|
Honda VFR800
The Honda VFR800 (Interceptor) is a sport touring motorcycle made by Honda since 1998. The model was the successor to the VFR750F and shares the V4 engine configuration with the Honda VF and VFR series. Fifth Generation: 1998–2001 VFR800Fi (RC46) Rather than being a direct development of the previous, carbureted VFR750F engine, the VFR800 engine was a detuned and longer-stroke power plant based on the fuel-injected engine designed for the RC45 of 1994. The RVF750R RC45 engine, although a development of the VFR750R RC30 and originally derived from the VFR750F RC24, was very different from Honda's previous V4s as the gear drive for the camshafts was moved from the center of the engine to the engine's right-side (next to the clutch-pack). Another change was the two side-mounted radiators as opposed to one at the front of the engine front as on the VFR750. The engine was tuned for road use in the VFR800, so that torque was improved throughout the rev range while maximum power wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honda VF And VFR
The Honda VF and VFR series is a range of motorcycles first introduced in 1982 by Honda featuring V4 engines (hence the "VF" prefix). History In 1969 Honda revealed the CB750 superbike, establishing the template for the Universal Japanese Motorcycle with a range of transverse inline-fours. Relishing technological innovation, Honda unexpectedly moved on to adopt the V4 ("VF") configuration. However, some of the early VF models suffered mechanical problems, mainly as a result of poor quality camshafts (the "chocolate cams"). Honda, alarmed that they were losing their hard-won reputation for reliability, moved to introduce the VFR750 motorcycles featuring gear-driven ohc cams and a very high build quality. The first three or four iterations of VFR motorcycles re-established Honda's reputation for quality, and the motorcycles received almost universal praise from journalists and riders alike. The VFR was originally a 750 cc, but became an 800 cc in due course. New models fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honda
is a Japanese public multinational conglomerate manufacturer of automobiles, motorcycles, and power equipment, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, reaching a production of 400 million by the end of 2019, as well as the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines measured by volume, producing more than 14 million internal combustion engines each year. Honda became the second-largest Japanese automobile manufacturer in 2001. In 2015, Honda was the eighth largest automobile manufacturer in the world. Honda was the first Japanese automobile manufacturer to release a dedicated luxury brand, Acura, in 1986. Aside from their core automobile and motorcycle businesses, Honda also manufactures garden equipment, marine engines, personal watercraft, power generators, and other products. Since 1986, Honda has been involved with artificial intelligence/robotics research and released their ASIMO rob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honda VFR750R
The Honda VFR750R, model code 'RC30', is a fully faired, solo-seat-only racing motorcycle created for homologation purposes for the World Superbike Championship by Honda Racing Corporation (HRC). It was first released to the Japanese market in 1987, released in Europe in 1988 then the United States in 1990. There were only 3,000 made and they sold for - a very large amount for a production bike at the time. Engine The 748 cc 16-valve gear driven double overhead camshaft liquid-cooled RC24-derived 90° V4 produced at 9,500 rpm for the restricted Japanese model and @ 11,000 rpm elsewhere. It contained race-inspired components. These included such items as titanium connecting rods that reduced reciprocating weight ( lighter and eight times the cost) and gear driven camshafts. The engine firing configuration was very different from the road-going VFR750F from which it was derived with a 360° 'big bang' crank arrangement instead of the smoother 180°. This fea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immobiliser
An immobiliser or immobilizer is an electronic security device fitted to a motor vehicle that prevents the engine from being started unless the correct key (''transponder'' or ''smart key'') is present. This prevents the vehicle from being " hot wired" after entry has been achieved and thus reduces motor vehicle theft. Research shows that the uniform application of immobilisers reduced the rate of car theft by 40%. Description The electric immobiliser/alarm system was invented by St. George Evans and Edward Birkenbuel and patented in 1919. They developed a 3x3 grid of double-contact switches on a panel mounted inside the car so when the ignition switch was activated, current from the battery (or magneto) went to the spark plugs allowing the engine to start, or immobilizing the vehicle and sounding the horn. The system settings could be changed each time the car was driven. Modern immobiliser systems are automatic, meaning the owner does not have to remember to activate it. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choke Valve
In internal combustion engines with carburetors, a choke valve or choke modifies the air pressure in the intake manifold, thereby altering the air–fuel ratio entering the engine. Choke valves are generally used in naturally aspirated engines to supply a richer fuel mixture when starting the engine. Most choke valves in engines are butterfly valves mounted upstream of the carburetor jet to produce a higher partial vacuum, which increases the fuel draw. In heavy industrial or fluid engineering contexts, including oil and gas production, a choke valve or choke is a particular design of valve with a solid cylinder placed inside another slotted or perforated cylinder. Carburetor A choke valve is sometimes installed in the carburetor of internal combustion engines. Its purpose is to restrict the flow of air, thereby enriching the fuel-air mixture while starting the engine. Depending on engine design and application, the valve can be activated manually by the operator of the engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Idle (engine)
Idling refers to running a vehicle's engine when the vehicle is not in motion. This commonly occurs when drivers are stopped at a red light, waiting while parked outside a business or residence, or otherwise stationary with the engine running. When idling, the engine runs without any loads except the engine accessories. Idle speed Idle speed, sometimes simply called "idle", is the rotational speed an engine runs at when the engine is idling, that is when the engine is uncoupled from the drivetrain and the throttle pedal is not depressed. In combustion engines, idle speed is generally measured in revolutions per minute (rpm) of the crankshaft. At idle speed, the engine generates enough power to run reasonably smoothly and operate its ancillaries (water pump, alternator, and, if equipped, other accessories such as power steering), but usually not enough to perform useful work, such as moving an automobile. The opposite of idle speed is redline, the maximum rotational speed the engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Fuel Injection
Manifold injection is a mixture formation system for internal combustion engines with external mixture formation. It is commonly used in engines with spark ignition that use petrol as fuel, such as the Otto engine, and the Wankel engine. In a manifold-injected engine, the fuel is injected into the intake manifold, where it begins forming a combustible air-fuel mixture with the air. As soon as the intake valve opens, the piston starts sucking in the still forming mixture. Usually, this mixture is relatively homogeneous, and, at least in production engines for passenger cars, approximately stoichiometric; this means that there is an even distribution of fuel and air across the combustion chamber, and enough, but not more air present than what is required for the fuel's complete combustion. The injection timing and measuring of the fuel amount can be controlled either mechanically (by a fuel distributor), or electronically (by an engine control unit). Since the 1970s and 1980s, manifol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen Sensor
An oxygen sensor (or lambda sensor, where lambda refers to air–fuel equivalence ratio, usually denoted by λ) or probe or sond, is an electronic device that measures the proportion of oxygen (O2) in the gas or liquid being analysed. It was developed by Robert Bosch GmbH during the late 1960s under the supervision of Dr. Günter Bauman. The original sensing element is made with a thimble-shaped zirconia ceramic coated on both the exhaust and reference sides with a thin layer of platinum and comes in both heated and unheated forms. The planar-style sensor entered the market in 1990 and significantly reduced the mass of the ceramic sensing element, as well as incorporating the heater within the ceramic structure. This resulted in a sensor that started sooner and responded faster. The most common application is to measure the exhaust-gas concentration of oxygen for internal combustion engines in automobiles and other vehicles in order to calculate and, if required, dynamically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic Converter
A catalytic converter is an exhaust emission control device that converts toxic gases and pollutants in exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine into less-toxic pollutants by catalyzing a redox reaction. Catalytic converters are usually used with internal combustion engines fueled by gasoline or diesel, including lean-burn engines, and sometimes on kerosene heaters and stoves. The first widespread introduction of catalytic converters was in the United States automobile market. To comply with the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency's stricter regulation of exhaust emissions, most gasoline-powered vehicles starting with the 1975 model year are equipped with catalytic converters. These "two-way" converters combine oxygen with carbon monoxide (CO) and unburned hydrocarbons (HC) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). Although two-way converters on gasoline engines were rendered obsolete in 1981 by "three-way" converters that also reduce oxides of nitrogen (); they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telescopic Fork
A telescopic fork is a form of motorcycle front suspension whose use is so common that it is virtually universal. The telescopic fork uses fork tubes and sliders which contain the springs and dampers. The main advantages of the telescopic fork are that (i) it is simple in design and relatively cheap to manufacture and assemble; (ii) it is lighter than older designs using external components and linkage systems; and (iii) it has a clean and simple appearance that bikers find attractive. Telescopic forks sometimes have gaiters to protect the fork tubes from abrasion and corrosion. A more modern (and more expensive) version of the conventional telescopic fork is the inverted or "USD" (upside-down) fork. BMW's patented telelever front suspension appears at first glance to be conventional telescopic fork, but the fork tubes contain neither springs nor damping. Instead, a wishbone and an inboard monoshock perform suspension duties, and the forks serve to locate the front wheel an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crankcase
In a piston engine, the crankcase is the housing that surrounds the crankshaft. In most modern engines, the crankcase is integrated into the engine block. Two-stroke engines typically use a crankcase-compression design, resulting in the fuel/air mixture passing through the crankcase before entering the cylinder(s). This design of the engine does not include an oil sump in the crankcase. Four-stroke engines typically have an oil sump at the bottom of the crankcase and the majority of the engine's oil is held within the crankcase. The fuel/air mixture does not pass through the crankcase in a four-stroke engine, however a small amount of exhaust gasses often enter as "blow-by" from the combustion chamber. The crankcase often forms the lower half of the main bearing journals (with the bearing caps forming the other half), although in some engines the crankcase completely surrounds the main bearing journals. An ''open-crank'' engine has no crankcase. This design was used in early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
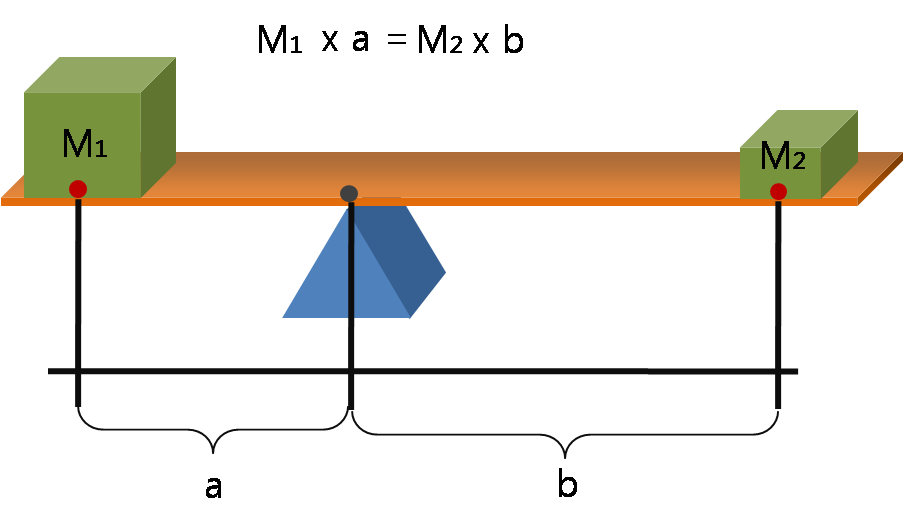
Lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or ''fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is divided into three types. Also, leverage is mechanical advantage gained in a system. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater output force, which is said to provide leverage. The ratio of the output force to the input force is the mechanical advantage of the lever. As such, the lever is a mechanical advantage device, trading off force against movement. Etymology The word "lever" entered English around 1300 from Old French, in which the word was ''levier''. This sprang from the stem of the verb ''lever'', meaning "to raise". The verb, in turn, goes back to the Latin ''levare'', itself from the adjective ''levis'', meaning "light" (as in "not heavy"). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |










.jpg)