy-Nagy, Siegfried Kracauer and Walter Benjamin. Overview Among theorists working within contemporary culture, this field of study often overlaps with film studies, psychoanalytic theory, sex studies, queer theory, and the study of television; it can also include video game studies, comics, traditional artistic media, advertising, the Internet, and any other medium that has a crucial visual component. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bildwissenschaft
''Bildwissenschaft'' is an academic discipline in the German-speaking world. Similar to visual studies, and defined in relation to art history, ''Bildwissenschaft'' (approximately, "image-science") refers to a number of different approaches to images, their interpretation and their social significance. Originating in the early 20th century, the field has become more prominent since the 1990s. In the contemporary period, significant theorists and practitioners of ''Bildwissenschaft'' have included , Gottfried Boehm, Hans Belting, Horst Bredekamp and , each of whom have developed distinct orientations toward their subject matter. Etymology ''Wissenschaft'' (from ''Wissen'', meaning "knowledge") is similar in meaning to "science", but is used differently and with different connotations. Whereas "science" typically refers specifically to empirical investigations in the natural sciences and social sciences, ''Wissenschaft'' does not carry the same methodological implications. Neverthel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New Yorker
''The New Yorker'' is an American weekly magazine featuring journalism, commentary, criticism, essays, fiction, satire, cartoons, and poetry. Founded as a weekly in 1925, the magazine is published 47 times annually, with five of these issues covering two-week spans. Although its reviews and events listings often focus on the Culture of New York City, cultural life of New York City, ''The New Yorker'' has a wide audience outside New York and is read internationally. It is well known for its illustrated and often topical covers, its commentaries on popular culture and eccentric American culture, its attention to modern fiction by the inclusion of Short story, short stories and literary reviews, its rigorous Fact-checking, fact checking and copy editing, its journalism on politics and social issues, and its single-panel cartoons sprinkled throughout each issue. Overview and history ''The New Yorker'' was founded by Harold Ross and his wife Jane Grant, a ''The New York Times, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
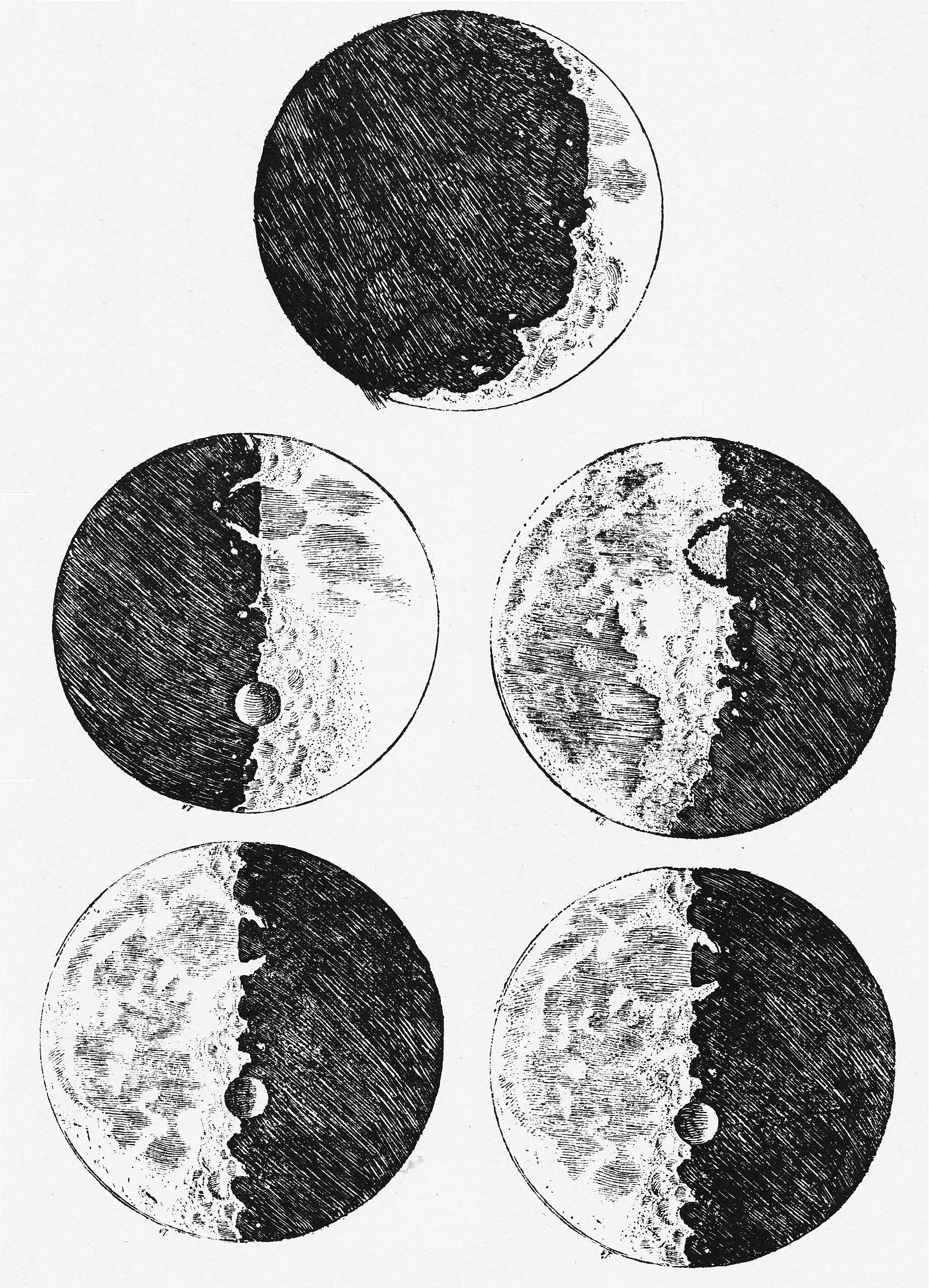
Nick Wilding
Nick Wilding is a British-born American historian. He became internationally known after exposing as a forgery a copy of Galileo’s “Sidereus Nuncius” that purportedly included Galileo’s own watercolors of the moon. Life Wilding studied English at New College, Oxford. After his B. A. with highest honors in 1992 he made in 1993 at the University of Warwick his Masters with a thesis on Renaissance. Subsequently, he conducted research at the European University Institute and in 2000 he received his doctorate for PhD with a dissertation on natural philosophy and communication in early modern Europe. He carried out postdoctoral research at Stanford University, and from 2002 to 2005 at University of Cambridge. 2005/2006 Wilding was at Columbia University, 2006/2007 at University of Miami, and since 2007 as Assistant (now Full) Professor at Georgia State University. In 2012 Wilding was able to prove on the basis of forensic evidence that a special edition of Sidereus Nuncius o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidereus Nuncius
''Sidereus Nuncius'' (usually ''Sidereal Messenger'', also ''Starry Messenger'' or ''Sidereal Message'') is a short astronomical treatise (or ''pamphlet'') published in New Latin by Galileo Galilei on March 13, 1610. It was the first published scientific work based on observations made through a telescope, and it contains the results of Galileo's early observations of the imperfect and mountainous Moon, the hundreds of stars that were unable to be seen in either the Milky Way or certain constellations with the naked eye, and the Medicean Stars (later Galilean moons) that appeared to be circling Jupiter.Raphael, Renée. ''Sidereus nuncius; or, A Sidereal Message, by Galileo Galilei''. Isis, Vol. 101, No. 3 (September 2010), pp. 644-645. Published by: The University of Chicago Press on behalf of The History of Science Society. The Latin word ''nuncius'' was typically used during this time period to denote ''messenger''; however, it was also (though less frequently) rendered as '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
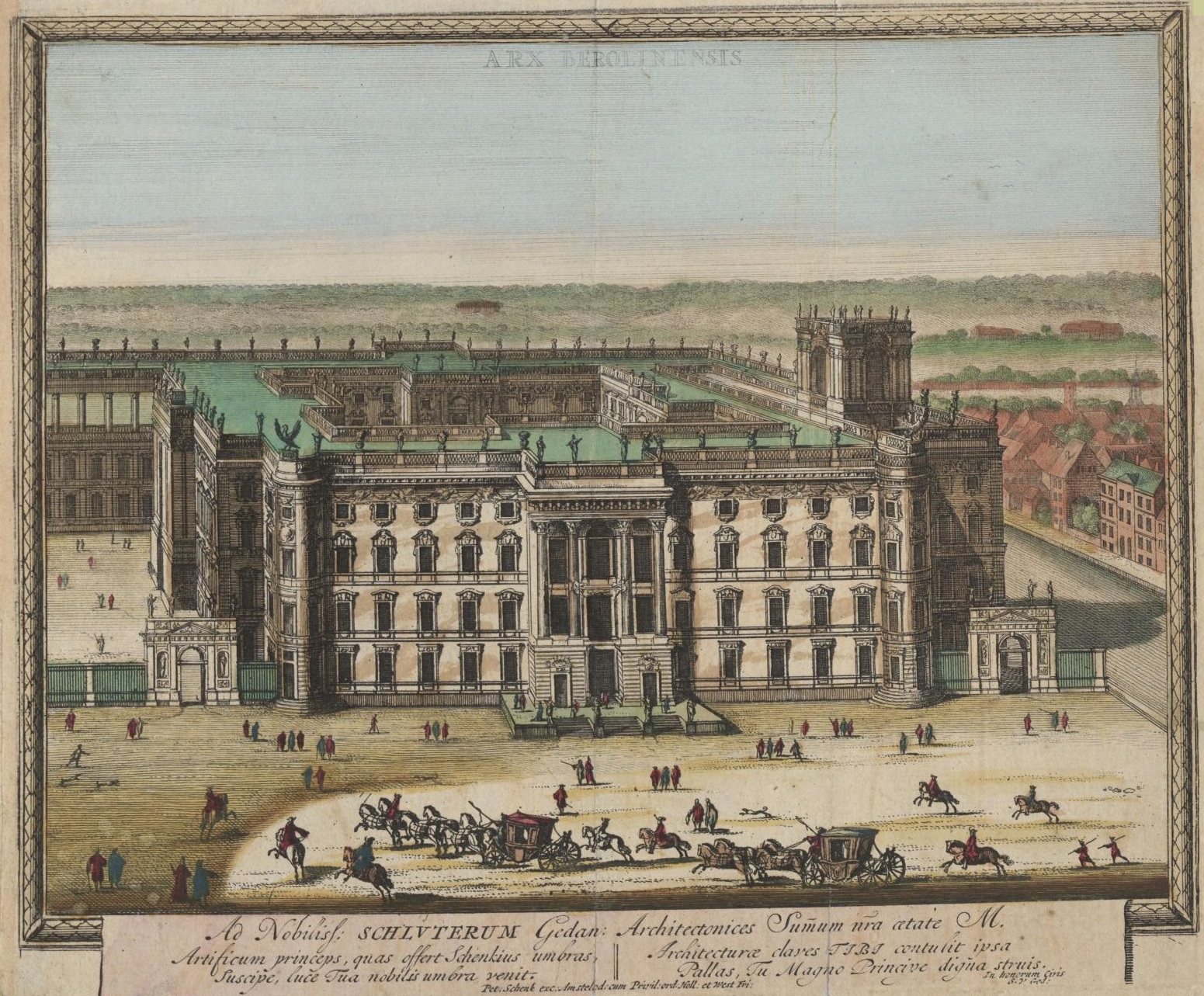
Berliner Stadtschloss
The Berlin Palace (german: Berliner Schloss), formally the Royal Palace (german: Königliches Schloss), on the Museum Island in the Mitte area of Berlin, was the main residence of the House of Hohenzollern from 1443 to 1918. Expanded by order of King Frederick I of Prussia according to plans by Andreas Schlüter from 1689 to 1713, it was thereafter considered a major work of Prussian Baroque architecture. The former royal palace was one of Berlin’s largest buildings and shaped the cityscape with its dome. Used for various government functions after the fall of the monarchy in 1918, it was damaged during the Allied bombing in World War II, and was demolished by the East German authorities in 1950. In the 1970s, it became the location of the modernist East German Palace of the Republic (the central government building of East Germany). After German reunification and several years of debate and discussion, particularly regarding the fraught historical legacy of both building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Universities Excellence Initiative
The Excellence Initiative of the German Council of Science and Humanities and the German Research Foundation (DFG) aims to promote cutting-edge research and to create outstanding conditions for young scholars at universities, to deepen cooperation between disciplines and institutions, to strengthen international cooperation of research, and to enhance the international appeal of excellent German universities. It is the result of lengthy negotiations between the federal government and the German states. Since almost all German universities are public (most private universities do not have the official German "Universitätsstatus"), and therefore mainly paid by taxes and generally egalitarian, there is no German Ivy League of private higher education institutions. However, the Excellence Initiative aims to strengthen some selected public universities more than others in order to raise their international visibility. Thus, the German "Universities of Excellence" are sometimes conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census Of Antique Works Of Art And Architecture Known In The Renaissance
The ''Census of Antique Works of Art and Architecture Known in the Renaissance'' (abbreviated ''Census'') is an interdisciplinary research project dedicated to the study of the reception of antiquity in the Renaissance. At the heart of the project is its scholarly database recording antique works of art and architecture known in the Renaissance in relation with the early modern sources documenting them. The project is based at the ''Institute of Art and Visual History'' at the ''Humboldt University of Berlin''. Scope The ''Census'' project came about as a means to acquire more clarity about the actual knowledge of antiquity during the Renaissance era. Since its inception, the project has pursued the goal of registering all antique monuments known in the Renaissance and the Renaissance documents relating to them. After focusing on figurative art and its reception up until 1527 in the early phase, the temporal limit was later moved to around 1600 and other classes of art, mainly arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.png)