|
Hopf Link
In mathematical knot theory, the Hopf link is the simplest nontrivial link with more than one component. It consists of two circles linked together exactly once, and is named after Heinz Hopf. Geometric realization A concrete model consists of two unit circles in perpendicular planes, each passing through the center of the other.. See in particulap. 77 This model minimizes the ropelength of the link and until 2002 the Hopf link was the only link whose ropelength was known. The convex hull of these two circles forms a shape called an oloid. Properties Depending on the relative orientations of the two components the linking number of the Hopf link is ±1. The Hopf link is a (2,2)-torus link with the braid word :\sigma_1^2.\, The knot complement of the Hopf link is R × ''S''1 × ''S''1, the cylinder over a torus. This space has a locally Euclidean geometry, so the Hopf link is not a hyperbolic link. The knot group of the Hopf link (the fund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometrization Conjecture
In mathematics, Thurston's geometrization conjecture states that each of certain three-dimensional topological spaces has a unique geometric structure that can be associated with it. It is an analogue of the uniformization theorem for two-dimensional surfaces, which states that every simply connected Riemann surface can be given one of three geometries ( Euclidean, spherical, or hyperbolic). In three dimensions, it is not always possible to assign a single geometry to a whole topological space. Instead, the geometrization conjecture states that every closed 3-manifold can be decomposed in a canonical way into pieces that each have one of eight types of geometric structure. The conjecture was proposed by , and implies several other conjectures, such as the Poincaré conjecture and Thurston's elliptization conjecture. Thurston's hyperbolization theorem implies that Haken manifolds satisfy the geometrization conjecture. Thurston announced a proof in the 1980s and since then sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disulfide
In biochemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) refers to a functional group with the structure . The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and is usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. In biology, disulfide bridges formed between thiol groups in two cysteine residues are an important component of the secondary and tertiary structure of proteins. ''Persulfide'' usually refers to compounds. In inorganic chemistry disulfide usually refers to the corresponding anion (−S−S−). Organic disulfides Symmetrical disulfides are compounds of the formula . Most disulfides encountered in organo sulfur chemistry are symmetrical disulfides. Unsymmetrical disulfides (also called heterodisulfides) are compounds of the formula . They are less common in organic chemistry, but most disulfides in nature are unsymmetrical. Properties The disulfide bonds are strong, with a typical bond dissociation energy of 60 kcal/mol (251&nbs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
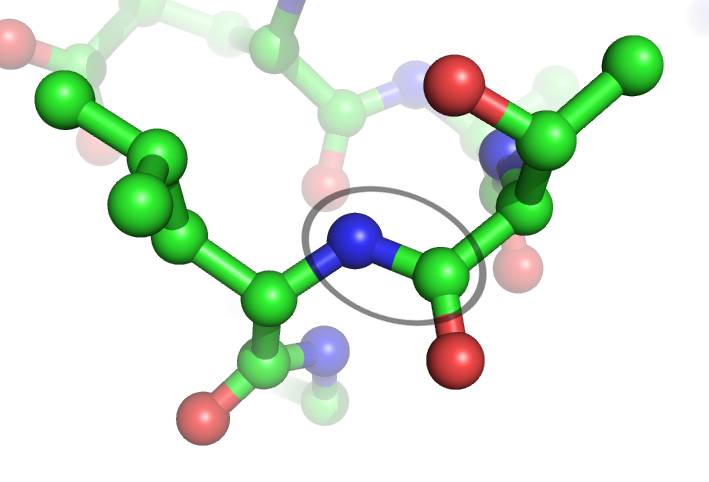
Peptide Bond
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein chain. It can also be called a eupeptide bond to distinguish it from an isopeptide bond, which is another type of amide bond between two amino acids. Synthesis When two amino acids form a ''dipeptide'' through a ''peptide bond'', it is a type of condensation reaction. In this kind of condensation, two amino acids approach each other, with the non-side chain (C1) carboxylic acid moiety of one coming near the non-side chain (N2) amino moiety of the other. One loses a hydrogen and oxygen from its carboxyl group (COOH) and the other loses a hydrogen from its amino group (NH2). This reaction produces a molecule of water (H2O) and two amino acids joined by a peptide bond (−CO−NH−). The two joined amino acids are called a dipeptide. The am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homotopy Groups Of Spheres
In the mathematical field of algebraic topology, the homotopy groups of spheres describe how spheres of various dimensions can wrap around each other. They are examples of topological invariants, which reflect, in algebraic terms, the structure of spheres viewed as topological spaces, forgetting about their precise geometry. Unlike homology groups, which are also topological invariants, the homotopy groups are surprisingly complex and difficult to compute. The -dimensional unit sphere — called the -sphere for brevity, and denoted as — generalizes the familiar circle () and the ordinary sphere (). The -sphere may be defined geometrically as the set of points in a Euclidean space of dimension located at a unit distance from the origin. The -th ''homotopy group'' summarizes the different ways in which the -dimensional sphere can be mapped continuously into the sphere . This summary does not distinguish between two mappings if one can be continuously deformed to the oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibration
The notion of a fibration generalizes the notion of a fiber bundle and plays an important role in algebraic topology, a branch of mathematics. Fibrations are used, for example, in postnikov-systems or obstruction theory. In this article, all mappings are continuous mappings between topological spaces. Formal definitions Homotopy lifting property A mapping p \colon E \to B satisfies the homotopy lifting property for a space X if: * for every homotopy h \colon X \times , 1\to B and * for every mapping (also called lift) \tilde h_0 \colon X \to E lifting h, _ = h_0 (i.e. h_0 = p \circ \tilde h_0) there exists a (not necessarily unique) homotopy \tilde h \colon X \times , 1\to E lifting h (i.e. h = p \circ \tilde h) with \tilde h_0 = \tilde h, _. The following commutative diagram shows the situation:^ Fibration A fibration (also called Hurewicz fibration) is a mapping p \colon E \to B satisfying the homotopy lifting property for all spaces X. The space B is called base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere () is a Geometry, geometrical object that is a solid geometry, three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre (geometry), centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubble (physics), Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. spherical Earth, The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres rolling, roll smoothly in any direction, so mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-sphere
In mathematics, a 3-sphere is a higher-dimensional analogue of a sphere. It may be embedded in 4-dimensional Euclidean space as the set of points equidistant from a fixed central point. Analogous to how the boundary of a ball in three dimensions is an ordinary sphere (or 2-sphere, a two-dimensional surface), the boundary of a ball in four dimensions is a 3-sphere (an object with three dimensions). A 3-sphere is an example of a 3-manifold and an ''n''-sphere. Definition In coordinates, a 3-sphere with center and radius is the set of all points in real, 4-dimensional space () such that :\sum_^3(x_i - C_i)^2 = ( x_0 - C_0 )^2 + ( x_1 - C_1 )^2 + ( x_2 - C_2 )^2+ ( x_3 - C_3 )^2 = r^2. The 3-sphere centered at the origin with radius 1 is called the unit 3-sphere and is usually denoted : :S^3 = \left\. It is often convenient to regard as the space with 2 complex dimensions () or the quaternions (). The unit 3-sphere is then given by :S^3 = \left\ or :S^3 = \left\. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hopf Fibration
In the mathematical field of differential topology, the Hopf fibration (also known as the Hopf bundle or Hopf map) describes a 3-sphere (a hypersphere in four-dimensional space) in terms of circles and an ordinary sphere. Discovered by Heinz Hopf in 1931, it is an influential early example of a fiber bundle. Technically, Hopf found a many-to-one continuous function (or "map") from the -sphere onto the -sphere such that each distinct ''point'' of the -sphere is mapped from a distinct great circle of the -sphere . Thus the -sphere is composed of fibers, where each fiber is a circle — one for each point of the -sphere. This fiber bundle structure is denoted :S^1 \hookrightarrow S^3 \xrightarrow S^2, meaning that the fiber space (a circle) is embedded in the total space (the -sphere), and (Hopf's map) projects onto the base space (the ordinary -sphere). The Hopf fibration, like any fiber bundle, has the important property that it is locally a product space. However it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricolorable
In the mathematical field of knot theory, the tricolorability of a knot is the ability of a knot to be colored with three colors subject to certain rules. Tricolorability is an isotopy invariant, and hence can be used to distinguish between two different (non- isotopic) knots. In particular, since the unknot is not tricolorable, any tricolorable knot is necessarily nontrivial. Rules of tricolorability In these rules a strand in a knot diagram will be a piece of the string that goes from one undercrossing to the next. A knot is tricolorable if each strand of the knot diagram can be colored one of three colors, subject to the following rules:Weisstein, Eric W. (2010). ''CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathematics'', Second Edition, p.3045. . quoted at Accessed: May 5, 2013. :1. At least two colors must be used, and :2. At each crossing, the three incident strands are either all the same color or all different colors. Some references state instead that all three colors must be used.Gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Group
In mathematics, the free group ''F''''S'' over a given set ''S'' consists of all words that can be built from members of ''S'', considering two words to be different unless their equality follows from the group axioms (e.g. ''st'' = ''suu''−1''t'', but ''s'' ≠ ''t''−1 for ''s'',''t'',''u'' ∈ ''S''). The members of ''S'' are called generators of ''F''''S'', and the number of generators is the rank of the free group. An arbitrary group ''G'' is called free if it is isomorphic to ''F''''S'' for some subset ''S'' of ''G'', that is, if there is a subset ''S'' of ''G'' such that every element of ''G'' can be written in exactly one way as a product of finitely many elements of ''S'' and their inverses (disregarding trivial variations such as ''st'' = ''suu''−1''t''). A related but different notion is a free abelian group; both notions are particular instances of a free object from universal algebra. As such, free groups are defined by their universal property. History Free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Abelian Group
In mathematics, a free abelian group is an abelian group with a basis. Being an abelian group means that it is a set with an addition operation that is associative, commutative, and invertible. A basis, also called an integral basis, is a subset such that every element of the group can be uniquely expressed as an integer combination of finitely many basis elements. For instance the two-dimensional integer lattice forms a free abelian group, with coordinatewise addition as its operation, and with the two points (1,0) and (0,1) as its basis. Free abelian groups have properties which make them similar to vector spaces, and may equivalently be called free the free modules over the integers. Lattice theory studies free abelian subgroups of real vector spaces. In algebraic topology, free abelian groups are used to define chain groups, and in algebraic geometry they are used to define divisors. The elements of a free abelian group with basis B may be described in several equivalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |