|
Holycross
Holycross () is a village and civil parish in County Tipperary, Ireland. It is one of 21 civil parishes in the barony of Eliogarty. The civil parish straddles two counties and the baronies of Eliogarty and of Middle Third (South Tipperary). It is also an ecclesiastical parish in the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Cashel and Emly. The village developed around the Cistercian Holy Cross Abbey on the River Suir. Its population was 715 at the 2016 census. Transport The Thurles to Clonmel via Cashel bus route serves Holycross. The nearest railway station is Thurles railway station at approximately 6 kilometres distance. Village pub History Holy Cross Abbey was founded in 1180 by King Domnall Mór Ua Briain and was renovated and added to during the 15th century. It became a place of pilgrimage when a relic of the True Cross was presented to the Cistercian monks. The monastery was suppressed by King Henry VIII during the 16th century. The Abbey was abandoned circa 1650, fell into ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
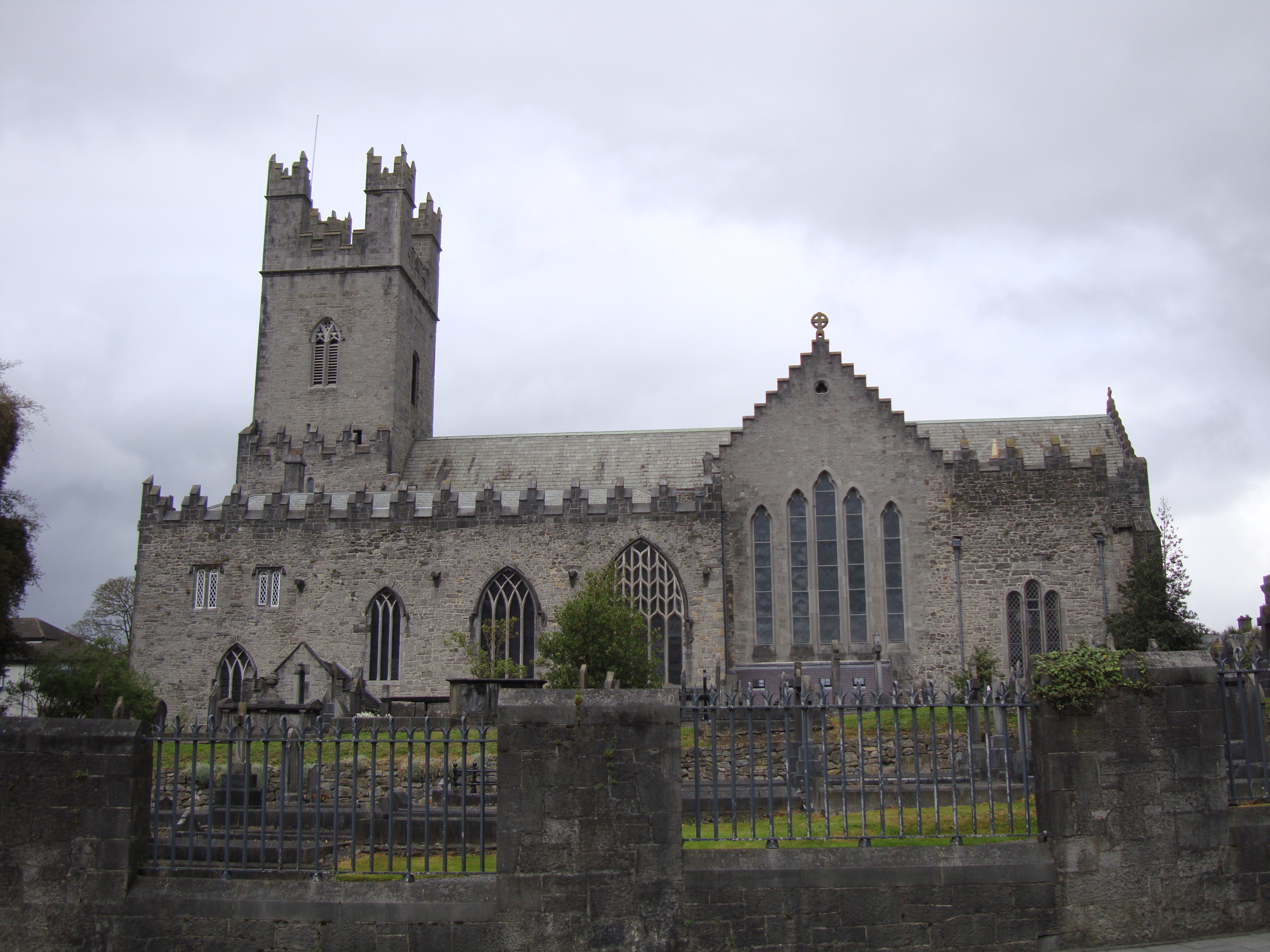
Holy Cross Abbey
Holy Cross Abbey ''(Mainistir na Croise Naofa)'' was a Cistercian monastery in Holycross near Thurles, County Tipperary, Ireland, situated on the River Suir. It takes its name from a relic of the True Cross or Holy Rood. History A supposed fragment of the True Cross was brought to Ireland by the Plantagenet Queen Isabella of Angoulême, around 1233. She was the widow of King John and bestowed the relic on the original Cistercian Monastery in Thurles founded in 1169 by King Donal O'Brien of Thomond, which she then rebuilt. With time, Holy Cross Abbey and the sacred relic of the True Cross became a place of medieval pilgrimage, and with the Protestant Reformation, also a rallying-point for the dispossessed and victims of religious persecution. As a symbol and inspiration for the defence of the Catholic faith, resistance and the struggle for freedom, it drew a complaint by Sir Henry Sidney, Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, to Queen Elizabeth I in 1567. The Annals of the Kingdom o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Suir
The River Suir ( ; ga, an tSiúr or ''Abhainn na Siúire'' ) is a river in Ireland that flows into the Atlantic Ocean through Waterford after a distance of . The catchment area of the Suir is 3,610 km2.South Eastern River Basin District Management System. Page 38 Its long term average flow rate is 76.9 cubic metres per second (m3/s), about twice the flow of either the (37.4 m3/s) or the (42.9 m3/s) before these join, but a little less than the Barrow's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Third (South Tipperary)
Middle Third (Irish: ''An Trian Meánach''; also spelled Middlethird) is a barony in County Tipperary, Ireland. This geographical unit of land is one of 12 baronies in County Tipperary. Its chief town is Cashel. The barony lies between Eliogarty to the north (whose chief town is Thurles), Iffa and Offa East to the south (whose chief town is Clonmel), Clanwilliam to the west (whose chief town is Tipperary) and Slievardagh to the east (whose chief town is Mullinahone). It is currently administered by Tipperary County Council. Legal context Baronies were created after the Norman invasion of Ireland as divisions of counties and were used the administration of justice and the raising of revenue. While baronies continue to be officially defined units, they have been administratively obsolete since 1898. However, they continue to be used in land registration and in specification, such as in planning permissions. In many cases, a barony corresponds to an earlier Gaelic túath which h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Archdiocese Of Cashel And Emly
The Archdiocese of Cashel and Emly ( ga, Ard-Deoise Chaisil agus Imligh) is an ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church ( particularly the Roman Catholic or Latin Church) located in mid-western Ireland and the metropolis of the eponymous ecclesiastical province. The cathedral church of the archdiocese is the Cathedral of the Assumption in Thurles, County Tipperary. The incumbent archbishop of the archdiocese is Kieran O'Reilly. History The original dioceses of Cashel and Emly were established by the Synod of Ráth Breasail in 1111. Diocese of Cashel The Diocese of Cashel was elevated to the rank of ecclesiastical province, which was roughly co-extensive with the traditional province of Munster, by the Synod of Kells in 1152. Since the Papal Legate, Giovanni Paparoni, awarded the pallium to Donat O'Lonergan in 1158, his successors have ruled the ecclesiastical province of Cashelalso sometimes known as Munster until 26 January 2015. Diocese of Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eliogarty
Eliogarty (Irish: ''Éile Uí Fhógarta'') is a barony in County Tipperary, Ireland. This geographical unit of land is one of 12 baronies in County Tipperary. Its chief town is Thurles. The barony lies between Ikerrin to the north (whose chief town is Roscrea), Kilnamanagh Upper to the west (whose chief town is Borrisoleigh), Middle Third to the south (whose chief town is Cashel) and County Kilkenny to the east. It is currently administered by Tipperary County Council. Legal context Baronies were created after the Norman invasion of Ireland as divisions of counties and were used the administration of justice and the raising of revenue. While baronies continue to be officially defined units, they have been administratively obsolete since 1898. However, they continue to be used in land registration and in specification, such as in planning permissions. In many cases, a barony corresponds to an earlier Gaelic túath which had submitted to the Crown. This is probably true in the ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
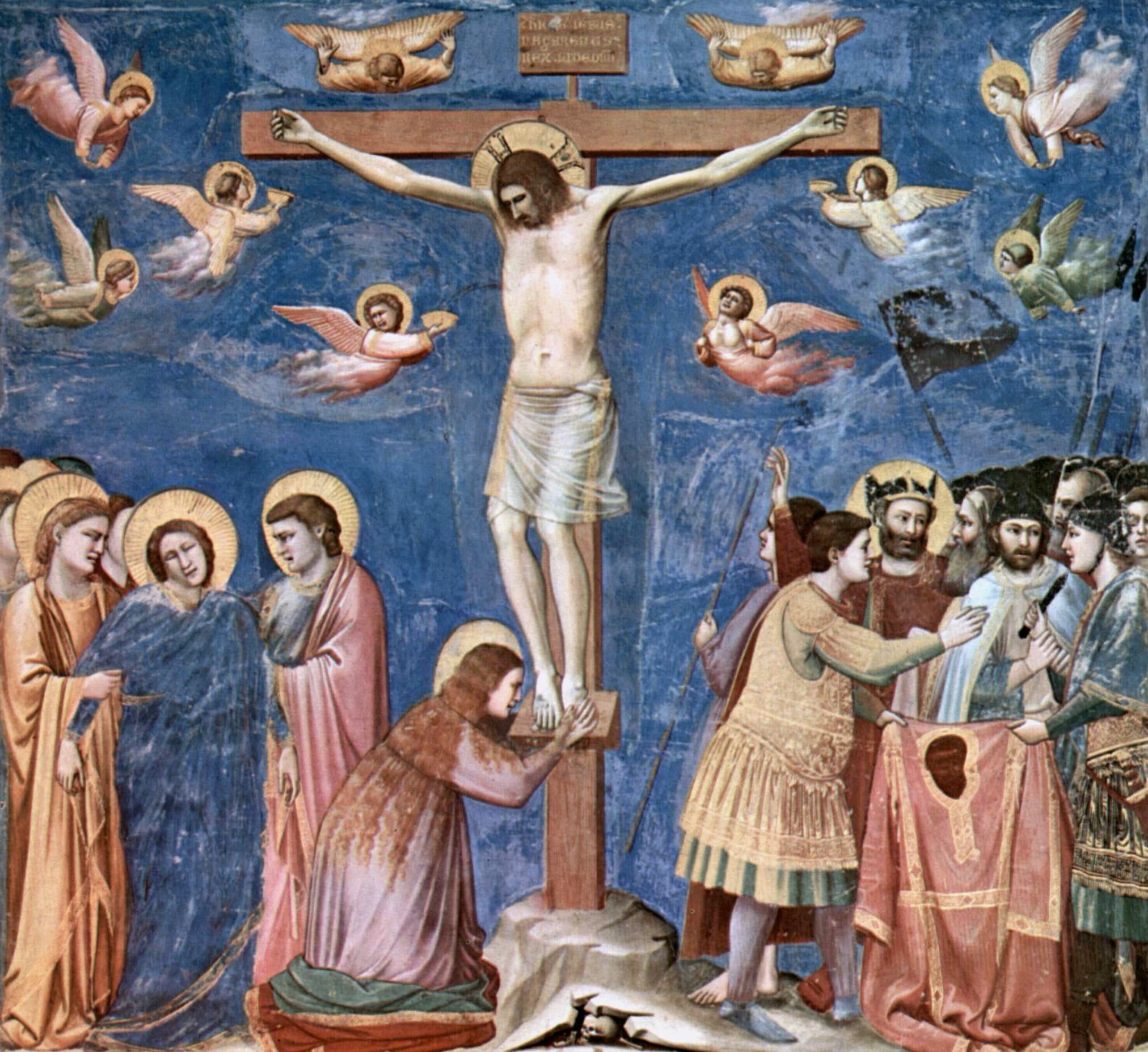
True Cross
The True Cross is the cross upon which Jesus was said to have been crucified, particularly as an object of religious veneration. There are no early accounts that the apostles or early Christians preserved the physical cross themselves, although protective use of the sign of the cross was common by at least the 2nd century. Post-Nicene historians such as Socrates of Constantinople relate that Helena, the mother of the Roman emperor ConstantineI, travelled to the Holy Land in the years 326–328, founding churches and establishing relief agencies for the poor. The late 4th-century historians Gelasius of Caesarea and Tyrannius Rufinus claimed that while there she discovered the hiding place of three crosses that were believed to have been used at the crucifixion of Jesus and the two thieves, St. Dismas and Gestas, executed with him. To one cross was affixed the titulus bearing Jesus's name, but according to Rufinus, Helena was not sure until a miracle revealed that this was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domnall Mór Ua Briain
Domnall Mór Ua Briain, or Domnall Mór mac Toirrdelbaig Uí Briain, was King of Thomond in Ireland from 1168 to 1194 and a claimant to the title King of Munster. He was also styled King of Limerick, a title belonging to the O'Brien dynasty since Brian Boru's annexation of the Norse city in the 10th century. History Domnall Mór ("Donall the Great") was the third son of Toirdhealbhach mac Diarmada Ua Briain, King of Munster, who reigned from 1142 to 1167. He ascended to the throne in 1168 after the death of his eldest brother, Muirchertach, who had succeeded their father as king. Muirchertach was killed at the instigation of his cousin Conchobar mac Muirchertach Ua Briain. His other brother Brian of Slieve Bloom was blinded in 1169. The same year, Domnall entered into conflict with the High King of Ireland, Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair and was forced to pay him a tribute of 300 cows. In 1171, he submitted to King Henry II of England at Cashel, but he continued to fight successf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
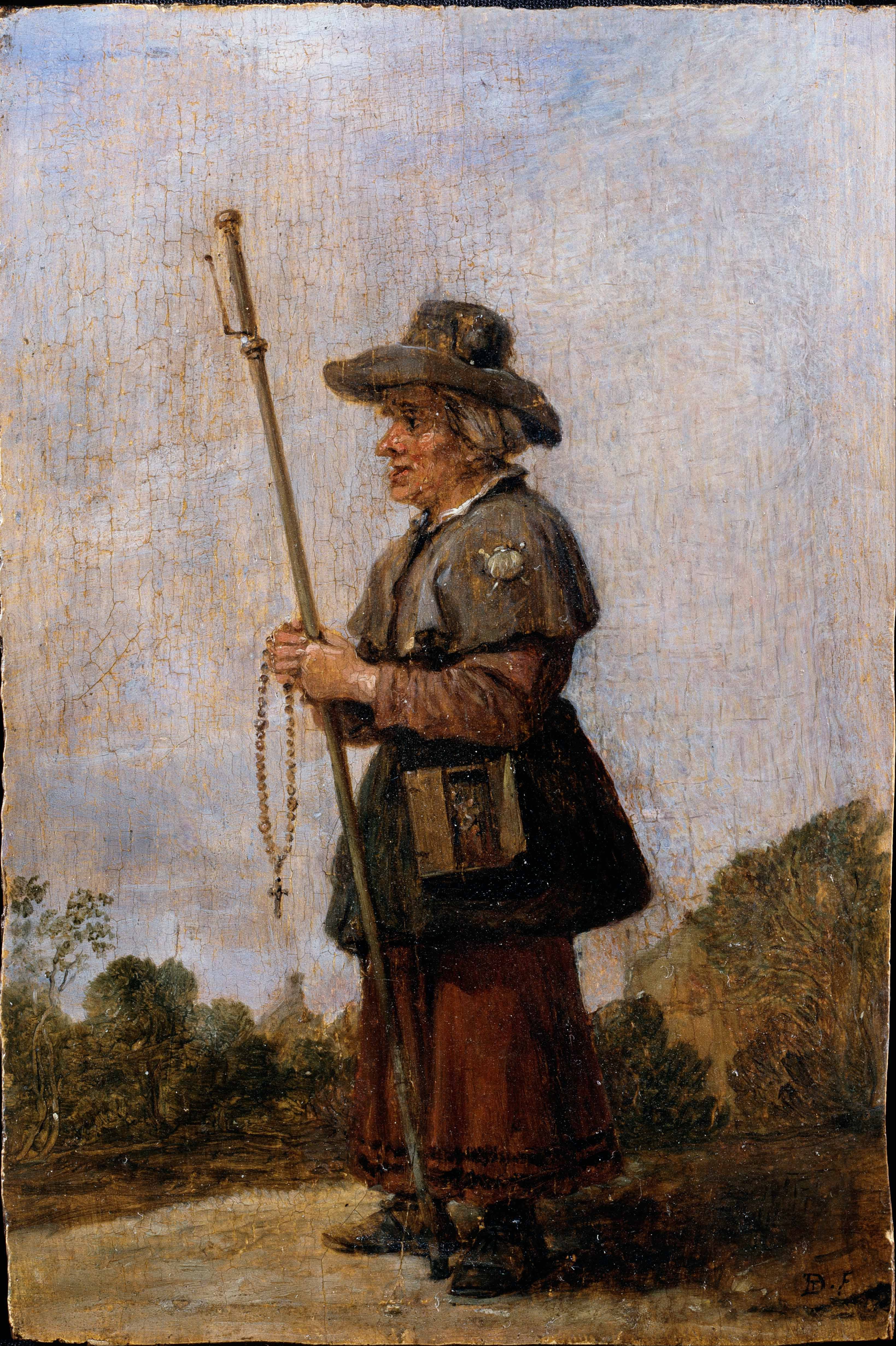
Pilgrimage
A pilgrimage is a journey, often into an unknown or foreign place, where a person goes in search of new or expanded meaning about their self, others, nature, or a higher good, through the experience. It can lead to a personal transformation, after which the pilgrim returns to their daily life. Background Pilgrimages frequently involve a journey or search of moral or spiritual significance. Typically, it is a journey to a shrine or other location of importance to a person's beliefs and faith, although sometimes it can be a metaphorical journey into someone's own beliefs. Many religions attach spiritual importance to particular places: the place of birth or death of founders or saints, or to the place of their "calling" or spiritual awakening, or of their connection (visual or verbal) with the divine, to locations where miracles were performed or witnessed, or locations where a deity is said to live or be "housed", or any site that is seen to have special spiritual powers. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relic
In religion, a relic is an object or article of religious significance from the past. It usually consists of the physical remains of a saint or the personal effects of the saint or venerated person preserved for purposes of veneration as a tangible memorial. Relics are an important aspect of some forms of Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, shamanism, and many other religions. ''Relic'' derives from the Latin ''reliquiae'', meaning "remains", and a form of the Latin verb ''relinquere'', to "leave behind, or abandon". A reliquary is a shrine that houses one or more religious relics. In classical antiquity In ancient Greece, a polis, city or Greek temple, sanctuary might claim to possess, without necessarily displaying, the remains of a venerated hero as a part of a Greek hero cult, hero cult. Other venerable objects associated with the hero were more likely to be on display in sanctuaries, such as spears, shields, or other weaponry; chariots, ships or Figurehead (object), figureheads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republic Of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island. Around 2.1 million of the country's population of 5.13 million people resides in the Greater Dublin Area. The sovereign state shares its only land border with Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. It is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, with the Celtic Sea to the south, St George's Channel to the south-east, and the Irish Sea to the east. It is a unitary, parliamentary republic. The legislature, the , consists of a lower house, ; an upper house, ; and an elected President () who serves as the largely ceremonial head of state, but with some important powers and duties. The head of government is the (Prime Minister, literally 'Chief', a title not used in English), who is elected by the Dáil and appointed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistercian
The Cistercians, () officially the Order of Cistercians ( la, (Sacer) Ordo Cisterciensis, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contributions of the highly-influential Saint Bernard of Clairvaux, known as the Latin Rule. They are also known as Bernardines, after Saint Bernard himself, or as White Monks, in reference to the colour of the "cuculla" or cowl (choir robe) worn by the Cistercians over their habits, as opposed to the black cowl worn by Benedictines. The term ''Cistercian'' derives from ''Cistercium,'' the Latin name for the locale of Cîteaux, near Dijon in eastern France. It was here that a group of Benedictine monks from the monastery of Molesme founded Cîteaux Abbey in 1098, with the goal of following more closely the Rule of Saint Benedict. The best known of them were Robert of Molesme, Alberic of Cîteaux and the English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |