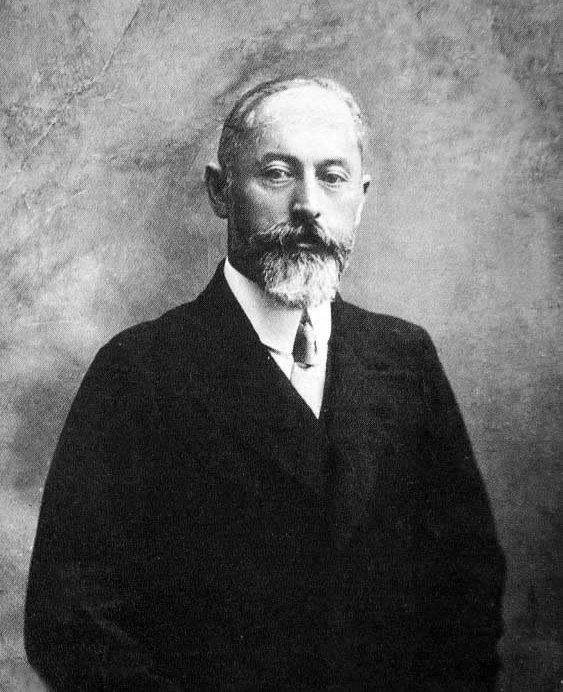|
History Of Russian Journalism
The History of Russian journalism covers writing for newspapers, magazines, and the electronic media since the 18th century. The main themes are low levels of literacy, censorship and government control, and the emphasis on politics and political propaganda in the media. 19th century In the autocratic Russian Empire, freedom of the press was not allowed, and political journalism was strongly discouraged, although discussions of economic and social issues were allowed, particularly in the provinces, as the central government otherwise lacked sufficient sources of information. Until the 1860s, adventuresome Russians obtained their political news surreptitiously from foreign newspapers smuggled into the country. Writers such as Alexander Radishchev (1749–1802) who wanted to portray Russian conditions were sharply censored or punished. Official press releases were issued through several ministries, such as the war department's ''Russky Invalid'' 1813–1917. The first privately owne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Radishchev
Alexander Nikolayevich Radishchev (russian: Алекса́ндр Никола́евич Ради́щев; – ) was a Russian author and social critic who was arrested and exiled under Catherine the Great. He brought the tradition of radicalism in Russian literature to prominence with his 1790 novel ''Journey from St. Petersburg to Moscow''. His depiction of socio-economic conditions in Russia resulted in his exile to Siberia until 1797. He was the grandfather of painter Alexey Bogolyubov. Biography Radishchev was born on an estate just outside Moscow, into a minor noble family of Tatar descent, tracing its roots back to defeated princes who entered into the service of Ivan the Terrible after the conquest of Kazan in 1552, the Tsar offering them, in exchange of baptism, to work for him and being allotted lands of some twenty-two thousand acres, a number their descendants will keep upgrading by serving the Tsars over the generations. His father, Nicholas Afanasevich Radische ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon
Pierre-Joseph Proudhon (, , ; 15 January 1809, Besançon – 19 January 1865, Paris) was a French socialist,Landauer, Carl; Landauer, Hilde Stein; Valkenier, Elizabeth Kridl (1979) 959 "The Three Anticapitalistic Movements". ''European Socialism: A History of Ideas and Movements from the Industrial Revolution to Hitler's Seizure of Power''. University of California Press. pp. 59, 63. "In France, post-Utopian socialism begins with Peter Joseph Proudhon. .. roudhonwas the most profound thinker among pre-Marxian socialists."Eatwell, Roger; Wright, Anthony (1999). ''Contemporary Political Ideologies'' (2nd ed.). London: Continuum. p. 82. .Newman, Michael (2005). ''Socialism: A Very Short Introduction''. Oxford University Press. p. 15. .Docherty, James C.; Lamb, Peter, eds. (2006). ''Historical Dictionary of Socialism''. Historical Dictionaries of Religions, Philosophies, and Movements. 73 (2nd ed.). Lanham, Maryland: The Scarecrow Press. p. 284. . See also Lamb, Peter (2015). ''H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Duranty
Walter Duranty (25 May 1884 – 3 October 1957) was an Anglo-American journalist who served as Moscow bureau chief of ''The New York Times'' for fourteen years (1922–1936) following the Bolshevik victory in the Russian Civil War (1918–1921). In 1932, Duranty received a Pulitzer Prize for a series of reports about the Soviet Union, eleven of which were published in June 1931. He was later criticized for his subsequent denial of the widespread famine (1930–1933) in the USSR, most particularly the Holodomor. Beginning in 1990, there were calls for the Pulitzer board to revoke Duranty's prize. The Pulitzer Board declined to revoke the award and in 2003 said the articles which it examined in making the award did not contain "clear and convincing evidence of deliberate deception". Early life and career Duranty was born in a middle-class Merseyside family to Emmeline (née Hutchins) and William Steel Duranty. His grandparents had moved to Birkenhead on the Wirral from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Bukharin
Nikolai Ivanovich Bukharin (russian: Никола́й Ива́нович Буха́рин) ( – 15 March 1938) was a Bolshevik revolutionary, Soviet politician, Marxist philosopher and economist and prolific author on revolutionary theory. As a young man, he spent six years in exile working closely with fellow exiles Vladimir Lenin and Leon Trotsky. After the revolution of February 1917, he returned to Moscow, where his Bolshevik credentials earned him a high rank in the party, and after the October Revolution became editor of their newspaper ''Pravda.'' Within the Bolshevik Party, Bukharin was initially a left communist, but gradually moved to the right from 1921. His strong support for and defence of the New Economic Policy (NEP) eventually saw him lead the Right Opposition. By late 1924, this stance had positioned Bukharin favourably as Joseph Stalin's chief ally, with Bukharin soon elaborating Stalin's new theory and policy of Socialism in One Country. Together, Bukh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trud (Russian Newspaper)
''Trud'' (russian: Труд, en, Labor) is a Russian newspaper. ''Truds first issue was on February 19, 1921, in Moscow, in what was then the Soviet Union. Under the Soviet state, the paper published the work of famous writers and poets, including Vladimir Mayakovsky, Nikolai Rubtsov, Yuri Nagibin, and Yevgeny Yevtushenko. Prior to the dissolution of the Soviet Union, ''Trud'' was the press organ of the All-Union Central Council of Trade Unions. It emphasized labor and economic analyses and included official decrees and orders. In 1990 the paper's circulation reached 21.5 million, the world's largest according to the ''Guinness Book of Records''. In the years following the end of the Soviet Union, about 21 million of these readers were lost and the paper fell into decline. In 2007, the media asset management group PromSvyazCapital created the holding company Media3. Media3's holdings included ''Trud'', other newspapers including '' Arguments and Facts'', and other assets. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pravda
''Pravda'' ( rus, Правда, p=ˈpravdə, a=Ru-правда.ogg, "Truth") is a Russian broadsheet newspaper, and was the official newspaper of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, when it was one of the most influential papers in the country with a newspaper circulation, circulation of 11 million. The newspaper began publication on 5 May 1912 in the Russian Empire, but was already extant abroad in January 1911. It emerged as a leading newspaper of the Soviet Union after the October Revolution. The newspaper was an organ of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, Central Committee of the CPSU between 1912 and 1991. After the dissolution of the Soviet Union ''Pravda'' was sold off by President of Russia, Russian President Boris Yeltsin to a Greek business family in 1996, and the paper came under the control of their private company Pravda International. In 1996, there was an internal dispute between the owners of Pravda International and some of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Izvestia
''Izvestia'' ( rus, Известия, p=ɪzˈvʲesʲtʲɪjə, "The News") is a daily broadsheet newspaper in Russia. Founded in 1917, it was a newspaper of record in the Soviet Union until the Soviet Union's dissolution in 1991, and describes itself now as a "national newspaper" of Russia. The word ''izvestiya'' in Russian means "bring news" or "tidings", "herald" (an official messenger bringing news), derived from the verb ''izveshchat'' ("to inform", "to notify"). Origin The newspaper began as the ''News of the Petrograd Soviet of Workers Deputies'' on in Petrograd. Initially, the paper expressed Menshevik and Socialist-Revolutionary Party views. In August 1917, it took the title ''News of the Central Executive Committee of the Petrograd Soviet of Workers' and Soldiers' Deputies''. By October 1917 it became ''News of the Central Executive Committee of the Soviets of Working and Military Deputies'', and was eventually re-titled ''News of the Soviets of People's Deputies'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ha-Melitz
''Ha-Melitz'' or ''HaMelitz'' (Hebrew: ) was the first Hebrew newspaper in the Russian Empire. It was founded by Alexander Zederbaum in Odessa in 1860. History ''Ha-Melitz'' first appeared as a weekly, and it began to appear daily in 1886. From 1871, it was published in Saint Petersburg. Publication was suspended several times for lack of support or by order of the authorities. In 1893, Leon Rabinowitz succeeded Zederbaum as the editor. ''Ha-Melitz'' was a representative of the progressive or ''haskalah'' movement, and even so severe a critic as Abraham Kovner admitted that it had been "more useful to the Jews than have the other Hebrew newspapers" (''Ḥeḳer Dabar,'' p. 52 ff., Warsaw, 1866). While it was not so literary or scientific as some of its contemporaries, ''Ha-Melitz'' usually had more news and debates of interest, and was consequently more popular. J. A. Goldenblum was for many years associated with Zederbaum in its publication. Abraham Shalom Friedberg and Ju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mensheviks
The Mensheviks (russian: меньшевики́, from меньшинство 'minority') were one of the three dominant factions in the Russian socialist movement, the others being the Bolsheviks and Socialist Revolutionaries. The factions emerged in 1903 following a dispute within the Russian Social Democratic Labour Party (RSDLP) between Julius Martov and Vladimir Lenin. The dispute originated at the 2nd Congress of the RSDLP, ostensibly over minor issues of party organization. Martov's supporters, who were in the minority in a crucial vote on the question of party membership, came to be called ''Mensheviks'', derived from the Russian ('minority'), while Lenin's adherents were known as ''Bolsheviks'', from ('majority'). Despite the naming, neither side held a consistent majority over the course of the entire 2nd Congress, and indeed the numerical advantage fluctuated between both sides throughout the rest of the RSDLP's existence until the Russian Revolution. The split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Martov
Julius Martov or L. Martov (Ма́ртов; born Yuliy Osipovich Tsederbaum; 24 November 1873 – 4 April 1923) was a politician and revolutionary who became the leader of the Mensheviks in early 20th-century Russia. He was arguably the closest friend Vladimir Lenin ever had, and was a friend and mentor of Leon Trotsky, who described him as the "Hamlet of Democratic Socialism".Figes, p. 468Trotsky, Leon ''The History of the Russian Revolution'' p. 1156 Early life Martov was born to a middle-class, educated and politically aware Jewish family in Constantinople, Ottoman Empire (modern day Istanbul). His sister was the fellow Menshevik leader Lydia Dan. Brought up in Odessa, he suffered constant humiliation as a schoolboy because of being Jewish. In his teens, he admired the Narodniks, but the famine crisis made him a Marxist: "It suddenly became clear to me how superficial and groundless the whole of my revolutionism had been until then, and how my subjective political romantic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moskovskiye Vedomosti
''Moskovskiye Vedomosti'' ( rus, Моско́вские ве́домости, p=mɐˈskofskʲɪje ˈvʲedəməsʲtʲɪ; ''Moscow News'') was Russia's largest newspaper by circulation before it was overtaken by Saint Petersburg dailies in the mid-19th century. Moscow University (founded in 1755) established the newspaper in 1756. With a circulation of 600, the newspaper was printed by the university press, featuring mainly official announcements and articles by university professors. In 1779, the press was leased to the first Russian journalist, Nikolay Novikov, who reformed the weekly thoroughly, introduced supplements on literature and art, and raised its circulation to 4,000. Novikov edited the ''Moscow News'' until 1789, but his immediate successors continued along the same lines. The university published the newspaper once a week until 1812, twice a week until 1842, thrice a week until 1859 and daily from 1859 until 1909. Mikhail Katkov, the paper's editor in 1850-1855 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
January Uprising
The January Uprising ( pl, powstanie styczniowe; lt, 1863 metų sukilimas; ua, Січневе повстання; russian: Польское восстание; ) was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at the restoration of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It began on 22 January 1863 and continued until the last insurgents were captured by the Russian forces in 1864. It was the longest-lasting insurgency in partitioned Poland. The conflict engaged all levels of society and arguably had profound repercussions on contemporary international relations and ultimately provoked a social and ideological paradigm shift in national events that went on to have a decisive influence on the subsequent development of Polish society. A confluence of factors rendered the uprising inevitable in early 1863. The Polish nobility and urban bourgeois circles longed for the semi-autonomous status they had enjoyed in Congress Poland before the previous insur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |