|
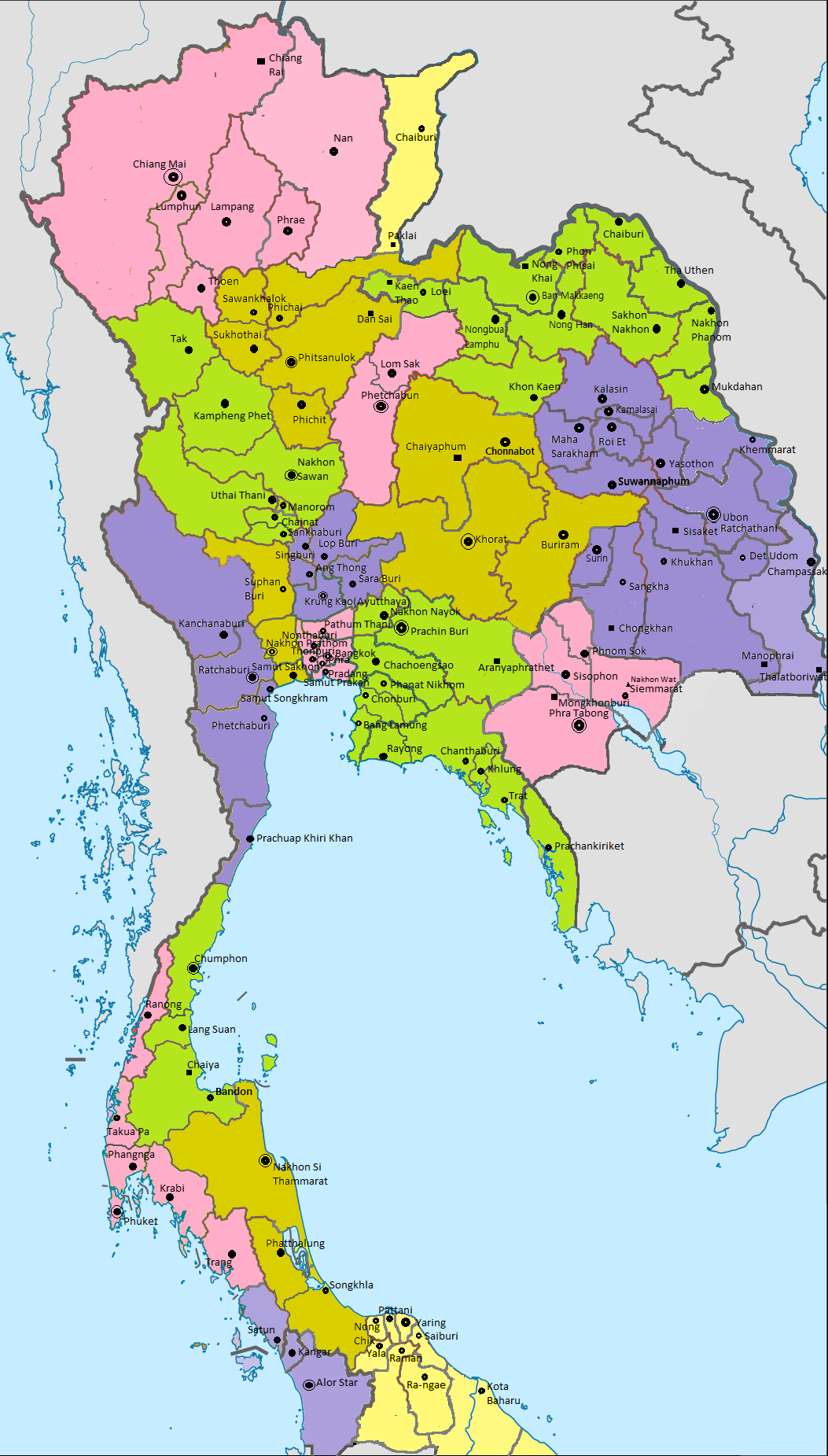
History Of Thailand
The Tai ethnic group migrated into mainland Southeast Asia over a period of centuries. The word ''Siam'' ( th, สยาม ) may have originated from Pali (''suvaṇṇabhūmi'', "land of gold") or Sanskrit श्याम (''śyāma'', "dark") or Mon ရာမည (''rhmañña'', "stranger"), probably the same root as Shan and Ahom. ''Xianluo'' () was the Chinese name for Ayutthaya Kingdom, merged from Suphannaphum city state centered in modern-day Suphan Buri and Lavo city state centered in modern-day Lop Buri. To the Thai, the name has mostly been ''Mueang Thai''. The country's designation as Siam by Westerners likely came from the Portuguese. Portuguese chronicles noted that the Borommatrailokkanat, king of the Ayutthaya Kingdom, sent an expedition to the Malacca Sultanate at the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula in 1455. Following their conquest of Malacca in 1511, the Portuguese sent a diplomatic mission to Ayutthaya. A century later, on 15 August 1612, ''The Glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tai People
Tai peoples are the populations who speak (or formerly spoke) the Tai languages. There are a total of about 93 million people of Tai ancestry worldwide, with the largest ethnic groups being Dai, Thais, Isan, Tai Yai (Shan), Lao, Tai Ahom, and Northern Thai peoples. The Tai are scattered through much of South China and Mainland Southeast Asia, with some (''e.g.'' Tai Ahom, Tai Khamti, Tai Phake, Tai Aiton) inhabiting parts of Northeast India. Tai peoples are both culturally and genetically very similar and therefore primarily identified through their language. Names Speakers of the many languages in the Tai branch of the Tai–Kadai language family are spread over many countries in Southern China, Indochina and Northeast India. Unsurprisingly, there are many terms used to describe the distinct Tai peoples of these regions. According to Michel Ferlus, the ethnonyms Tai/Thai (or Tay/Thay) would have evolved from the etymon *k(ə)ri: 'human being' through the following chain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia), and later with East Asia. The company seized control of large parts of the Indian subcontinent, colonised parts of Southeast Asia and Hong Kong. At its peak, the company was the largest corporation in the world. The EIC had its own armed forces in the form of the company's three Presidency armies, totalling about 260,000 soldiers, twice the size of the British army at the time. The operations of the company had a profound effect on the global balance of trade, almost single-handedly reversing the trend of eastward drain of Western bullion, seen since Roman times. Originally chartered as the "Governor and Company of Merchants of London Trading into the East-Indies", the company rose to account for half of the world's trade duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it the world's sixteenth-most populous country. Vietnam borders China to the north, and Laos and Cambodia to the west. It shares maritime borders with Thailand through the Gulf of Thailand, and the Philippines, Indonesia, and Malaysia through the South China Sea. Its capital is Hanoi and its largest city is Ho Chi Minh City (commonly known as Saigon). Vietnam was inhabited by the Paleolithic age, with states established in the first millennium BC on the Red River Delta in modern-day northern Vietnam. The Han dynasty annexed Northern and Central Vietnam under Chinese rule from 111 BC, until the first dynasty emerged in 939. Successive monarchical dynasties absorbed Chinese influences through Confucianism and Buddhism, and expanded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khmers
The Khmer people ( km, ជនជាតិខ្មែរ, ) are a Southeast Asian ethnic group native to Cambodia. They comprise over 90% of Cambodia's population of 17 million.Cambodia CIA World FactBook. They speak the , which is part of the larger Austroasiatic-language family found in parts of (including , |
Lan Na
The Lan Na Kingdom ( nod, , , "Kingdom of a Million Rice Fields"; th, อาณาจักรล้านนา, , ), also known as Lannathai, and most commonly called Lanna or Lanna Kingdom, was an Indianized state centered in present-day Northern Thailand from the 13th to 18th centuries. The cultural development of the Northern Thai people had begun long before as successive kingdoms preceded Lan Na. As a continuation of the kingdom of Ngoenyang, Lan Na emerged strong enough in the 15th century to rival the Ayutthaya Kingdom, with whom wars were fought. However, the Lan Na Kingdom was weakened and became a tributary state of the Taungoo Dynasty in 1558. Lan Na was ruled by successive vassal kings, though some enjoyed autonomy. The Burmese rule gradually withdrew but then resumed as the new Konbaung Dynasty expanded its influence. In 1775, Lan Na chiefs left the Burmese control to join Siam, leading to the Burmese–Siamese War (1775–76). Following the retreat of the Bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Chiang Mai
Kingdom of Rattanatingsa or Kingdom of Chiang Mai ( th, นครเชียงใหม่; full name: รัตนติงสาอภินวปุรีสรีคุรุรัฎฐพระนครเชียงใหม่; ) () was the vassal state of the Siamese Rattanakosin Kingdom in the 18th and 19th century before being annexed according to the centralization policies of Chulalongkorn in 1899. The kingdom was a successor of the medieval Lanna kingdom, which had been under Burmese rule for two centuries until it was captured by Siamese forces under Taksin of Thonburi in 1774. It was ruled by the Thipchak Dynasty and came under Thonburi tributary. Liberation from Burmese Rule Prince Kawila of the Tipchak dynasty, son of Saopha Chaikaew of Nakhon Lampang, and Phraya Chabaan, a Lanna noble, plotted the liberation of Lanna cities from Burmese authorities and decided to request support from King Taksin of Thonburi in 1774. Taksin sent Phraya Chakri (later Phuttha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sukhothai Kingdom
The Sukhothai Kingdom ( th, สุโขทัย, , IAST: , ) was a post-classical Thai kingdom (mandala) in Mainland Southeast Asia surrounding the ancient capital city of Sukhothai in present-day north-central Thailand. The kingdom was founded by Si Inthrathit in 1238 and existed as an independent polity until 1438, when it fell under the influence of the neighboring Ayutthaya after the death of Borommapan (Maha Thammaracha IV). Sukhothai was originally a trade center in Lavo—itself under the suzerainty of the Khmer Empire—when Central Thai people led by Pho Khun Bang Klang Hao, a local leader, revolted and gained their independence. Bang Klang Hao took the regnal name of Si Inthrathit and became the first monarch of the Phra Ruang dynasty. The kingdom was centralized and expanded to its greatest extent during the reign of Ram Khamhaeng the Great (1279–1298), who some historians considered to have introduced Theravada Buddhism and the initial Thai script to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngoenyang
The Kingdom of Hiran or Kingdom of Ngoenyang ( th, อาณาจักรหิรัญเงินยาง ) was an early mueang or kingdom of the Northern Thai people from the 7th through 13th centuries AD and was originally centered on Hiran, formerly Vieng Preuksa, in modern-day Thailand near today's Mae Sai District in Chiang Rai, and later on Ngoenyang or Chiang Saen. Ngoenyang was the successor to the mueang of Singhanavati. King Mangrai, the 17th king of Ngoenyang, went on to found Lanna. In contrast to most contemporary Tai states, Ngoenyang was mentioned in local chronicles, which provide some information about its history. In 545 AD, an earthquake destroyed the city of Naknakorn and thus the mueang of Singhanavati. Survivors gathered together and an elective monarchy was established there. The mueang was named Vieng Prueksa, as ''prueksa'' means "to counsel". After 93 years of elective monarchy, Phraya Kalavarnadishraj of the Lavo Kingdom forced the Vieng Prue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thai People
Thai people ( th, ชาวไทย; ''endonym''), Central Thai people ( th, คนภาคกลาง, sou, คนใต้, ตามโพร; ''exonym and also domestically'') or Siamese ( th, ชาวสยาม; ''historical exonym and sometimes domestically''), T(h)ai Noi people ( th, ไทยน้อย; ''historical endonym and sometimes domestically''), in a narrow sense, are a Tai ethnic group dominant in Central and Southern Thailand (Siam proper). Part of the larger Tai ethno-linguistic group native to Southeast Asia as well as Southern China and Northeast India, Thais speak the Sukhothai languages ( Central Thai and Southern Thai language), which is classified as part of the Kra–Dai family of languages. The majority of Thais are followers of Theravada Buddhism. As a result of government policy during the 1930s and 1940s resulting in successful forced assimilation of many the various ethno-linguistic groups in the country into the dominant Thai language and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent islands such as the Simeulue, Nias, Mentawai, Enggano, Riau Islands, Bangka Belitung and Krakatoa archipelago. Sumatra is an elongated landmass spanning a diagonal northwest–southeast axis. The Indian Ocean borders the northwest, west, and southwest coasts of Sumatra, with the island chain of Simeulue, Nias, Mentawai, and Enggano off the western coast. In the northeast, the narrow Strait of Malacca separates the island from the Malay Peninsula, which is an extension of the Eurasian continent. In the southeast, the narrow Sunda Strait, containing the Krakatoa Archipelago, separates Sumatra from Java. The northern tip of Sumatra is near the Andaman Islands, while off the southeastern coast lie the islands of Bangka and Belitung, Karim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mon Kingdoms
Mon kingdoms were polities established by the Mon-speaking people in parts of present-day Myanmar and Thailand. The polities ranged from Dvaravati and Haripuñjaya in present-day northern Thailand to Thaton, Hanthawaddy (1287–1539), and the Restored Hanthawaddy (1740–1757) in southern Myanmar. Early states The first recorded kingdom attributed to the Mon people is Dvaravati,Coedès 1968: 63, 76–77 which prospered until around 1000 CE when their capital was sacked by the Khmer Empire and a significant portion of the inhabitants fled west to present-day Lower Burma and eventually founded new polities. Another Mon-speaking state Haripuñjaya also existed in northern Thailand down to the late 13th century.Coedès 1968: 208 Thaton (9th century?–1057?) According to the colonial period scholarship, the Mon established small polities (or large city-states) in Lower Burma in the 9th century. Both the city of Thaton and Pegu (Bago) are believed to have been established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |