|
Hohhot Shengle International Airport
Hohhot Shengle International Airport () is an airport being built to serve Hohhot, the capital of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region in north China. Once completed it will replace the existing Baita International Airport as the city's main airport. It is located in Qiaoshiying Township, Horinger County, south of the city center. History Hohhot is currently served by Baita International Airport. With the rapid expansion of the city, the airport is now surrounded by urban area. It has no more room to expand to accommodate growing traffic, while the presence of the airport in the middle of the city has severely restricted urban development. In April 2012, the city of Hohhot launched the project to build a new airport to replace Baita Airport. It chose a site in Qiaoshiying Township, Horinger County, south of the city center, and named it Hohhot Shengle International Airport. The name refers to Shengle, capital of the Kingdom of Dai in the 4th century CE. In September 2013, an of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohhot
Hohhot,; abbreviated zh, c=呼市, p=Hūshì, labels=no formerly known as Kweisui, is the capital of Inner Mongolia in the north of the People's Republic of China, serving as the region's administrative, economic and cultural center.''The New Encyclopædia Britannica'', 15th Edition (1977), Vol. I, p. 275. Its population was 3,446,100 inhabitants as of the 2020 census, of whom 2,944,889 lived in the metropolitan area consisting of 4 urban districts (including Hohhot Economic and Development Zone) plus the Tümed Left Banner. The name of the city in Mongolian means "Blue City", although it is also wrongly referred to as the "Green City."Perkins (1999), p. 212. The color blue in Mongol culture is associated with the sky, eternity and purity. In Chinese, the name can be translated as ''Qīng Chéng'' () The name has also been variously romanized as Kokotan, Kokutan, Kuku-hoton, Huhohaot'e, Huhehot, Huhot, or Köke qota. The city is a seat of the Inner Mongolia University, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Mongolia
Inner Mongolia, officially the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China. Its border includes most of the length of China's border with the country of Mongolia. Inner Mongolia also accounts for a small section of China's border with Russia (Zabaykalsky Krai). Its capital is Hohhot; other major cities include Baotou, Chifeng, Tongliao, and Ordos. The autonomous region was established in 1947, incorporating the areas of the former Republic of China provinces of Suiyuan, Chahar, Rehe, Liaobei, and Xing'an, along with the northern parts of Gansu and Ningxia. Its area makes it the third largest Chinese administrative subdivision, constituting approximately and 12% of China's total land area. Due to its long span from east to west, Inner Mongolia is geographically divided into eastern and western divisions. The eastern division is often included in Northeastern China (Dongbei) with major cities including Tongliao, Chifeng, Hai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horinger County
Horinger ( Mongolian: Қорин Гэр сиыан ''Qorin Ger siyan''; ) is a county of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, North China, it is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Hohhot, the capital of Inner Mongolia, bordering Shanxi province to the southeast. History The site of Shengle () to the northwest of the present-day county seat of Horinger was the capital of the Xianbei Kingdom of Dai during the Sixteen Kingdoms Period of Chinese history. People's Daily, UPDATED: 13:56, May 04, 2006 Climate Transport * |
Hohhot Baita International Airport
Hohhot Baita International Airport is an international airport serving Hohhot, the capital of Inner Mongolia, China. It is the largest airport in Inner Mongolia and lies east of downtown Hohhot. Its name Baita, meaning White Pagoda, derives from Wanbu Huayanjing Pagoda; one of the historical attractions in Hohhot which lies south-east of the airport. In 2013 it served 6,150,282 passengers. History Hohhot Baita Airport was opened on 1 October 1958. In the mid-1980s and 1990s, it underwent two expansions and in June 2007 a new terminal was constructed. The new terminal covers an area of with 11 parking jetways and is capable of handling three million passengers each year. Its runway was also lengthened and its widened to accommodate jumbo jets such as the Airbus A380. It served as one of the diversion airports for air traffic during the 2008 Summer Olympics. With the rapid expansion of the city, Baita Airport is now surrounded by urban area and has no more room to expand to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dai (Sixteen Kingdoms)
Dai, also rendered as Tai and sometimes known in historiography as the Tuoba Dai (), was a dynastic state of China ruled by the Tuoba clan of Xianbei descent, during the era of Sixteen Kingdoms (although it is not listed as one of the 16). It existed from AD 310 to 376, with its capital at Shengle (near modern Horinger County of Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China). The name "Dai" originated when Tuoba Yilu was appointed the Duke of Dai (代公) by the Western Jin dynasty in 310, as a reward for helping Liu Kun, the Governor of Bingzhou (并州), fight against the Xiongnu-led Han Zhao dynasty. The fief was later promoted from a duchy to a principality in 315. Dai was conquered in 376 by the Former Qin dynasty, and its descendants later established the Northern Wei dynasty in 386. Chieftains of Tuoba Clan 219–377 (as Princes of Dai 315–377) Tuoba clan family tree Notes References See also * List of past Chinese ethnic groups * Five Barbarians * Yujiulü ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Aviation Administration Of China
The Civil Aviation Administration of China (CAAC; ) is the Chinese civil aviation authority under the Ministry of Transport. It oversees civil aviation and investigates aviation accidents and incidents. As the aviation authority responsible for China, it concludes civil aviation agreements with other aviation authorities, including those of the Special administrative regions of China which are categorized as "special domestic." It directly operated its own airline, China's aviation monopoly, until 1988. The agency is headquartered in Dongcheng District, Beijing. The CAAC does not share the responsibility of managing China's airspace with the Central Military Commission under the regulations in the Civil Aviation Law of the People's Republic of China. History On November 2, 1949, shortly after the founding of the People's Republic of China, the CCP Central Committee decided to found the Civil Aviation Agency under the name of the People's Revolutionary Military Commission, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Development And Reform Commission
The National Development and Reform Commission of the People's Republic of China (NDRC), formerly State Planning Commission and State Development Planning Commission, is a macroeconomic management agency under the State Council, which has broad administrative and planning control over the economy of Mainland China. It has reputation of being the "mini-state council". The candidate for the chairperson of the NDRC is nominated by the Premier of the People's Republic of China and approved by the National People's Congress. Since February 2017 the commission has been headed by He Lifeng. Synopsis The NDRC's functions are to study and formulate policies for economic and social development, maintain the balance of economic development, and to guide restructuring of the economic system of Mainland China. The NDRC has twenty-six functional departments/bureaus/offices with an authorized staff size of 890 civil servants. Prior to 2018, it was also responsible for enforcing China's a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
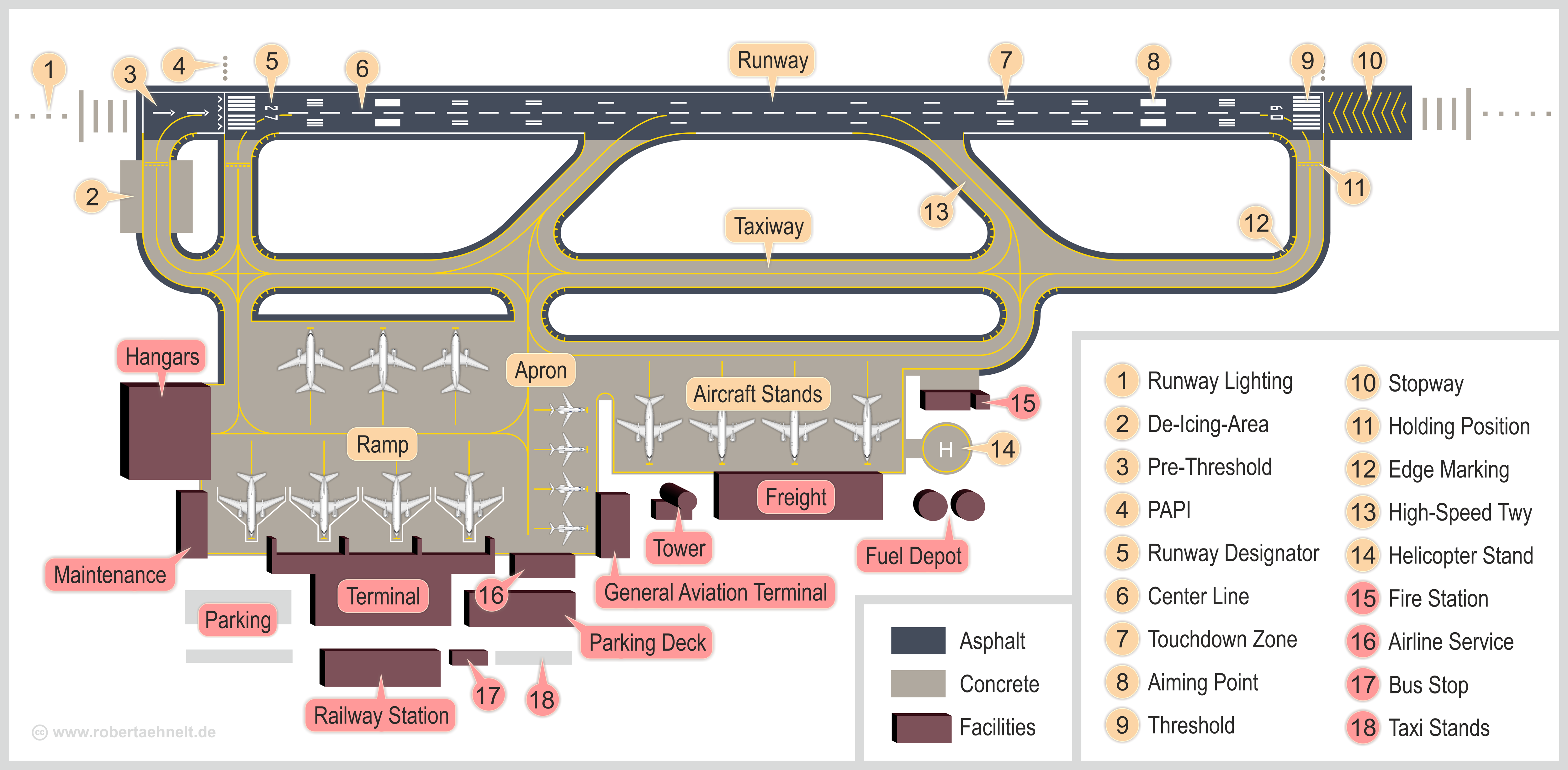
Taxiway
A taxiway is a path for aircraft at an airport connecting runways with aprons, hangars, terminals and other facilities. They mostly have a hard surface such as asphalt or concrete, although smaller general aviation airports sometimes use gravel or grass. Most airports do not have a specific speed limit for taxiing (though some do). There is a general rule on safe speed based on obstacles. Operators and aircraft manufacturers might have limits. Typical taxi speeds are 20–30 knots (37–56 km/h; 23–35 mph). High-speed exit Busy airports typically construct high-speed or rapid-exit taxiways to allow aircraft to leave the runway at higher speeds. This allows the aircraft to vacate the runway quicker, permitting another to land or take off in a shorter interval of time. This is accomplished by reducing the angle the exiting taxiway intercepts the runway at to 30 degrees, instead of 90 degrees, thus increasing the speed at which the aircraft can exit the runway onto the taxiway. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airport Apron
The airport apron, apron, flight line, ramp, or tarmac is the area of an airport where aircraft are parked, unloaded or loaded, refueled, boarded, or maintained. Although the use of the apron is covered by regulations, such as lighting on vehicles, it is typically more accessible to users than the runway or taxiway. However, the apron is not usually open to the general public, and a permit may be required to gain access. An apron's designated areas for aircraft parking are called ''aircraft stands''. By extension, the term ''apron'' is also used to identify the air traffic control position responsible for coordinating movement on this surface at busier airports. When the aerodrome control tower does not have control over the apron, the use of the apron may be controlled by an ''apron management service'' (''apron control'' or ''apron advisory'') to provide coordination between the users. Apron control allocates aircraft parking stands (gates) and communicates this information to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohhot Metro
Hohhot Metro or Hohhot Rail Transit is a rapid transit, metro system in Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China. Lines Line 1 The first phase of Line 1 is long. The color for Line 1 is . Line 1 began construction in April 2016 and was opened on 29 December 2019. Line 2 The first phase of Line 2 is long. It was opened on 1 October 2020. The color for Line 2 is blue. Future Development Lines 3, 4, 5 and 6 are under planning. See also * Baotou Metro * Rapid transit in China References {{Rapid transit in Asia Hohhot Metro, Hohhot Rapid transit in China Rail transport in Inner Mongolia Transport infrastructure in China 2019 establishments in China Railway lines opened in 2019 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airports In Inner Mongolia
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Operating airports is extremely complicated, with a complex system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tourism and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpeg/1200px-Siège_de_Beijing_(1213-1214).jpeg)