|
History Of The Western Steppe
This article summarizes the History of the western steppe, which is the western third of the Eurasian steppe, that is, the grasslands of Ukraine and southern Russia. It is intended as a summary and an index to the more-detailed linked articles. It is a companion to History of the central steppe and History of the eastern steppe. All dates are approximate since there are few exact starting and ending dates. This summary article does not list the uncertainties, which are many. For these, see the linked articles. Geography The area is approximately triangular. The line between forest and steppe began near the mouth of the Danube on the Black Sea and ran northeast toward Kazan and then turned south along the western side of the Ural Mountains. This was not a sharp line but rather a broad band of often deciduous forest-steppe. Its nature and location is hard to establish since most of it has now been cleared for agriculture. The southern boundary runs northeast and then east-south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuban River
The Kuban; Circassian: Псыжъ, ''Psyẑ'' or Псыжь, ''Psyź'' ; abq, Къвбина, ''Q̇vbina'' ; Karachay–Balkar: Къобан, ''Qoban''; Nogai: Кобан, ''Qoban'') is a river in Russia that flows through the Western Caucasus and drains into the Sea of Azov. The Kuban runs mostly through Krasnodar Krai for , but also in the Karachay–Cherkess Republic, Stavropol Krai and the Republic of Adygea. The Kuban flows north and west from its source near Mount Elbrus in the Caucasus Mountains, eventually reaching Temryuk Bay in the Sea of Azov. It is navigable up to Krasnodar. Major cities on the river are Karachayevsk, Cherkessk, Nevinnomyssk, Armavir, Novokubansk, Kropotkin, Ust-Labinsk, Krasnodar and Temryuk. Despite its name, Slavyansk-na-Kubani lies not on the Kuban River, but on its distributary the Protoka. Geography and hydrology The river originates on the slopes of Mount Elbrus and forms at the merger of its two tributaries, Ullukam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarian Plain
The Great Hungarian Plain (also known as Alföld or Great Alföld, hu, Alföld or ) is a plain occupying the majority of the modern territory of Hungary. It is the largest part of the wider Pannonian Plain. (However, the Great Hungarian plain was not part of the ancient Roman province Pannonia). Its territory significantly shrank due to its eastern and southern boundaries being rewritten by the new political borders created after World War I when the Treaty of Trianon was signed in 1920. Boundaries Its boundaries are the Carpathians in the north and east, the Transdanubian Mountains and the Dinaric Alps in the southwest, and approximately the Sava river in the south. Geography Plain in Hungary Its territory covers approximately of Hungary, approximately 56% of its total area of . The highest point of the plain is Hoportyó (); the lowest point is the Tisza River. The terrain ranges from flat to rolling plains. The most important Hungarian writers inspired by and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Colonies Of The Northern Euxine Sea (Black Sea)
Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all known varieties of Greek. **Mycenaean Greek, most ancient attested form of the language (16th to 11th centuries BC). **Ancient Greek, forms of the language used c. 1000–330 BC. **Koine Greek, common form of Greek spoken and written during Classical antiquity. **Medieval Greek or Byzantine Language, language used between the Middle Ages and the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople. **Modern Greek, varieties spoken in the modern era (from 1453 AD). *Greek alphabet, script used to write the Greek language. *Greek Orthodox Church, several Churches of the Eastern Orthodox Church. *Ancient Greece, the ancient civilization before the end of Antiquity. *Old Greek, the language as spoken from Late Antiquity to around 1500 AD. Other uses * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronovo Culture
The Andronovo culture (russian: Андроновская культура, translit=Andronovskaya kul'tura) is a collection of similar local Late Bronze Age cultures that flourished 2000–1450 BC,Grigoriev, Stanislav, (2021)"Andronovo Problem: Studies of Cultural Genesis in the Eurasian Bronze Age" in Open Archaeology 2021 (7), p.3: "...By Andronovo cultures we may understand only Fyodorovka and Alakul cultures..."Parpola, Asko, (2020)"Royal 'Chariot' Burials of Sanauli near Delhi and Archaeological Correlates of Prehistoric Indo-Iranian Languages" in Studia Orientalia Electronica, Vol. 8, No. 1, Oct 23, 2020, p.188: "...the Alakul’ culture (c.2000–1700 BCE) in the west and the Fëdorovo culture (c.1850–1450 BCE) in the east..." in western Siberia and the central Eurasian Steppe. Some researchers have preferred to term it an archaeological complex or archaeological horizon. The slightly older Sintashta culture (2050–1900 BC), formerly included within the Andro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Srubna Culture
The Srubnaya culture (russian: Срубная культура, Srubnaya kul'tura, ua, Зрубна культура, Zrubna kul'tura), also known as Timber-grave culture, was a Late Bronze Age 1850–1450 BC cultureParpola, Asko, (2012)"Formation of the Indo-European and Uralic (Finno-Ugric) language families in the light of archaeology: Revised and integrated ‘total’ correlations" in Mémoires de la Société Finno-Ougrienne, Helsinki, p. 140. in the eastern part of Pontic–Caspian steppe. It is a successor of the Yamna culture, Catacomb culture and Poltavka culture. It is co-ordinate and probably closely related to the Andronovo culture, its eastern neighbor. Whether the Srubnaya culture originated in the east, west, or was a local development, is disputed among archaeologists. The Srubnaya culture is generally associated with archaic Iranian speakers. The name comes from Russian сруб (''srub''), "timber framework", from the way graves were constructed Distribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamna Culture
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture of the region between the Southern Bug, Dniester, and Ural rivers (the Pontic steppe), dating to 3300–2600 BCE. It was discovered by Vasily Gorodtsov following his archaelogical excavations near Siversky Donets in 1901—1903. Its name derives from its characteristic burial tradition: (romanization: ) is a Russian adjective that means 'related to pits ()', as these people used to bury their dead in tumuli ( kurgans) containing simple pit chambers. The people of the Yamnaya culture were likely the result of a genetic admixture between the descendants of Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers (EHG)The Eastern European hunter-gatherers were themselves mostly descended from ancient North Eurasians, related to the pala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sredny Stog Culture
The Sredny Stog culture (, romanized: ''Serednʹostohivsʹka kulʹtura'') is a pre-Kurgan archaeological culture from the 5th millennium BC. It is named after the Russian term for the Dnieper river islet of today's Seredny Stih, Ukraine, where it was first located. Distribution The Sredny Stog culture was situated across the Dnieper river on both its shores, with sporadic settlements to the west and east. It seems to have had contact with the agricultural Cucuteni-Trypillian culture in the west, centered on modern-day Moldova, and was a contemporary of the Khvalynsk culture in the north-east, located in the middle Volga region. Sites One of the sites most associated with this culture is Deriivka (Ukrainian: Деріївка, Russian: Дериевка), located on the right bank of the Omelnik, a tributary of the Dnieper, and is the largest site within the Sredny Stog culture complex, being about in area. Characteristics The Sredny Stog people lived rather mobile lives. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tripolye Culture
Trypillia ( ua , Трипiлля) is a selo in Obukhiv Raion (district) of Kyiv Oblast in central Ukraine, with 2,800 inhabitants (as of 1 January 2005). It belongs to Ukrainka urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine. Trypillia lies about south from Kyiv on the Dnipro. Trypillia is the site of an ancient mega-settlement dating to 4300–4000 BCE belonging to the Cucuteni-Trypillian culture. Settlements of this culture were as large as 200 hectares. This proto-city is just one of 2440 Cucuteni-Trypillia settlements discovered so far in Moldova and Ukraine. 194 (8%) of these settlements had an area of more than 10 hectares between 5000–2700 BCE and more than 29 settlements had an area in the range 100–450 hectares. History It was near Trypillia that archaeologist Vikentiy Khvoyka discovered an extensive Neolithic site of the Cucuteni-Trypillian culture, one of the major Neolithic-Chalcolithic cultures of eastern Europe. Khvoika reported his findings in 1897 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mounted Archery
A horse archer is a cavalryman armed with a bow and able to shoot while riding from horseback. Archery has occasionally been used from the backs of other riding animals. In large open areas, it was a highly successful technique for hunting, for protecting the herds, and for war. It was a defining characteristic of the Eurasian nomads during antiquity and the medieval period, as well as the Iranian peoples, (Alans, Scythians, Sarmatians, Parthians, Sassanid Persians) and Indians in antiquity, and by the Hungarians, Mongols, Chinese, and the Turkic peoples during the Middle Ages. By the expansion of these peoples, the practice also spread to Eastern Europe (via the Sarmatians and the Huns), Mesopotamia, and East Asia. In East Asia, horse archery came to be particularly honored in the samurai tradition of Japan, where horse archery is called Yabusame. The term mounted archer occurs in medieval English sources to describe a soldier who rode to battle but who dismounted to shoot. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pastoral Nomadism
Nomadic pastoralism is a form of pastoralism in which livestock are herding, herded in order to seek for fresh pastures on which to Grazing, graze. True nomads follow an irregular pattern of movement, in contrast with transhumance, where seasonal pastures are fixed. However, this distinction is often not observed and the term 'nomad' used for both—and in historical cases the regularity of movements is often unknown in any case. The herded livestock include cattle, water buffalo, yaks, llamas, sheep, goats, reindeer, horses, donkeys or camels, or mixtures of species. Nomadic pastoralism is commonly practised in regions with little arable land, typically in the developing world, especially in the steppe lands north of the agricultural zone of Eurasia. Of the estimated 30–40 million nomadic pastoralists worldwide, most are found in nomadic pastoralism in Central Asia, central Asia and the Sahel region of North and West Africa, such as Fulani people, Fulani, Tuaregs, and Toubou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
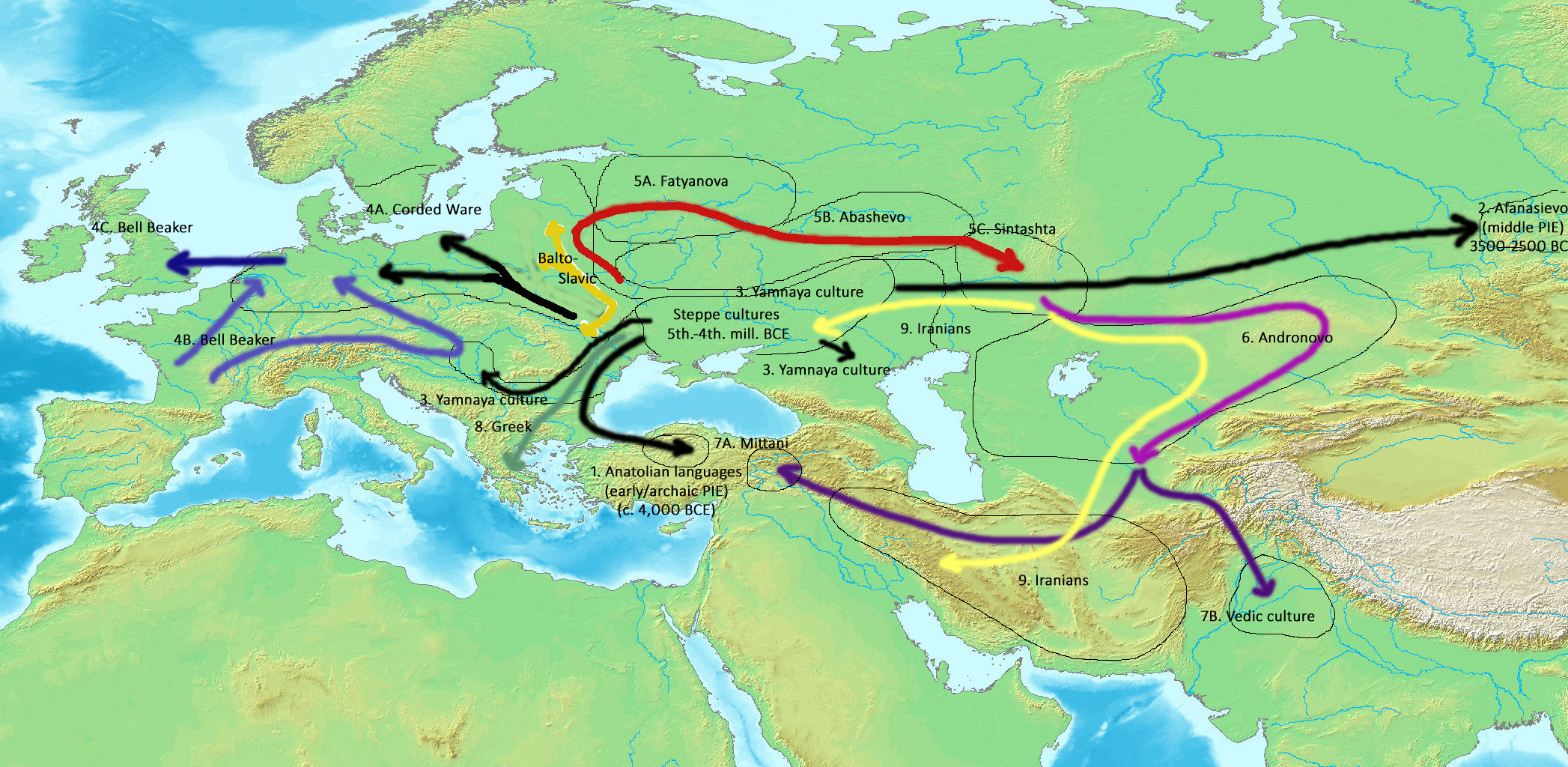
Kurgan Hypothesis
The Kurgan hypothesis (also known as the Kurgan theory, Kurgan model, or steppe theory) is the most widely accepted proposal to identify the Proto-Indo-European homeland from which the Indo-European languages spread out throughout Europe and parts of Asia. It postulates that the people of a Kurgan culture in the Pontic steppe north of the Black Sea were the most likely speakers of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). The term is derived from the Russian ''kurgan'' (), meaning tumulus or burial mound. The steppe theory was first formulated by Otto Schrader (1883) and V. Gordon Childe (1926), then systematized in the 1950s by Marija Gimbutas, who used the term to group various prehistoric cultures, including the Yamnaya (or Pit Grave) culture and its predecessors. In the 2000s, David Anthony instead used the core Yamnaya culture and its relationship with other cultures as a point of reference. Gimbutas defined the Kurgan culture as composed of four successive periods, wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |