|
History Of Robots
The history of robots has its origins in the ancient world. During the industrial revolution, humans developed the structural engineering capability to control electricity so that machines could be powered with small motors. In the early 20th century, the notion of a humanoid machine was developed. The first uses of modern robots were in factories as industrial robots. These industrial robots were fixed machines capable of manufacturing tasks which allowed production with less human work. Digitally programmed industrial robots with artificial intelligence have been built since the 2000s. Early legends Concepts of artificial servants and companions date at least as far back as the ancient legends of Cadmus, who is said to have sown dragon teeth that turned into soldiers and Pygmalion whose statue of Galatea came to life. Many ancient mythologies included artificial people, such as the talking mechanical handmaidens (Ancient Greek: (Kourai Khryseai); "Golden Maidens") built by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
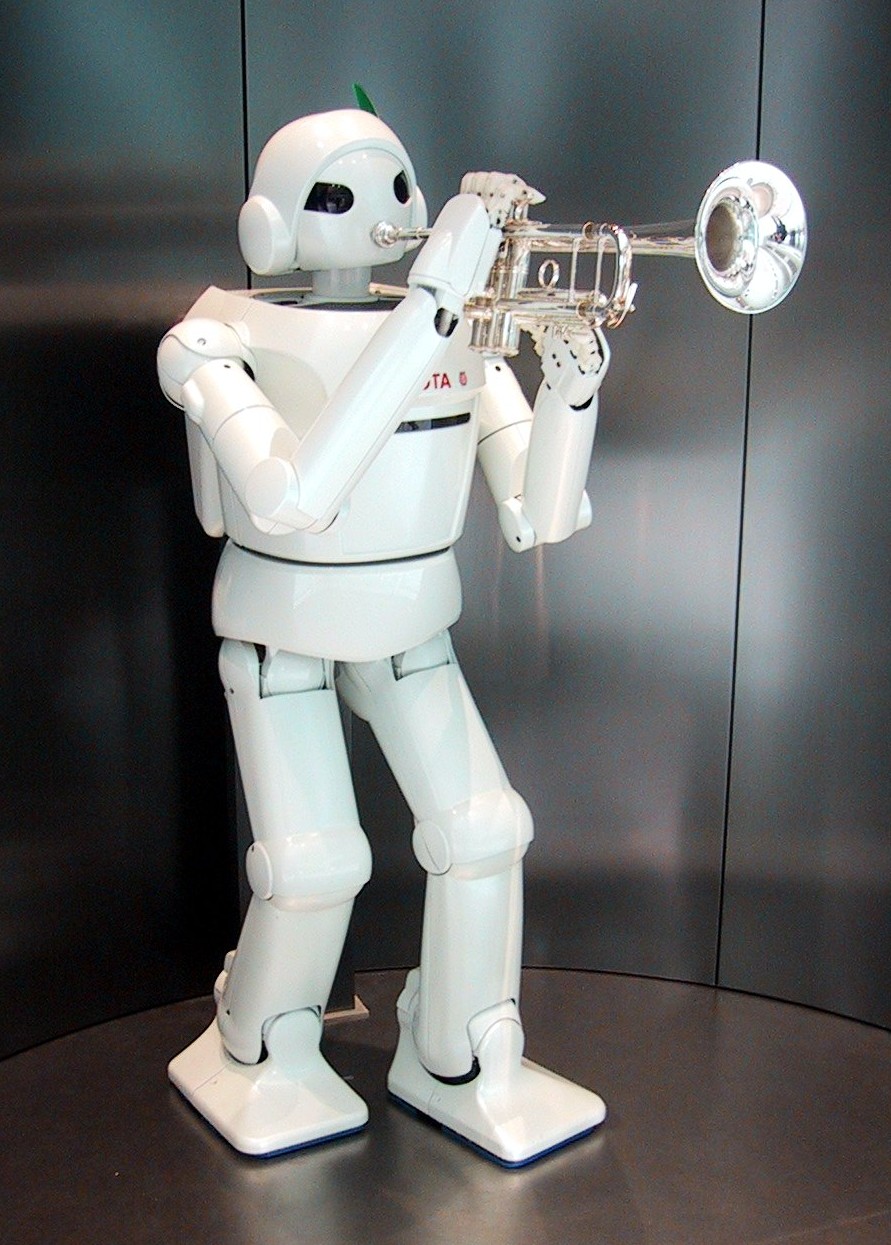
Toyota Robot At Toyota Kaikan
is a Japanese Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda and incorporated on . Toyota is one of the Automotive industry#By manufacturer, largest automobile manufacturers in the world, producing about 10 million vehicles per year. The company was originally founded as a spinoff of Toyota Industries, a machine maker started by Sakichi Toyoda, Kiichiro's father. Both companies are now part of the Toyota Group, one of the largest conglomerates in the world. While still a department of Toyota Industries, the company developed its first product, the Toyota Type A engine, Type A engine in 1934 and its first passenger car in 1936, the Toyota AA. After World War II, Toyota benefited from Japan's alliance with the United States to learn from American automakers and other companies, which would give rise to The Toyota Way (a management philosophy) and the Toyota Produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galatea (mythology)
Galatea (; grc-gre, Γαλάτεια; "she who is milk-white") is a name popularly applied to the statue carved of ivory by Pygmalion of Cyprus, which then came to life in Greek mythology. In modern English, the name usually alludes to that story. Galatea is also the name of Polyphemus's object of desire in Theocritus's ''Idylls VI'' and ''XI'' and is linked with Polyphemus again in the myth of Acis and Galatea in Ovid's ''Metamorphoses''. Galatea is mentioned in Book XVIII of The Iliad: "Bright Galatea quits her pearly bed". Etymology Though the name "Galatea" has become so firmly associated with Pygmalion's statue as to seem antique, its use in connection with Pygmalion originated with a post-classical writer. No extant ancient text mentions the statue's name, Reinhold notes that the first edition of Lemprière's '' Bibliotheca Classica'' (1788), does not have an entry for "Galatea", which was inserted in later editions. although Pausanias mentions a statue of Calm, Galene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jataka Tales
The Jātakas (meaning "Birth Story", "related to a birth") are a voluminous body of literature native to India which mainly concern the previous births of Gautama Buddha in both human and animal form. According to Peter Skilling, this genre is "one of the oldest classes of Buddhist literature."Skilling, Peter (2010). ''Buddhism and Buddhist Literature of South-East Asia,'' pp. 161-162. Some of these works are also considered great works of literature in their own right. In these stories, the future Buddha may appear as a king, an outcast, a deva, an animal—but, in whatever form, he exhibits some virtue that the tale thereby inculcates. Often, Jātaka tales include an extensive cast of characters who interact and get into various kinds of trouble - whereupon the Buddha character intervenes to resolve all the problems and bring about a happy ending. The Jātaka genre is based on the idea that the Buddha was able to recollect all his past lives and thus could use these memorie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Mu Of Zhou
King Mu of Zhou (), personal name Ji Man, was the fifth king of the Zhou dynasty of China. The dates of his reign are 976–922 BC or 956–918 BC. Life King Mu came to the throne after his father King Zhao’s death during his tour to the South. King Mu was perhaps the most pivotal king of the Zhou dynasty, reigning nearly 55 years, from ca. 976 BC to ca. 922 BC. Mu was more ambitious than wise, yet he was able to introduce reforms that changed the nature of the Zhou government, transforming it from a hereditary system to one that was based on merit and knowledge of administrative skills. During Mu’s reign, the Zhou Dynasty was at its peak, and Mu tried to stamp out invaders in the western part of China and ultimately expand Zhou’s influence to the east. In the height of his passion for conquests, he led an immense army against the Quanrong, who inhabited the western part of China. His travels allowed him to contact many tribes and swayed them to either join under the Zhou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daoist
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the ''Tao'' (, 'Thoroughfare'); the ''Tao'' is generally defined as the source of everything and the ultimate principle underlying reality. The ''Tao Te Ching'', a book containing teachings attributed to Laozi (), together with the later writings of Zhuangzi, are both widely considered the keystone works of Taoism. Taoism teaches about the various disciplines for achieving perfection through self-cultivation. This can be done through the use of Taoist techniques and by becoming one with the unplanned rhythms of the all, called "the way" or "Tao". Taoist ethics vary depending on the particular school, but in general tend to emphasize ''wu wei'' (action without intention), naturalness, simplicity, spontaneity and the Three Treasures: , compassion, , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liezi
The ''Liezi'' () is a Taoist text attributed to Lie Yukou, a c. 5th century BC Hundred Schools of Thought philosopher. Although there were references to Lie's ''Liezi'' from the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, a number of Chinese and Western scholars believe that the content of the current text was compiled around the 4th century CE by Zhang Zhan. Textual history The first two references to the ''Liezi'' book are from the Former Han Dynasty. The editor Liu Xiang notes he eliminated repetitions in ''Liezi'' and rearranged it into eight chapters (''pian'' ). The Book of Han bibliography section () says it has eight chapters () and concludes that since the '' Zhuangzi'' quotes Liezi, he must have lived before Zhuangzi. There is a three-century historical gap until the next evidence of the ''Liezi'': the Jin dynasty commentary by Zhang Zhan (fl. ca. 370 CE). Zhang's preface claims his ''Liezi'' copy was transmitted down from his grandfather. All received ''Liezi'' texts derive from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mozi
Mozi (; ; Latinized as Micius ; – ), original name Mo Di (), was a Chinese philosopher who founded the school of Mohism during the Hundred Schools of Thought period (the early portion of the Warring States period, –221 BCE). The ancient text ''Mozi'' contains material ascribed to him and his followers. Mozi taught that everyone is equal in the eyes of heaven. He believed that the decision of who is in power should be based on meritocracy, or those who are worthy of power should receive power. Mozi invoked heaven and called upon the Sage Kings to support his precedents. Born in what is now Tengzhou, Shandong Province, Mozi founded the school of Mohism, which argued strongly against both Confucianism and Daoism. Mozi's philosophy emphasized universal love, social order, the will of heaven, sharing, and honoring the worthy. During the Warring States period, Mohism was actively developed and practiced in many states, but fell out of favor when the legalist Qin dynasty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lu Ban
Lu Ban (–444BC). was a Chinese architect or master carpenter, structural engineer, and inventor, during the Zhou Dynasty. He is revered as the Chinese Deity (Patron) of builders and contractors. Life Lu Ban was born in the state of Lu; a few sources claim he was born further to the west, in Dunhuang, to a family of carpenters or artisans during the Spring and Autumn period of the Zhou dynasty. His original name was He was also referred to as or Pan. He was supposed to have been an indifferent pupil until his love of learning was kindled by the scholar Zi Xia. He later learned woodworking from Bao Laodong. The great demand for his work supposedly compelled him to invent or improve several carpenter's tools—the saw, the square, the planer, the drill, the shovel, and an ink marking tool—to complete his many projects more quickly. His wife was also credited with inventing the umbrella in order to permit him to work in inclement weather. Inventions According to tradition, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Asian
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former Soviet republics of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan, which are colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as the countries all have names ending with the Persian suffix "-stan", meaning "land of". The current geographical location of Central Asia was formerly part of the historic region of Turkistan, also known as Turan. In the pre-Islamic and early Islamic eras ( and earlier) Central Asia was inhabited predominantly by Iranian peoples, populated by Eastern Iranian-speaking Bactrians, Sogdians, Chorasmians and the semi-nomadic Scythians and Dahae. After expansion by Turkic peoples, Central Asia also became the homeland for the Kazakhs, Uzbeks, Tatars, Turkmen, Kyrgyz, and Uyghurs; Turkic languages largely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epic Of King Gesar
The Epic of King Gesar ( Tibetan, Bhutanese: གླིང་གེ་སར །), also spelled Geser (especially in Mongolian contexts) or Kesar (), is a work of epic literature of Tibet and greater Central Asia. The epic originally developed around 200 BCE or 300 BCE and about 600 CE. Following this, folk balladeers continued to pass on the story orally; this enriched the plot and embellished the language. The story reached its final form and height of popularity in the early 12th Century. The Epic relates the heroic deeds of the culture hero Gesar, the fearless lord of the legendary kingdom of Ling (). It is recorded variously in poetry and prose, through oral poetry performance, and is sung widely throughout Central Asia and North East of South Asia. Its classic version is to be found in central Tibet. Some 100 bards of this epic (, "tale") are still active today in the Gesar belt of China. Tibetan, Mongolian, Buryat, Balti, Ladakhi and Monguor singers maintain th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddha Shakyamuni
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lumbini, in what is now Nepal, to royal parents of the Shakya clan, but renounced his home life to live as a wandering ascetic ( sa, śramaṇa). After leading a life of begging, asceticism, and meditation, he attained enlightenment at Bodh Gaya in what is now India. The Buddha thereafter wandered through the lower Indo-Gangetic Plain, teaching and building a monastic order. He taught a Middle Way between sensual indulgence and severe asceticism, leading to Nirvana, that is, freedom from ignorance, craving, rebirth, and suffering. His teachings are summarized in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind that includes meditation and instruction in Buddhist ethics such as right effort, mindfulness, and ''jhana''. He died in Kushina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daoxuan
Daoxuan (; 596–667) was an eminent Tang dynasty Chinese Buddhist monk. He is perhaps best known as the patriarch of the Four-part Vinaya school (). Daoxuan wrote both the ''Continued Biographies of Eminent Monks'' (Xù gāosēng zhuàn 續高僧傳 ) and the ''Standard Design for Buddhist Temple Construction''. Legends retold in his biographies also associate him to a relic of the Buddha which came to be called Daoxuan's tooth (''Daoxuan foya'' 道宣佛牙), one of the four tooth relics enshrined in the capital of Chang'an during the Tang dynasty. He is said to have received the relic from Nezha (; Sanskrit: Naṭa), a divinity associated with Indra. Daoxuan wrote five commentaries on the Four-part Vinaya known as the Five Great Works of Mount Zhongnan. He was also part of the translation team that assisted Xuanzang in translating sutras from Sanskrit into Chinese. Daoxuan was an influential cataloguer. His catalogue of Buddhist scriptures, the ''Catalogue of the Inner Cano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

-black_bg.jpg)
.jpg)



.png)

.jpg)