|
Honeywell V. Sperry Rand
''Honeywell, Inc. v. Sperry Rand Corp., et al.'', 180 U.S.P.Q. 673 ( D. Minn. 1973) (Case 4-67 Civil 138, 180 USPO 670), was a landmark U.S. federal court case that in October 1973 invalidated the 1964 patent for the ENIAC, the world's first general-purpose electronic digital computer. The decision included: that the ENIAC inventors had derived the subject matter of the electronic digital computer from the Atanasoff–Berry computer (ABC), prototyped in 1939 by John Atanasoff and Clifford Berry; gave legal recognition to Atanasoff as the inventor of the first electronic digital computer; and put the invention of the electronic digital computer in the public domain. Dispute origins The case was a combination of two separate lawsuits: one brought by Sperry Rand Corporation and its holding company Illinois Scientific Developments against Honeywell Corporation in Washington, D.C. charging Honeywell with patent infringement and demanding royalties, and a countersuit filed in Minne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States District Court For The District Of Minnesota
The United States District Court for the District of Minnesota (in case citations, D. Minn.) is the United States district court, federal district court whose jurisdiction is the state of Minnesota. Its two primary courthouses are in Minneapolis, Minnesota, Minneapolis and Saint Paul, Minnesota, Saint Paul. Cases are also heard in the federal courthouses of Duluth, Minnesota, Duluth and Fergus Falls, Minnesota, Fergus Falls. Appeals from the District of Minnesota are taken to the United States Court of Appeals for the Eighth Circuit (except for patent claims and claims against the U.S. government under the Tucker Act, which are appealed to the United States Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit, Federal Circuit). United States Attorney The United States Attorney's Office for the District of Minnesota represents the United States in civil and criminal litigation in the court. One notable former U.S. Attorney for the District was Cushman K. Davis, who later became govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John W
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herman Goldstine
Herman Heine Goldstine (September 13, 1913 – June 16, 2004) was a mathematician and computer scientist, who worked as the director of the IAS machine at Princeton University's Institute for Advanced Study and helped to develop ENIAC, the first of the modern electronic digital computers. He subsequently worked for many years at IBM as an IBM Fellow, the company's most prestigious technical position. Early life Herman Heine Goldstine was born in Chicago in 1913 to Jewish parents. He attended the University of Chicago, where he joined the Phi Beta Kappa fraternity, and graduated with a degree in Mathematics in 1933, a master's degree in 1934, and a PhD in 1936. For three years he was a research assistant under Gilbert Ames Bliss, an authority on the mathematical theory of external ballistics. Career Early career In 1939 Goldstine began a teaching career at the University of Michigan, until the United States' entry into World War II, when he joined the U.S. Army. BRL and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-licensing Agreement
A cross-licensing agreement is a contract between two or more parties where each party grants rights to their intellectual property to the other parties. Patent law In patent law, a cross-licensing agreement is an agreement according to which two or more parties grant a license to each other for the exploitation of the subject-matter claimed in one or more of the patents each owns. Usually, this type of agreement happens between two parties in order to avoid litigation or to settle an infringement dispute. Very often, the patents that each party owns covers different essential aspects of a given commercial product. Thus by cross licensing, each party maintains their freedom to bring the commercial product to market. The term "cross licensing" implies that neither party pays monetary royalties to the other party, although this may be the case. For example, Microsoft and JVC entered into a cross license agreement in January 2008. Each party, therefore, is able to practice the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sherman Antitrust Act
The Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 (, ) is a United States antitrust law which prescribes the rule of free competition among those engaged in commerce. It was passed by Congress and is named for Senator John Sherman, its principal author. The Sherman Act broadly prohibits 1) anticompetitive agreements and 2) unilateral conduct that monopolizes or attempts to monopolize the relevant market. The Act authorizes the Department of Justice to bring suits to enjoin (i.e. prohibit) conduct violating the Act, and additionally authorizes private parties injured by conduct violating the Act to bring suits for treble damages (i.e. three times as much money in damages as the violation cost them). Over time, the federal courts have developed a body of law under the Sherman Act making certain types of anticompetitive conduct per se illegal, and subjecting other types of conduct to case-by-case analysis regarding whether the conduct unreasonably restrains trade. The law attempts to prevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert F
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and '' berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kite Sharpless
A kite is a tethered heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create lift and drag forces. A kite consists of wings, tethers and anchors. Kites often have a bridle and tail to guide the face of the kite so the wind can lift it. Some kite designs don’t need a bridle; box kites can have a single attachment point. A kite may have fixed or moving anchors that can balance the kite. The name is derived from kite, the hovering bird of prey. The lift that sustains the kite in flight is generated when air moves around the kite's surface, producing low pressure above and high pressure below the wings. The interaction with the wind also generates horizontal drag along the direction of the wind. The resultant force vector from the lift and drag force components is opposed by the tension of one or more of the lines or tethers to which the kite is attached. The anchor point of the kite line may be static or moving (e.g., the towing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Burks
Arthur Walter Burks (October 13, 1915 – May 14, 2008) was an American mathematician who worked in the 1940s as a senior engineer on the project that contributed to the design of the ENIAC, the first general-purpose electronic digital computer. Decades later, Burks and his wife Alice Burks outlined their case for the subject matter of the ENIAC having been derived from John Vincent Atanasoff. Burks was also for several decades a faculty member at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. Early life and education Burks was born in Duluth, Minnesota. He earned his B.A. in mathematics and physics from DePauw University in Greencastle, Indiana in 1936 and his M.A. and Ph.D. in philosophy from the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor in 1937 and 1941, respectively. The Moore School The summer after obtaining his Ph.D., the young Dr. Burks moved to Philadelphia, Pennsylvania and enrolled in the national defense electronics course offered by the University of Pennsylvania's Moore Sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Mauchly
John William Mauchly (August 30, 1907 – January 8, 1980) was an American physicist who, along with J. Presper Eckert, designed ENIAC, the first general-purpose electronic digital computer, as well as EDVAC, BINAC and UNIVAC I, the first commercial computer made in the United States. Together they started the first computer company, the Eckert–Mauchly Computer Corporation (EMCC), and pioneered fundamental computer concepts, including the stored program, subroutines, and programming languages. Their work, as exposed in the widely read ''First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC'' (1945) and as taught in the Moore School Lectures (1946), influenced an explosion of computer development in the late 1940s all over the world. Biography John W. Mauchly was born on August 30, 1907, to Sebastian and Rachel (Scheidemantel) Mauchly in Cincinnati, Ohio. He moved with his parents and sister, Helen Elizabeth (Betty), at an early age to Chevy Chase, Maryland, when Sebastian Mauchly obtained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
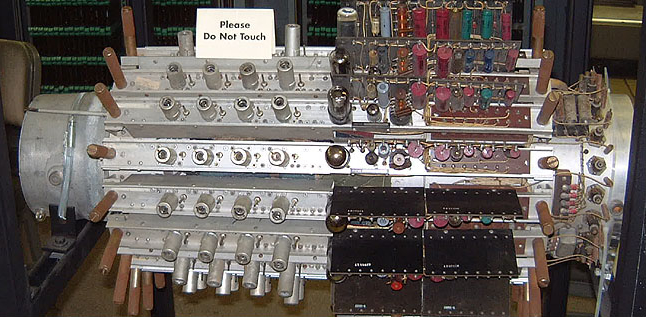
Delay-line Memory
Delay-line memory is a form of computer memory, now obsolete, that was used on some of the earliest digital computers. Like many modern forms of electronic computer memory, delay-line memory was a refreshable memory, but as opposed to modern random-access memory, delay-line memory was sequential-access. Analog delay line technology had been used since the 1920s to delay the propagation of analog signals. When a delay line is used as a memory device, an amplifier and a pulse shaper are connected between the output of the delay line and the input. These devices recirculate the signals from the output back into the input, creating a loop that maintains the signal as long as power is applied. The shaper ensures the pulses remain well-formed, removing any degradation due to losses in the medium. The memory capacity is determined by dividing the time taken to transmit one bit into the time it takes for data to circulate through the delay line. Early delay-line memory systems had ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philco-Ford
Philco (an acronym for Philadelphia Battery Company) is an American electronics manufacturer headquartered in Philadelphia. Philco was a pioneer in battery, radio, and television production. In 1961, the company was purchased by Ford and, from 1966, renamed "Philco-Ford". Ford sold the company to GTE in 1974, and it was purchased by Philips in 1981. In North America, the Philco brand is currently owned by Philips. In other markets, the Philco International brand is owned by Electrolux. In the early 1920s, Philco made storage batteries, "socket power" battery eliminator units (plug-in transformers), and battery chargers. With the invention of the rectifier tube, which made it practical to power radios by electrical outlets, in 1928, Philco entered the radio business. They followed other radio makers such as RCA, Atwater-Kent, Zenith Electronics, Freshman Masterpiece, FADA Radio (Frank A. D'Andrea Radio), and AH Grebe into the battery-powered radio business. By the end of 1930, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energy, digital industry, additive manufacturing and venture capital and finance, but has since divested from several areas, now primarily consisting of the first four segments. In 2020, GE ranked among the Fortune 500 as the 33rd largest firm in the United States by gross revenue. In 2011, GE ranked among the Fortune 20 as the 14th most profitable company, but later very severely underperformed the market (by about 75%) as its profitability collapsed. Two employees of GE – Irving Langmuir (1932) and Ivar Giaever (1973) – have been awarded the Nobel Prize. On November 9, 2021, the company announced it would divide itself into three investment-grade public companies. On July 18, 2022, GE unveiled the brand names of the companies it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |