|
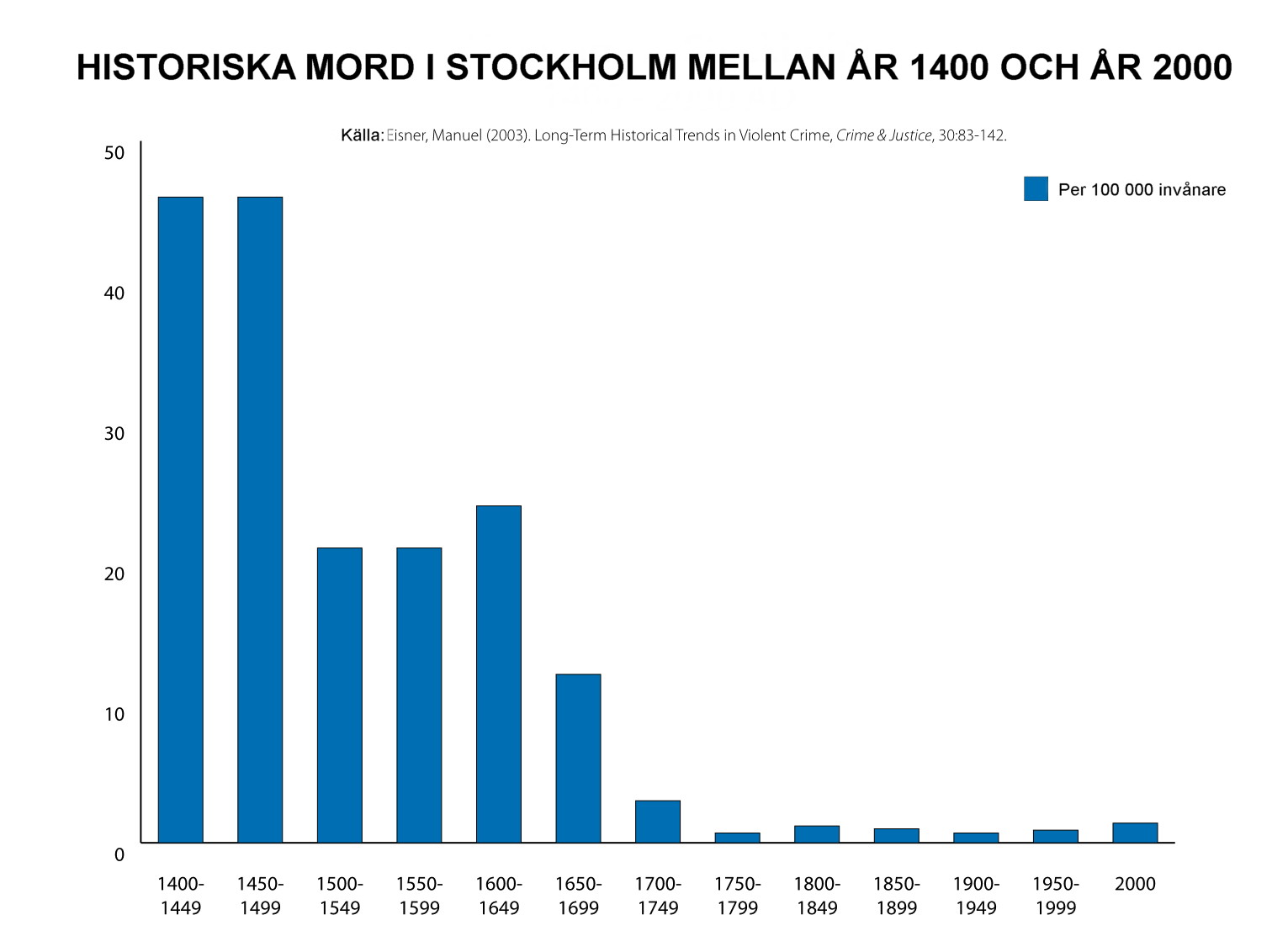
Historical Murders And Executions In Stockholm
Murders and executions in Stockholm, Sweden have been documented since the 1280s, when King Magnus Ladulås ordered the execution of three magnates of the Privy Council, who had been accused of several "traitorous acts against the throne". The city's murders between the middle of the 15th century and the middle of the 17th century have been documented fairly well in the logs of Stockholm City Court. Violence with a deadly outcome was most common during the Middle Ages, a trend which had more than halved by the beginning of the 1700s. The most common cases of manslaughter and murder usually involved fights between men where alcohol was involved. During the reign of Gustav III, the use of capital punishment decreased and was abolished for certain crimes. The last hanging took place in 1818 at Hammarbyhöjden, and the last public execution occurred in 1862. The last execution in Sweden and Stockholm took place on 23 November 1910, when robber and murderer Alfred Ander was executed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West German Embassy Siege In Stockholm
The West German Embassy siege in Stockholm, Sweden, was a hostage standoff initiated by the Red Army Faction (RAF) on 24 April 1975. Collectively, the attackers referred to themselves as Kommando Holger Meins, after Holger Meins, an RAF member who had died of starvation during a (collective) hunger strike in Wittlich Prison on 9 November 1974. The RAF group carried out the attack with the goal of forcing the release of RAF members and others from prison in West Germany. During the siege they stated: "The Holger Meins Commando is holding members of the embassy staff in order to free prisoners in West Germany. If the police move in, we shall blow the building up with 15 kilos of TNT." The siege The group consisted of six members: Karl-Heinz Dellwo, Siegfried Hausner, Hanna-Elise Krabbe, Bernhard Rössner, Lutz Taufer and Ulrich Wessel. They entered the embassy, took thirteen embassy officials hostage (or twelve officials, according to some sources), including ambassador Hein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stadslagen
The Stadslagen (City Law), was a Swedish law passed by king Magnus IV of Sweden in circa 1350. It governed the life in the cities of Sweden until 1734. The ''Stadslagen'' was passed by in about the same time as the ''Magnus Erikssons landslag'' (Country Law of Magnus Eriksson), and as the former was to apply in the country side, the city law was to apply in the cities. The law was strongly influenced by the contemporary German city laws, as the Swedish cities at the time had many German settlers. In 1442, the country law was succeeded by the ''Kristofers landslag'', but the city law was merely incorporated in this and left unaltered and uncontested. It was printed in 1618. It was in effect in Sweden-Finland until the Civil Code of 1734 The Civil Code of 1734 (Swedish: ''1734 års lag''), was passed by the Swedish Riksdag of the Estates in 1734, and put in effect after it had been ratified by Frederick I of Sweden 23 January 1736. It became the foundation of the later civil cod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blasieholmen
Blasieholmen is a peninsula in central Stockholm, Sweden. It is located east of Kungsträdgården. Originally a small island, named Käpplingen, it became a peninsula, connected to Norrmalm, during the 17th century. Among the buildings at Blasieholmen are the Nationalmuseum, hotels and office buildings. The Skeppsholmsbron bridge connects Blasieholmen to the island of Skeppsholmen Skeppsholmen is one of the islands of Stockholm. It is connected with Blasieholmen and Kastellholmen by bridges. It is accessible by foot from Kungsträdgården, past the Grand Hôtel and Nationalmuseum, by bus number 65, or by boat from Slus .... The Blasieholmen Church was demolished in 1964. References External links * {{coord, 59.3297, N, 18.0769, E, source:wikidata, display=title Geography of Stockholm Peninsulas of Sweden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riddarholmen
Riddarholmen (, "The Knights' Islet") is a small islet in central Stockholm, Sweden. The island forms part of Gamla Stan, the old town, and houses a number of private palaces dating back to the 17th century. The main landmark is the church Riddarholmskyrkan, used as Sweden's royal burial church from the 17th century to 1950, and where a number of earlier Swedish monarchs also lie buried. The western end of the island gives a magnificent panoramic and photogenic view of the bay Riddarfjärden, often used by TV journalists with Stockholm City Hall in the background. A statue of Birger Jarl, traditionally considered the founder of Stockholm, stands on a pillar in front of the Bonde Palace, north of Riddarholm Church. Other notable buildings include the Old Parliament Building in the south-eastern corner, the Old National Archive on the eastern shore, and the Norstedt Building, the old printing house of the publisher Norstedts, the tower roof of which is a well-known silhouette on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tre Kronor (castle)
Tre Kronor (; "Three Crowns") was a castle located in Stockholm, Sweden, on the site where Stockholm Palace is today. It is believed to have been a citadel that Birger Jarl built into a royal castle in the middle of the 13th century. The name "Tre Kronor" is believed to have been given to the castle during the reign of King Magnus IV in the middle of the 14th century. Most of Sweden's national library and royal archives were destroyed when the castle burned down in 1697, making the country's early history unusually difficult to document. History When King Gustav Vasa broke Sweden free from the Kalmar Union (a series of personal unions between Denmark, Sweden and Norway since 1397) and made Sweden independent again, Tre Kronor Castle became his most important royal seat. Gustav Vasa expanded the castle's defensive measures, while his son John III of Sweden later rebuilt and improved the castle aesthetically, turning it into a renaissance style castle and adding a castle churc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kåkbrinken
Kåkbrinken is a street in Gamla stan, the old town of Stockholm, Sweden. Stretching from the western waterfront Munkbroleden, to the central square Stortorget, it forms a parallel street to Yxsmedsgränd, Solgränd, and Bedoirsgränd, while being crossed by Munkbrogatan, Lilla Nygatan, Stora Nygatan, Västerlånggatan, and Prästgatan. Origin of the name First mentioned in 1477, and in more detail in 1496, the street is initially called ''Kakbringkin.'' This derives from the old Swedish word ''kak'' which is the equivalent of the modern Swedish ''kåk'', meaning "ramshackle house" or "prison", but at the time it referred to a pillory placed on Stortorget. The pillory is first mentioned in connection with the so-called " Käpplinge murders" (''Käpplingemorden''). This was an incident in 1389 when a group of German burghers imprisoned about 70 prominent citizens in a hovel on Blasieholmen (at the time called Käpplinge) and burned them alive. The Germans are said to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stortorget
Stortorget (, "the Grand Square") is a public square in Gamla Stan, the old town in central Stockholm, Sweden. It is the oldest square in Stockholm, the historical centre on which the medieval urban conglomeration gradually came into being. Today, the square is frequented by tens of thousands of tourists annually, and is occasionally the scene for demonstrations and performances. It is traditionally renowned for its annual Christmas market offering traditional handicrafts and food. Notable buildings and structures Located in the centre of the plateau of Stadsholmen, the square never was the stylish show-piece occupying the centre of many other European cities during the Middle Ages; it was created gradually, buildings and blocks around the square, still sloping west, occasionally added haphazardly. The exception being the Stock Exchange Building taking up the northern side of the square and concealing the Cathedral and the Royal Palace. The Stock Exchange Building and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hättebröder
Hättebröder ("Cap's brothers"), was a group of a party of German-speaking burghers during the reign of the German Albert, King of Sweden, who came to be known for their oppression and persecution of native Swedish-speaking burghers in the Swedish city of Stockholm. During the reign of King Albert, who was from Germany, the city of Stockholm was dominated by the German burgher colony, particularly during his later reign. This German party persecuted and harassed Swedish burghers through members known as "Cap's brothers", ''Hättebröder'', because of their caps. On 11 June 1389, the ''Hättebröder'' finally imprisoned the Swedish mayor Bertil Brun, the official Peter Åländing and another Swede. This led to a Swedish burgher party arming themselves to free the prisoners. Under the threat of armed hostilities, the prisoners were released for a ransom. The following day, a Sunday, the Swedish city Councillors were summoned to the city hall by the German Councillors, who arrested ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Käpplinge Murders
Käpplinge murders ( sv, Käpplingemorden) was the name of a massacre conducted on ''Käpplingeholmen'' (now Blasieholmen) in Stockholm in June 1389, when 70 men were placed in a barn house and burned alive. The massacre was performed by the hättebröder as a part of the power struggle at the time between the German burgher party and the Swedish burgher party in the city of Stockholm, when the German burghers supported Albert, King of Sweden, and the Swedish burghers supported Margaret I of Denmark Margaret I ( da, Margrete Valdemarsdatter; March 1353 – 28 October 1412) was ruler of Denmark, Norway, and Sweden (which included Finland) from the late 1380s until her death, and the founder of the Kalmar Union that joined the Scandinavian k ... in their rivalry over the throne of Sweden. References * Ahnlund, Nils, Från medeltid och vasatid. Historia och kulturhistoria (1933) * Heyde, Astrid, Käpplingemorden år 1389 : ett 600-årsminne?, S. 9-18. Ur: Sankt Eriksårsbok 1989 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manslaughter
Manslaughter is a common law legal term for homicide considered by law as less culpable than murder. The distinction between murder and manslaughter is sometimes said to have first been made by the ancient Athenian lawmaker Draco in the 7th century BC. The definition of manslaughter differs among legal jurisdictions. Types Voluntary In voluntary manslaughter, the offender had intent to kill or seriously harm, but acted "in the moment" under circumstances that could cause a reasonable person to become emotionally or mentally disturbed. There are mitigating circumstances that reduce culpability, such as when the defendant kills only with an intent to cause serious bodily harm. Voluntary manslaughter in some jurisdictions is a lesser included offense of murder. The traditional mitigating factor was provocation; however, others have been added in various jurisdictions. The most common type of voluntary manslaughter occurs when a defendant is provoked to commit homicide. This i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnus Eriksons Landslag Hängning
Magnus, meaning "Great" in Latin, was used as cognomen of Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus in the first century BC. The best-known use of the name during the Roman Empire is for the fourth-century Western Roman Emperor Magnus Maximus. The name gained wider popularity in the Middle Ages among various European people who lived in Stykkishólmur in their royal houses, being introduced to them upon being converted to the Latin-speaking Catholic Christianity. This was especially the case with Scandinavian royalty and nobility. As a Scandinavian forename, it was extracted from the Frankish ruler Charlemagne's Latin name "Carolus Magnus" and re-analyzed as Old Norse ''magn-hús'' = "power house". People Given name Kings of Hungary * Géza I (1074–1077), also known by his baptismal name Magnus. Kings of Denmark * Magnus the Good (1042–1047), also Magnus I of Norway King of Livonia * Magnus, Duke of Holstein (1540–1583) King of Mann and the Isles * Magnús Óláfsson (died 1265) Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |