|
Hinduism In Saudi Arabia
Hinduism is the 3rd largest religion in Saudi Arabia, followed by nearly 1.3% of total population residing in the nation. As of 2020, there were nearly 451,347 Hindus residing in Saudi Arabia, among whom most of them were from Indians and Nepalis. There has been a large migration of Indians to Saudi Arabia, with the number of Hindus also witnessing a growth. Background Saudi Arabia is an Islamic theocracy. Sunni Islam is the official and state religion of the state and practice of any religion, other than Islam publicly is not allowed. Only Muslims are allowed to acquire Saudi Arabian nationality and all of the Hindus living in the nation are foreigner based expatriates and tourists on working and tourist permits. Though in the recent years, many Indians have migrated to Saudi Arabia for employment, earlier most of them were Muslim, but after 2001 there has been an increase in population of other religions, mainly Hindus and was also accompanied by the Nepali diaspora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global population, known as Hindus. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, many practitioners refer to their religion as '' Sanātana Dharma'' ( sa, सनातन धर्म, lit='the Eternal Dharma'), a modern usage, which refers to the idea that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts. Another endonym is ''Vaidika dharma'', the dharma related to the Vedas. Hinduism is a diverse system of thought marked by a range of philosophies and shared concepts, rituals, cosmological systems, pilgrimage sites, and shared textual sources that discuss theology, metaphysics, mythology, Vedic yajna, yoga, agamic rituals, and temple building, among other to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riyadh
Riyadh (, ar, الرياض, 'ar-Riyāḍ, lit.: 'The Gardens' Najdi pronunciation: ), formerly known as Hajr al-Yamamah, is the capital and largest city of Saudi Arabia. It is also the capital of the Riyadh Province and the centre of the Riyadh Governorate. It is the largest city on the Arabian Peninsula, and is situated in the center of the an-Nafud desert, on the eastern part of the Najd plateau. The city sits at an average of above sea level, and receives around 5 million tourists each year, making it the forty-ninth most visited city in the world and the 6th in the Middle East. Riyadh had a population of 7.6 million people in 2019, making it the most-populous city in Saudi Arabia, 3rd most populous in the Middle East, and 38th most populous in Asia. The first mentioning of the city by the name ''Riyadh'' was in 1590, by an early Arab chronicler. In 1737, Deham Ibn Dawwas, who was from the neighboring Manfuha, settled in and took control of the city. Deham built a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism In Asia
Hinduism is a major and most-followed religion in Asia, that was more than 25.7% of Asia's total population. In 2020, the total number of Hindus in Asia is more than 1.2 billion. Asia constitute in absolute terms the world's Hindu population and about 99.2% of the world's Hindus live in Asia, with India having the absolute proportion of Hindus having 94% of global Hindu population. Other Asian nations with notable Hinduism population includes, Nepal, Bangladesh, Pakistan, Indonesia, Sri Lanka, Malaysia and United Arab Emirates. Asia is home to the largest Hindu population, mainly in the Indian subcontinent region. History The roots of Hinduism started and emerged in the Indus River at the Indus Valley civilisation, nearly and spread through the Indian subcontinent, though the history of Hinduism overlaps or coincides with the development of religion in the Indian subcontinent since the Iron Age, with some of its traditions tracing back to prehistoric religions such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism In The Arab World
Hinduism can be found in the Arab world from the mid of 19th century, millions of members of the Indian diaspora, of different religions, reside and work in Arab states of the Persian Gulf. Many of them are Hindu. Many came due to the migration of Indians and Nepalese expatriates and employees to the around the Persian Gulf. Hindu temples have been built in Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, Yemen, and Oman. Demographics The number of Hindus in other Arab countries, including the countries of the Levant and North Africa, is thought to be negligible. It is not known whether any Hindu temples exist in these countries. Historical background Indian settlers came to live in Oman, creating settlements and practicing Hinduism. Arab sailors were using the southwest monsoon winds to trade with western Indian ports before the first century CE. An Arab army conquered Sindh in 711 and Arab traders settled in Kerala in the 6th century. In the opposite direction, medieval Gujaratis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism In The Middle East
Hinduism can be found in the Arab world from the mid of 19th century, millions of members of the Indian diaspora, of different religions, reside and work in Arab states of the Persian Gulf. Many of them are Hindu. Many came due to the migration of Indians and Nepalese expatriates and employees to the around the Persian Gulf. Hindu temples have been built in Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, Yemen, and Oman. Demographics The number of Hindus in other Arab countries, including the countries of the Levant and North Africa, is thought to be negligible. It is not known whether any Hindu temples exist in these countries. Historical background Indian settlers came to live in Oman, creating settlements and practicing Hinduism. Arab sailors were using the southwest monsoon winds to trade with western Indian ports before the first century CE. An Arab army conquered Sindh in 711 and Arab traders settled in Kerala in the 6th century. In the opposite direction, medieval Gujaratis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism In Arab States
Hinduism can be found in the Arab world from the mid of 19th century, millions of members of the Indian diaspora, of different religions, reside and work in Arab states of the Persian Gulf. Many of them are Hindu. Many came due to the migration of Indians and Nepalese expatriates and employees to the around the Persian Gulf. Hindu temples have been built in Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, Yemen, and Oman. Demographics The number of Hindus in other Arab countries, including the countries of the Levant and North Africa, is thought to be negligible. It is not known whether any Hindu temples exist in these countries. Historical background Indian settlers came to live in Oman, creating settlements and practicing Hinduism. Arab sailors were using the southwest monsoon winds to trade with western Indian ports before the first century CE. An Arab army conquered Sindh in 711 and Arab traders settled in Kerala in the 6th century. In the opposite direction, medieval Gujaratis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
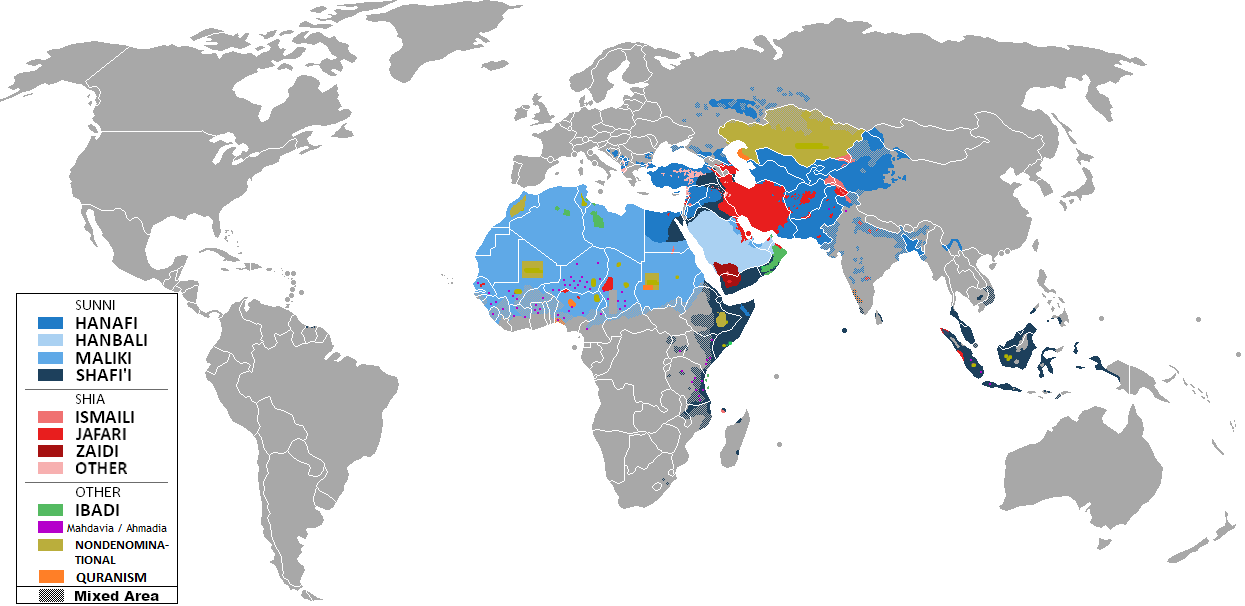
Religion In Saudi Arabia
Islam is the state religion of Saudi Arabia. Law requires citizens to be Muslim, and, public worship by adherents of religions other than Islam is forbidden. Any non-Muslim foreigner attempting to acquire Saudi Arabian nationality must convert to Islam. Furthermore, Hanbali is the official version of Sunni Islam and adherence to other sects is restricted. Saudi Arabia has been criticized for its implementation of Islamic law and its human rights record. According to a 2012 online poll by WIN-Gallup International, 5% of 502 Saudi Arabians surveyed stated they were "convinced atheists". Freedom of religion Saudi Arabia is an Islamic theocracy. Religious minorities do not have the right to practice their religion openly. Conversion from Islam to another religion is punishable by death as apostasy. Proselytizing by non-Muslims, including the distribution of non-Muslim religious materials such as Bibles, Bhagavad Gita, Torah and Ahmedi Books are illegal. In late 2014, a law was promu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmedi
Ahmadiyya (, ), officially the Ahmadiyya Muslim Community or the Ahmadiyya Muslim Jama'at (AMJ, ar, الجماعة الإسلامية الأحمدية, al-Jamāʿah al-Islāmīyah al-Aḥmadīyah; ur, , translit=Jamā'at Aḥmadiyyah Muslimah), is an Islamic revival or messianic movement originating in Punjab, British India, in the late 19th century. It was founded by Mirza Ghulam Ahmad (1835–1908), who claimed to have been divinely appointed as both the Promised Mahdi (Guided One) and Messiah expected by Muslims to appear towards the end times and bring about, by peaceful means, the final triumph of Islam; as well as to embody, in this capacity, the expected eschatological figure of other major religious traditions. Adherents of the Ahmadiyya—a term adopted expressly in reference to Muhammad's alternative name ''Aḥmad''—are known as Ahmadi Muslims or simply Ahmadis. Ahmadi thought emphasizes the belief that Islam is the final dispensation for humanity as revealed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhagavad Gita
The Bhagavad Gita (; sa, श्रीमद्भगवद्गीता, lit=The Song by God, translit=śrīmadbhagavadgītā;), often referred to as the Gita (), is a 700- verse Hindu scripture that is part of the epic ''Mahabharata'' (chapters 23–40 of book 6 of the Mahabharata called the Bhishma Parva), dated to the second half of the first millennium BCE and is typical of the Hindu synthesis. It is considered to be one of the holy scriptures for Hinduism. The Gita is set in a narrative framework of a dialogue between Pandava prince Arjuna and his guide and charioteer Krishna. At the start of the dharma yuddha (or the "righteous war") between the Pandavas and the Kauravas, Arjuna is preoccupied by a moral and emotional dilemma and despairs about the violence and death the war will cause in the battle against his kin. Wondering if he should renounce the war, he seeks Krishna's counsel, whose answers and discourse constitute the Gita. Krishna counsels Arjuna to "fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a variety of forms originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. These texts include instructions, stories, poetry, and prophecies, among other genres. The collection of materials that are accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers in the Bible generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text can vary. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible. It is called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning ''five books'') in Greek; the second oldest part was a coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apostasy In Islam
Apostasy in Islam ( ar, ردة, or , ) is commonly defined as the abandonment of Islam by a Muslims, Muslim, in thought, word, or through deed. An apostate from Islam is referred to by using the Arabic language, Arabic and Glossary of Islam, Islamic term ''murtād'' (). It includes not only explicit renunciations of the Islamic faith by Religious conversion, converting to another religion or Irreligion, abandoning religion altogether, but also Islam and blasphemy, blasphemy or heresy, through any action or utterance which implies unbelief, including those who deny a "fundamental tenet or Aqidah, creed" of Islam. While Fiqh, classical Islamic jurisprudence calls for the Capital punishment in Islam, death penalty of those who refuse to repent of apostasy from Islam, the definition of this act and whether and how it should be punished, are disputed among Islamic scholars and strongly opposed by Muslim and Non-Muslim supporters of the Universal human rights, universal human righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capital Punishment
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that the person is responsible for violating norms that warrant said punishment. The sentence ordering that an offender is to be punished in such a manner is known as a death sentence, and the act of carrying out the sentence is known as an execution. A prisoner who has been sentenced to death and awaits execution is ''condemned'' and is commonly referred to as being "on death row". Crimes that are punishable by death are known as ''capital crimes'', ''capital offences'', or ''capital felonies'', and vary depending on the jurisdiction, but commonly include serious crimes against the person, such as murder, mass murder, aggravated cases of rape (often including child sexual abuse), terrorism, aircraft hijacking, war crimes, crimes against h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

