|
Homestake Mine (South Dakota)
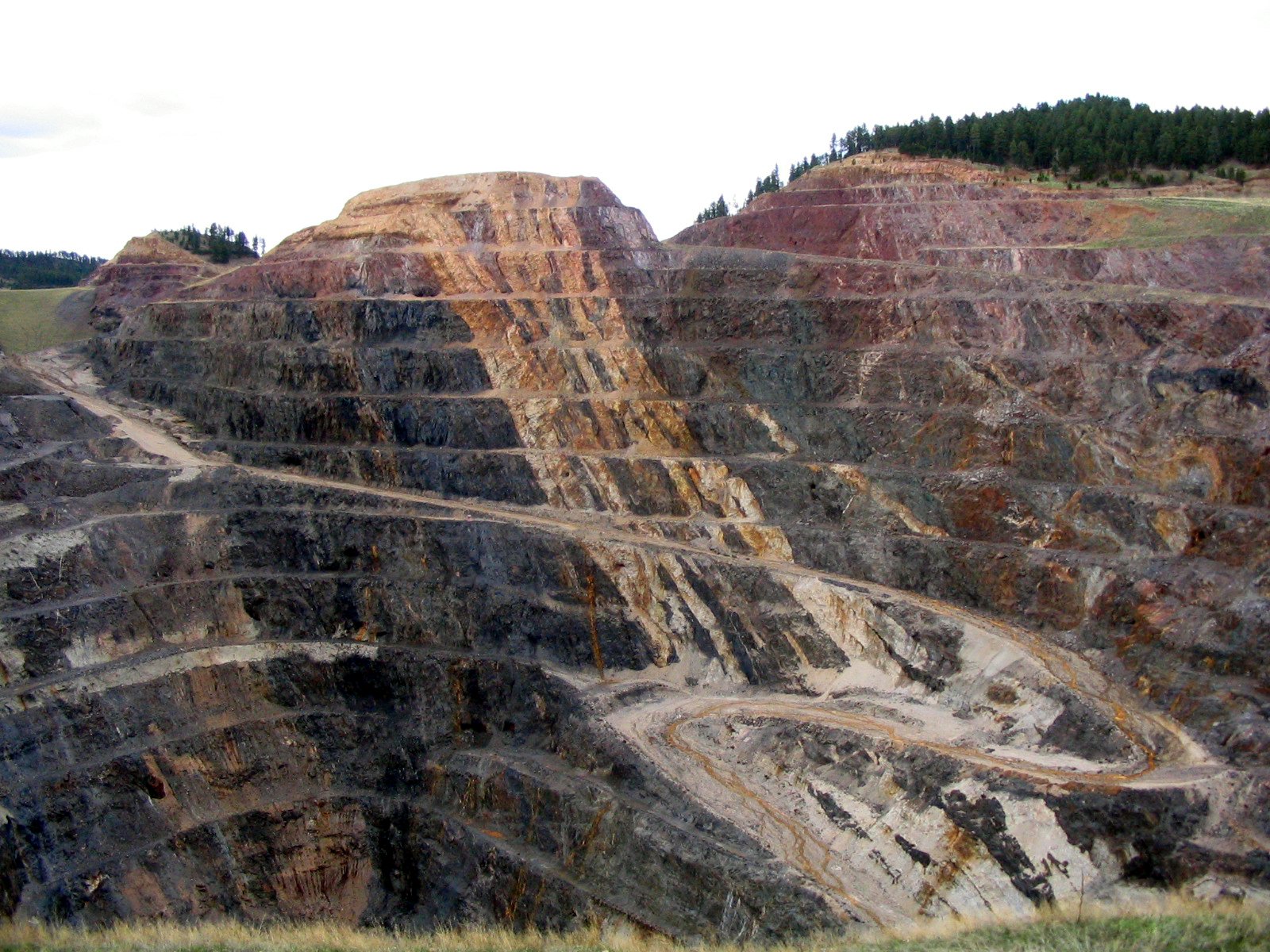
The Homestake Mine was a deep underground gold mine (8,000 feet or 2,438 m) located in Lead, South Dakota. Until it closed in 2002 it was the largest and deepest gold mine in North America. The mine produced more than of gold during its lifetime. This is about or a volume of gold roughly equal to 18,677 US gallons. The Homestake Mine is famous in scientific circles because of the work of a deep underground laboratory that was established there in the mid-1960s. This was the site where the solar neutrino problem was first discovered, in what is known as the Homestake Experiment. Raymond Davis Jr. conducted this experiment in the mid-1960s, which was the first to observe solar neutrinos. On July 10, 2007, the mine was selected by the National Science Foundation as the location for the Deep Underground Science and Engineering Laboratory (DUSEL). It won over several candidates, including the Henderson Mine near Empire, Colorado. History The Homestake deposit was discovered by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homestake Mine Pit , which was concluded to be formed of gypsum
{{disambig ...
Homestake may refer to: * Homestake experiment, an experiment headed by astrophysicists Raymond Davis, Jr. and John N. Bahcall in the late 1960s * Homestake Pass, a mountain pass in the Rocky Mountains of Montana in the United States * Homestake Mining Company, one of the largest gold mining businesses in the United States from the 19th century through the beginning of the 21st ** Homestake Mine (other), the name for several mines in the United States * Homestake, a formation on Mars analyzed by Opportunity rover ''Opportunity'', also known as MER-B (Mars Exploration Rover – B) or MER-1, is a robotic rover that was active on Mars from 2004 until 2018. ''Opportunity'' was operational on Mars for sols (). Launched on July 7, 2003, as part of NASA's M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Fort Laramie (1868)
The Treaty of Fort Laramie (also the Sioux Treaty of 1868) is an agreement between the United States and the Oglala, Miniconjou, and Brulé bands of Lakota people, Yanktonai Dakota and Arapaho Nation, following the failure of the first Fort Laramie treaty, signed in 1851. The treaty is divided into 17 articles. It established the Great Sioux Reservation including ownership of the Black Hills, and set aside additional lands as "unceded Indian territory" in the areas of South Dakota, Wyoming, and Nebraska, and possibly Montana. It established that the US government would hold authority to punish not only white settlers who committed crimes against the tribes but also tribe members who committed crimes and were to be delivered to the government, rather than to face charges in tribal courts. It stipulated that the government would abandon forts along the Bozeman Trail and included a number of provisions designed to encourage a transition to farming and to move the tribes "cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Washington Merrill
Charles Washington Merrill (December 21, 1869 – February 5, 1958) was an American mining metallurgist. Biography He was born in Concord, New Hampshire to Sylvester and Clara L. (née French) Merrill. He attended elementary and high school in Alameda, California and then attended the College of Mining of the University of California, where he received a Bachelor of Science in 1891. After his graduation he was first connected with the noted old Standard Consolidated mine in Bodie, California, and from there went to the Harqua Hala mine in Arizona, thence to the Montana Mining Company in Marysville, California. In 1899, he became affiliated with the widely known Homestake Mining Company of South Dakota as a metallurgist, and in this capacity he manifested the brilliant talents which became the foundation of his future career. He became extensively known by his work, and acquired material prosperity, and his creation of new methods, particularly in the process of extracting gold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
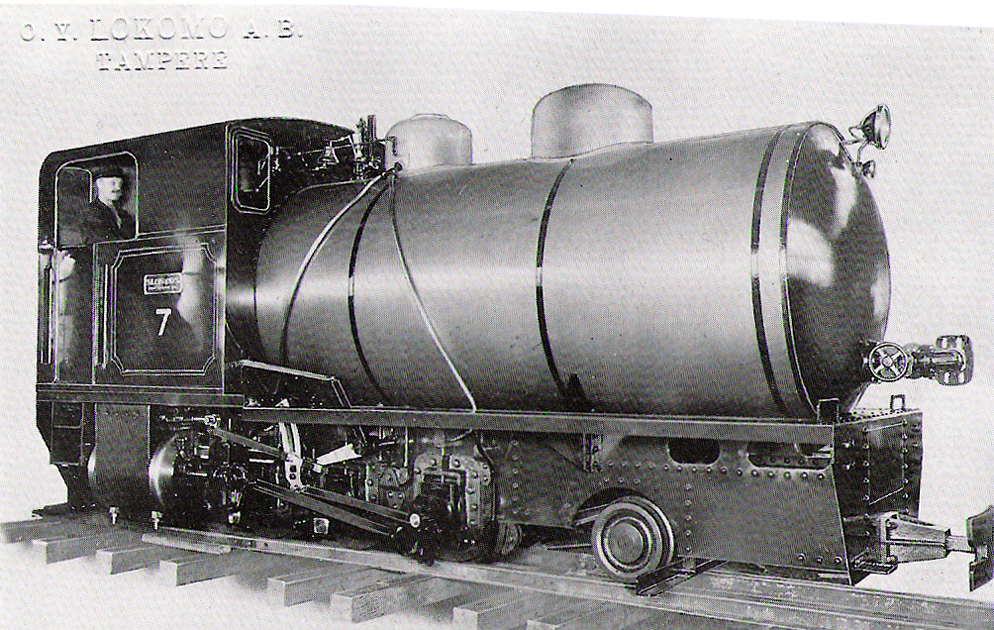
Compressed Air Locomotive
A fireless locomotive is a type of locomotive which uses reciprocating engines powered from a reservoir of compressed air or steam, which is filled at intervals from an external source. They offer advantages over conventional steam locomotives of lower cost per unit, cleanliness, and decreased risk from fire or boiler explosion; these are counterbalanced by the need for a source to refill the locomotive, and by the limited range afforded by the reservoir. They were desirable in situations where smoke from a firebox would be too noxious, or where there was risk of fire or explosion. Typical usage was in a mine, or a food or chemical factory. They were also used where a source of air or steam was readily available, and for moving loads within limited areas, such as a switch yard or within an industrial factory. They were eventually replaced for most uses by diesel and battery electric locomotives fitted with protective appliances; these are described as flame-proof locomotives. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homestake Mine, South Dakota, 1900
Homestake may refer to: * Homestake experiment, an experiment headed by astrophysicists Raymond Davis, Jr. and John N. Bahcall in the late 1960s * Homestake Pass, a mountain pass in the Rocky Mountains of Montana in the United States * Homestake Mining Company, one of the largest gold mining businesses in the United States from the 19th century through the beginning of the 21st ** Homestake Mine (other), the name for several mines in the United States * Homestake, a formation on Mars analyzed by Opportunity rover#Endeavour crater, Opportunity rover, which was concluded to be formed of gypsum {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Hills & Fort Pierre Railroad
The Black Hills and Fort Pierre Railroad (BH&FP) was a narrow gauge in the of the of . It was created by the |
New York Stock Exchange
The New York Stock Exchange (NYSE, nicknamed "The Big Board") is an American stock exchange in the Financial District of Lower Manhattan in New York City. It is by far the world's largest stock exchange by market capitalization of its listed companies at US$30.1 trillion as of February 2018. The average daily trading value was approximately 169 billion in 2013. The NYSE trading floor is at the New York Stock Exchange Building on 11 Wall Street and 18 Broad Street and is a National Historic Landmark. An additional trading room, at 30 Broad Street, was closed in February 2007. The NYSE is owned by Intercontinental Exchange, an American holding company that it also lists (). Previously, it was part of NYSE Euronext (NYX), which was formed by the NYSE's 2007 merger with Euronext. History The earliest recorded organization of securities trading in New York among brokers directly dealing with each other can be traced to the Buttonwood Agreement. Previously, securiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homestake Mining Company
Homestake Mining Company was one of the largest gold mining businesses in the United States and the owner of the Homestake Mine in Lead, South Dakota. Founded in 1877, it was acquired by Barrick Gold in December 2001. Homestake was the longest-listed stock in the history of the New York Stock Exchange. History On April 9, 1876 Moses and Fred Manuel established the Homestake Mine near Bobtail Gultch in South Dakota in the Black Hills. George Hearst (father of William Randolph Hearst), Lloyd Tevis, and his brother-in-law James Ben Ali Haggin bought the 10-acre Homestake Mine from its discoverer, Moses Manuel, for $70,000, and incorporated the Homestake Mining Company on November 5, 1877. On January 25, 1879, the company became a public company via an initial public offering on the New York Stock Exchange, the first mining stock ever listed. It grew to be the largest gold mine in the United States. In 1910 and 1917, the company established hydroelectricity plants. They were sol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stamp Mill
A stamp mill (or stamp battery or stamping mill) is a type of mill machine that crushes material by pounding rather than grinding, either for further processing or for extraction of metallic ores. Breaking material down is a type of unit operation. Description A stamp mill consists of a set of heavy steel (iron-shod wood in some cases) stamps, loosely held vertically in a frame, in which the stamps can slide up and down. They are lifted by cams on a horizontal rotating shaft. As the cam moves from under the stamp, the stamp falls onto the ore below, crushing the rock, and the lifting process is repeated at the next pass of the cam. Each one frame and stamp set is sometimes called a "battery" or, confusingly, a "stamp" and mills are sometimes categorised by how many stamps they have, i.e. a "10 stamp mill" has 10 sets. They usually are arranged linearly, but when a mill is enlarged, a new line of them may be constructed rather than extending the line. Abandoned mill sites (as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur De Wint Foote
Arthur De Wint Foote (1849–1933) was an American civil engineer and mining engineer who impacted the development of the American West with his innovative engineering works and entrepreneurial ventures. In Northern California in the late 1890s, he designed and built the North Star Mine Powerhouse, the highest capacity impulse-turbine power-plant of the time, and now a California historic landmark; within that plant he designed and installed the then-largest Pelton wheel turbine. Later, he designed and built Foote's Crossing, a high bridge, and Foote's Crossing Road, both now memorialized as California and U.S. landmarks. Early years Born in Guilford, Connecticut, Foote's ancestry was English—from Yorkshire before 1630. After preparatory schooling as a youth, he attended Yale College's Sheffield Scientific School, but left in 1868 before graduating. From there he began his early career in business and construction ventures along the eastern seaboard of the US and in the We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sidney, Nebraska
Sidney is a city in and the county seat of Cheyenne County, Nebraska, United States. The city is north of the Colorado state line. The population was 6,757 at the 2010 census. History The city was named for Sidney Dillon, president of the Union Pacific Railroad. It was founded in 1867 by the Union Pacific and grew up around the military base of Fort Sidney (also known as Sidney Barracks), where soldiers were stationed to guard the transcontinental railroad against potential Indian attacks. The town became the southern terminus of the Sidney Black Hills Stage Road which used Clarke's Bridge (near Bridgeport, Nebraska) to allow military and civilian traffic to reach Fort Robinson, Red Cloud Agency, Spotted Tail Agency, Custer, South Dakota, and Deadwood, South Dakota in the late 1870s and 1880s. When the railroad reached Sidney, it was the end of a sub-division of the rail line and played host to a roundhouse, repair facilities, and a railroad hotel for passengers. Sidney i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deadwood, South Dakota
Deadwood (Lakota: ''Owáyasuta''; "To approve or confirm things") is a city that serves as county seat of Lawrence County, South Dakota, United States. It was named by early settlers after the dead trees found in its gulch. The city had its heyday from 1876 to 1879, after gold deposits had been discovered there, leading to the Black Hills Gold Rush. At its height, the city had a population of 25,000, attracting Old West figures such as Wyatt Earp, Calamity Jane, and Wild Bill Hickok (who was killed there). The population was 1,156 at the 2020 census. The entire town has been designated as a National Historic Landmark District, for its well-preserved Gold Rush-era architecture. Deadwood's proximity to Lead often prompts the two towns being collectively named "Lead-Deadwood". History 19th century The settlement of Deadwood began illegally in the 1870s, on land which had been granted to the Lakota people in the 1868 Treaty of Fort Laramie. The treaty had guaranteed owners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

%2C_Nebraska._Pawnee_reservation_and_relevant_Indian_territories.png)



.jpg)
