|
Hobson's Joint
A Hobson's joint or Hobson's coupling is a type of right-angle constant-velocity joint; rods bent 90° are able to transmit torque around a corner because they are all free to turn in their mounting holes in both legs of the coupling. Hobson's joints are used to make elbow engines, a novelty device, but also for practical purposes in tools and shaft-driven bicycle A shaft-driven bicycle is a bicycle that uses a drive shaft instead of a chain to transmit power from the pedals to the wheel. Shaft drives were introduced over a century ago, but were mostly supplanted by chain-driven bicycles due to the gear r ... gearing. External links * * * References Gears Rotating shaft couplings {{mech-engineering-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant-velocity Joint
Constant-velocity joints (also known as homokinetic or CV joints) are mechanical joints which allow a drive shaft to transmit power through a variable angle, at constant rotational speed, without an appreciable increase in friction or Backlash (engineering), play. They are mainly used in front-wheel drive vehicles. Modern rear-wheel drive cars with independent rear suspension typically use CV joints at the ends of the rear axle halfshafts and increasingly use them on the drive shaft. History The universal joint, one of the earliest means of transmitting power between two angled shafts, was invented by Gerolamo Cardano in the 16th century. The fact that it failed to maintain constant velocity during rotation was recognized by Robert Hooke in the 17th century, who proposed the first constant velocity joint, consisting of two Cardan joints offset by 90 degrees, so as to cancel out the velocity variations. This is the #Double_Cardan, "double Cardan". Many different types of consta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbow Engine
An elbow engine is a piston-based steam engine typically fed by steam or compressed air to drive a flywheel and/or mechanical load. It is based on a mechanism known as a Hobson's joint. Although not commonly used today for practical purposes, it is still built by hobbyists for its rarity and unconventionality. Principle of operation Elbow engines have two rotating, circular, cylinder blocks. Each block contains a ring of parallel cylinders and can itself rotate on a central axis, similar to a revolver cylinder. The two blocks are placed at 90° to each other. Each piston is L-shaped, and circular in cross section with one end fitted into each cylinder block. The two cylinder blocks rotate together, coupled only by the pistons. Engine output is taken from the rotation of one cylinder block. Pressure is supplied to each cylinder by means of a fixed plate forming a plain thrust bearing with the back of the cylinder block. This has two openings in it which supply and exhaust steam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaft-driven Bicycle
A shaft-driven bicycle is a bicycle that uses a drive shaft instead of a chain to transmit power from the pedals to the wheel. Shaft drives were introduced over a century ago, but were mostly supplanted by chain-driven bicycles due to the gear ranges possible with sprockets and derailleurs. Recently, due to advancements in internal gear technology, a small number of modern shaft-driven bicycles have been introduced. Shaft-driven bikes have a large bevel gear where a conventional bike would have its chain ring. This meshes with another bevel gear mounted on the drive shaft. The use of bevel gears allows the axis of the drive torque from the pedals to be turned through 90 degrees. The drive shaft then has another bevel gear near the rear wheel hub which meshes with a bevel gear on the hub where the rear sprocket would be on a conventional bike, and canceling out the first drive torque change of axis. The 90-degree change of the drive plane that occurs at the bottom bracket and ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
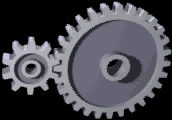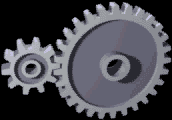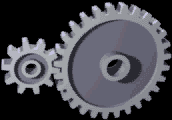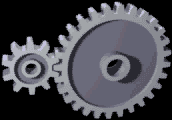
Gears
A gear is a rotating circular machine part having cut teeth or, in the case of a cogwheel or gearwheel, inserted teeth (called ''cogs''), which mesh with another (compatible) toothed part to transmit (convert) torque and speed. The basic principle behind the operation of gears is analogous to the basic principle of levers. A gear may also be known informally as a cog. Geared devices can change the speed, torque, and direction of a power source. Gears of different sizes produce a change in torque, creating a mechanical advantage, through their ''gear ratio'', and thus may be considered a simple machine. The rotational speeds, and the torques, of two meshing gears differ in proportion to their diameters. The teeth on the two meshing gears all have the same shape. Two or more meshing gears, working in a sequence, are called a gear train or a '' transmission''. The gears in a transmission are analogous to the wheels in a crossed, belt pulley system. An advantage of gears is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |