|
Home Equity Protection
Home price protection is an agreement that pays the homeowner if a particular home price index declines in value over a period of time after the protection is purchased. The protection is for a new or existing homeowner that wishes to protect the value of their home from future market declines. Scholarly research In 1999, Robert J. Shiller and Allan Weiss published an overview of the idea. Two similar programs had been tried in Illinois by municipalities: a 1978 Oak Park plan, which had never had a claim as of 1999, and a broader program covering the city of Chicago passed by voter referendum in 1987 and implemented in 1990. Another program was initiated 2002 as several scholars at Yale University worked in conjunction with a program in Syracuse, NY, which was developed with the intent of increasing home ownership in neighborhoods on the verge of collapse that were marred by ever declining home prices. The Syracuse non-profit program, called Home Headquarters, was sponsored by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert J
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe it entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including English, German, Dutch, Norwegian, Swedish, Scots, Danish, and Icelandic. It can be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
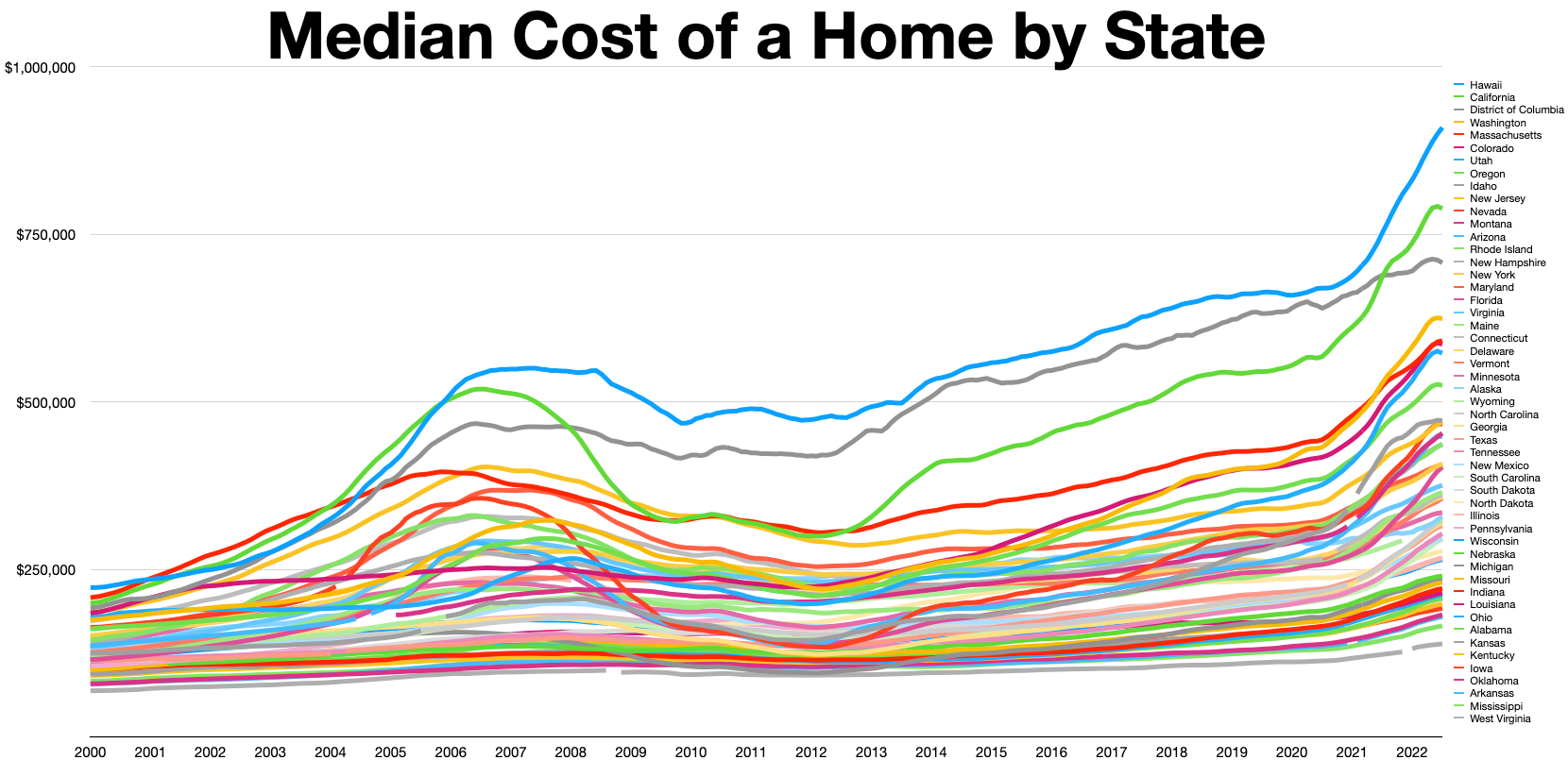
United States Housing Bubble
The 2000s United States housing bubble was a real-estate bubble affecting over half of the U.S. states. It was the impetus for the subprime mortgage crisis. Housing prices peaked in early 2006, started to decline in 2006 and 2007, and reached new lows in 2011. On December 30, 2008, the Case–Shiller home price index reported its largest price drop in its history. The credit crisis resulting from the bursting of the housing bubble is an important cause of the Great Recession in the United States. Increased foreclosure rates in 2006–2007 among U.S. homeowners led to a crisis in August 2008 for the subprime, Alt-A, collateralized debt obligation (CDO), mortgage, credit, hedge fund, and foreign bank markets. In October 2007, Henry Paulson, the U.S. Secretary of the Treasury, called the bursting housing bubble "the most significant risk to our economy". Any collapse of the U.S. housing bubble has a direct impact not only on home valuations, but mortgage markets, home buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Economics
Financial economics, also known as finance, is the branch of economics characterized by a "concentration on monetary activities", in which "money of one type or another is likely to appear on ''both sides'' of a trade".William F. Sharpe"Financial Economics", in Its concern is thus the interrelation of financial variables, such as share prices, interest rates and exchange rates, as opposed to those concerning the real economy. It has two main areas of focus: Merton H. Miller, (1999). The History of Finance: An Eyewitness Account, ''Journal of Portfolio Management''. Summer 1999. asset pricing, commonly known as "Investments", and corporate finance; the first being the perspective of providers of capital, i.e. investors, and the second of users of capital. It thus provides the theoretical underpinning for much of finance. The subject is concerned with "the allocation and deployment of economic resources, both spatially and across time, in an uncertain environment".See Fama and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial History Of The United States
The economic history of the United States is about characteristics of and important developments in the U.S. economy from colonial times to the present. The emphasis is on productivity and economic performance and how the economy was affected by new technologies, the change of size in economic sectors and the effects of legislation and government policy. Specialized business history is covered in American business history. Colonial economy The colonial economy was characterized by an abundance of land and natural resources and a severe scarcity of labor. This was the opposite of Europe and attracted immigrants despite the high death rate caused by New World diseases. From 1700 to 1774 the output of the thirteen colonies increased 12-fold, giving the colonies an economy about 30% the size of Britain's at the time of independence. Population growth was responsible for over three-quarters of the economic growth of the British American colonies. The free white population had th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Bubbles
An economic bubble (also called a speculative bubble or a financial bubble) is a period when current asset prices greatly exceed their intrinsic valuation, being the valuation that the underlying long-term fundamentals justify. Bubbles can be caused by overly optimistic projections about the scale and sustainability of growth (e.g. dot-com bubble), and/or by the belief that intrinsic valuation is no longer relevant when making an investment (e.g. Tulip mania). They have appeared in most asset classes, including equities (e.g. Roaring Twenties), commodities (e.g. Uranium bubble), real estate (e.g. 2000s US housing bubble), and even esoteric assets (e.g. Cryptocurrency bubble). Bubbles usually form as a result of either excess liquidity in markets, and/or changed investor psychology. Large multi-asset bubbles (e.g. 1980s Japanese asset bubble and the 2020–21 Everything bubble), are attributed to central banking liquidity (e.g. overuse of the Fed put). In the early stages of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foreclosure Consultant
Although the definition may vary by jurisdiction, foreclosure consultant generally means any person who makes any solicitation, representation, or offer to any owner to perform for compensation or who, for compensation, performs any service which the person in any manner represents will in any manner do any of the following: #Stop or postpone the foreclosure sale. #Obtain any forbearance from any beneficiary or mortgagee. #Assist the owner to exercise the right of reinstatement. #Obtain any extension of the period within which the owner may reinstate his or her obligation. #Obtain any waiver of an acceleration clause contained in any promissory note or contract secured by a deed of trust or mortgage on a residence in foreclosure or contained in any such deed of trust or mortgage. #Assist the owner to obtain a loan or advance of funds. #Avoid or ameliorate the impairment of the owner's credit resulting from the recording of a notice of default or the conduct of a foreclosure sale. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deed In Lieu Of Foreclosure
A deed in lieu of foreclosure is a deed instrument in which a mortgagor (i.e. the borrower) conveys all interest in a real property to the mortgagee (i.e. the lender) to satisfy a loan that is in default and avoid foreclosure proceedings. The deed in lieu of foreclosure offers several advantages to both the borrower and the lender. The principal advantage to the borrower is that it immediately releases him/her from most or all of the personal indebtedness associated with the defaulted loan. The borrower also avoids the public notoriety of a foreclosure proceeding and may receive more generous terms than he/she would in a formal foreclosure. Another benefit to the borrower is that it hurts his/her credit less than a foreclosure does. Advantages to a lender include a reduction in the time and cost of a repossession, lower risk of borrower revenge (metal theft and vandalism of the property before sheriff eviction), and additional advantages if the borrower subsequently files for b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Estate Trends
A real estate trend is any consistent pattern or change in the general direction of the real estate industry which, over the course of time, causes a statistically noticeable change. This phenomenon can be a result of the economy, a change in mortgage rates, consumer speculations, or other fundamental and non-fundamental reasons. Buyer agency growth At one time, all real estate brokers and agents, or Realtors, practiced "single agency", meaning they represented only the buyer or the seller. In the 1990s, the concept of buyer agency became popular, allowing a buyer to retain an agent who would represent the best interests of the buyer alone. The first national company to provide this service was The Buyer's Agent, Inc. A 2008 study by ''Consumer Reports'' indicates that prior to this development, a Realtor was presumed by state law to be working for the seller. The same study shows that buyers using buyer agents obtained a savings of $5000 in the price of the home as compared to pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Estate Economics
Real estate economics is the application of economic techniques to real estate markets. It tries to describe, explain, and predict patterns of prices, supply, and demand. The closely related field of housing economics is narrower in scope, concentrating on residential real estate markets, while the research on real estate trends focuses on the business and structural changes affecting the industry. Both draw on partial equilibrium analysis (supply and demand), urban economics, spatial economics, basic and extensive research, surveys, and finance. Overview of real estate markets The main participants in real estate markets are: * Users: These people are both owners and tenants. They purchase houses or commercial property as an investment and also to live in or utilize as a business. Businesses may or may not require buildings to use land. The land can be used in other ways, such as for agriculture, forestry or mining. * Owners: These people are pure investors. They do not occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Estate Appraisal
Real estate appraisal, property valuation or land valuation is the process of developing an opinion of value for real property (usually market value). Real estate transactions often require appraisals because they occur infrequently and every property is unique (especially their condition, a key factor in valuation), unlike corporate stocks, which are traded daily and are identical (thus a centralized Walrasian auction like a stock exchange is unrealistic). The location also plays a key role in valuation. However, since property cannot change location, it is often the upgrades or improvements to the home that can change its value. Appraisal reports form the basis for mortgage loans, settling estates and divorces, taxation, and so on. Sometimes an appraisal report is used to establish a sale price for a property. Besides the mandatory educational grade, which can vary from Finance to Construction Technology, most, but not all, countries require appraisers to have the license for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Estate Pricing
Real estate appraisal, property valuation or land valuation is the process of developing an opinion of value for real property (usually market value). Real estate transactions often require appraisals because they occur infrequently and every property is unique (especially their condition, a key factor in valuation), unlike corporate stocks, which are traded daily and are identical (thus a centralized Walrasian auction like a stock exchange is unrealistic). The location also plays a key role in valuation. However, since property cannot change location, it is often the upgrades or improvements to the home that can change its value. Appraisal reports form the basis for mortgage loans, settling estates and divorces, taxation, and so on. Sometimes an appraisal report is used to establish a sale price for a property. Besides the mandatory educational grade, which can vary from Finance to Construction Technology, most, but not all, countries require appraisers to have the license for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recession Of 2008
The Great Recession was a period of marked general decline, i.e. a recession, observed in national economies globally that occurred from late 2007 into 2009. The scale and timing of the recession varied from country to country (see map). At the time, the International Monetary Fund (IMF) concluded that it was the most severe economic and financial meltdown since the Great Depression. One result was a serious disruption of normal international relations. The causes of the Great Recession include a combination of vulnerabilities that developed in the financial system, along with a series of triggering events that began with the bursting of the United States housing bubble in 2005–2012. When housing prices fell and homeowners began to abandon their mortgages, the value of mortgage-backed securities held by investment banks declined in 2007–2008, causing several to collapse or be bailed out in September 2008. This 2007–2008 phase was called the subprime mortgage crisis. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |