|
Hilscher Netx Network Controller
The netX network controller family (based on ASICs), developed by Hilscher Gesellschaft für Systemautomation mbH, is a solution for implementing all proven Fieldbus and Real-Time Ethernet systems. It was the first Multi-Protocol ASIC which combines Real-Time-Ethernet and Fieldbus System in one solution. The Multiprotocol functionality is done over a flexible cpu sub system called XC. Through exchanging some microcode the XC is able to realize beside others a PROFINET IRT Switch, EtherCAT Slave, Ethernet Powerlink HUB, PROFIBUS, CAN bus, CC-Link Industrial Networks Interface. The Hilscher netX family {, class="wikitable" , - ! Controller !netX 52!netX 51netX 90 ! net ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Network
A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies, based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies. The nodes of a computer network can include personal computers, servers, networking hardware, or other specialised or general-purpose hosts. They are identified by network addresses, and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes, rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the transmission medium used to carry signals, bandwidth, communications pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Processing Unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, and input/output (I/O) operations specified by the instructions in the program. This contrasts with external components such as main memory and I/O circuitry, and specialized processors such as graphics processing units (GPUs). The form, design, and implementation of CPUs have changed over time, but their fundamental operation remains almost unchanged. Principal components of a CPU include the arithmetic–logic unit (ALU) that performs arithmetic and logic operations, processor registers that supply operands to the ALU and store the results of ALU operations, and a control unit that orchestrates the fetching (from memory), decoding and execution (of instructions) by directing the coordinated operations of the ALU, registers and other co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Ethernet
Industrial Ethernet (IE) is the use of Ethernet in an industrial environment with protocols that provide determinism and real-time control. Protocols for industrial Ethernet include EtherCAT, EtherNet/IP, PROFINET, POWERLINK, SERCOS III, CC-Link IE, and Modbus TCP. Many industrial Ethernet protocols use a modified Media Access Control (MAC) layer to provide low latency and determinism. Some microcontrollers such as Sitara provide industrial Ethernet support. Industrial Ethernet can also refer to the use of standard Ethernet protocols with rugged connectors and extended temperature switches in an industrial environment, for automation or process control. Components used in plant process areas must be designed to work in harsh environments of temperature extremes, humidity, and vibration that exceed the ranges for information technology equipment intended for installation in controlled environments. The use of fiber-optic Ethernet variants reduces the problems of electrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Networks
A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. The computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies, based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies. The nodes of a computer network can include personal computers, servers, networking hardware, or other specialised or general-purpose hosts. They are identified by network addresses, and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes, rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the transmission medium used to carry signals, bandwidth, communications protocols ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Automation
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines. Automation has been achieved by various means including mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, electronic devices, and computers, usually in combination. Complicated systems, such as modern factories, airplanes, and ships typically use combinations of all of these techniques. The benefit of automation includes labor savings, reducing waste, savings in electricity costs, savings in material costs, and improvements to quality, accuracy, and precision. Automation includes the use of various equipment and control systems such as machinery, processes in factories, boilers, and heat-treating ovens, switching on telephone networks, steering, and stabilization of ships, aircraft, and other applications and vehicles with reduced human in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I²C
I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit, ), alternatively known as I2C or IIC, is a synchronous, multi-controller/multi-target (master/slave), packet switched, single-ended, serial communication bus invented in 1982 by Philips Semiconductors. It is widely used for attaching lower-speed peripheral ICs to processors and microcontrollers in short-distance, intra-board communication. Several competitors, such as Siemens, NEC, Texas Instruments, STMicroelectronics, Motorola, Nordic Semiconductor and Intersil, have introduced compatible I2C products to the market since the mid-1990s. System Management Bus (SMBus), defined by Intel in 1995, is a subset of I2C, defining a stricter usage. One purpose of SMBus is to promote robustness and interoperability. Accordingly, modern I2C systems incorporate some policies and rules from SMBus, sometimes supporting both I2C and SMBus, requiring only minimal reconfiguration either by commanding or output pin use. Applications I2C is appropriate for peri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
I²S
I²S (Inter-IC Sound, pronounced "eye-squared-ess"), is an electrical serial bus interface standard used for connecting digital audio devices together. It is used to communicate PCM audio data between integrated circuits in an electronic device. The I²S bus separates clock and serial data signals, resulting in simpler receivers than those required for asynchronous communications systems that need to recover the clock from the data stream. Alternatively I²S is spelled I2S (pronounced eye-two-ess) or IIS (pronounced eye-eye-ess). Despite the similar name, I²S is unrelated to the bidirectional I²C (IIC) bus. History This standard was introduced in 1986 by Philips Semiconductor (now NXP Semiconductors) and was first revised June 5, 1996. The standard was last revised on February 17, 2022 and updated terms ''master'' and ''slave'' to ''controller'' and ''target''. Details The I²S protocol outlines one specific type of PCM digital audio communication with defined paramete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
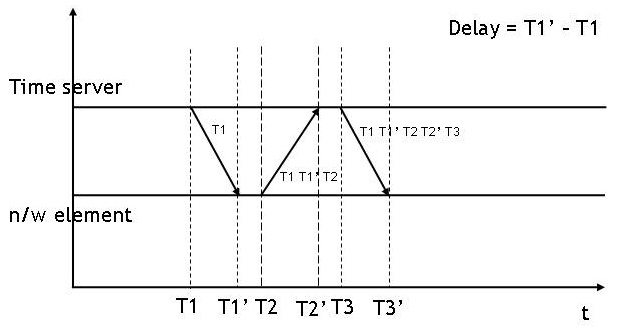
Precision Time Protocol
The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is a protocol used to synchronize clocks throughout a computer network. On a local area network, it achieves clock accuracy in the sub-microsecond range, making it suitable for measurement and control systems. PTP is employed to synchronize financial transactions, mobile phone tower transmissions, sub-sea acoustic arrays, and networks that require precise timing but lack access to satellite navigation signals. The first version of PTP, IEEE 1588-2002, was published in 2002. IEEE 1588-2008, also known as PTP Version 2 is not backward compatible with the 2002 version. IEEE 1588-2019 was published in November 2019 and includes backward-compatible improvements to the 2008 publication. IEEE 1588-2008 includes a ''profile'' concept defining PTP operating parameters and options. Several profiles have been defined for applications including telecommunications, electric power distribution and audiovisual. is an adaptation of PTP for use with Audio Vid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARM Architecture
ARM (stylised in lowercase as arm, formerly an acronym for Advanced RISC Machines and originally Acorn RISC Machine) is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures for computer processors, configured for various environments. Arm Ltd. develops the architectures and licenses them to other companies, who design their own products that implement one or more of those architectures, including system on a chip (SoC) and system on module (SOM) designs, that incorporate different components such as memory, interfaces, and radios. It also designs cores that implement these instruction set architectures and licenses these designs to many companies that incorporate those core designs into their own products. There have been several generations of the ARM design. The original ARM1 used a 32-bit internal structure but had a 26-bit address space that limited it to 64 MB of main memory. This limitation was removed in the ARMv3 series, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CC-Link Industrial Networks
The CC-Link Open Automation Networks Family are a group of open industrial networks that enable devices from numerous manufacturers to communicate. They are used in a wide variety of industrial automation applications at the machine, cell and line levels. History The CC-Link Partner Association (CLPA) offers a family of open-architecture networks. These originated with the CC-Link (Control & Communication) fieldbus in 1996, developed by Mitsubishi Electric Corporation. In 2000, this was released as an “Open” network so that independent automation equipment manufacturers could incorporate CLPA network compatibility into their products. In the same year, the CC-Link Partner Association (CLPA) was formed to manage and oversee the network technology and support manufacturer members. In 2007, the CLPA was the first organisation to introduce open gigabit Ethernet for automation with CC-Link IE (Industrial Ethernet). In 2018, the CLPA was the first organisation to combine open gigabit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Application-specific Integrated Circuit
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficiency video codec. Application-specific standard product (ASSP) chips are intermediate between ASICs and industry standard integrated circuits like the 7400 series or the 4000 series. ASIC chips are typically fabricated using metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) technology, as MOS integrated circuit chips. As feature sizes have shrunk and design tools improved over the years, the maximum complexity (and hence functionality) possible in an ASIC has grown from 5,000 logic gates to over 100 million. Modern ASICs often include entire microprocessors, memory blocks including ROM, RAM, EEPROM, flash memory and other large building blocks. Such an ASIC is often termed a SoC (system-on-chip). Designers of digital ASICs often use a hardware descrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAN Bus
A Controller Area Network (CAN bus) is a robust vehicle bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other's applications without a host computer. It is a message-based protocol, designed originally for multiplex electrical wiring within automobiles to save on copper, but it can also be used in many other contexts. For each device, the data in a frame is transmitted serially but in such a way that if more than one device transmits at the same time, the highest priority device can continue while the others back off. Frames are received by all devices, including by the transmitting device. History Development of the CAN bus started in 1983 at Robert Bosch GmbH. The protocol was officially released in 1986 at the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) conference in Detroit, Michigan. The first CAN controller chips were introduced by Intel in 1987, and shortly thereafter by Philips. Released in 1991, the Mercedes-Benz W140 was the first produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)