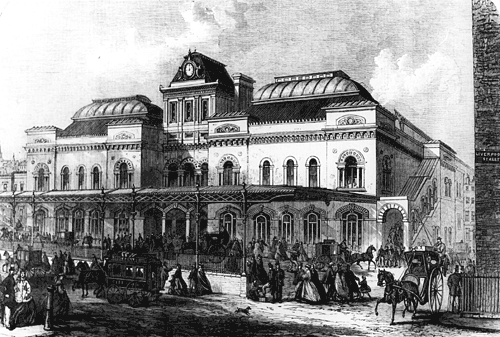|
Highgate Tube Station
Highgate is a London Underground station and former railway station in Archway Road, in the London Borough of Haringey in north London. The station takes its name from nearby Highgate Village. It is on the High Barnet branch of the Northern line, between East Finchley and Archway stations, and is in Travelcard Zone 3. The station was originally opened in 1867, on the Great Northern Railway's line between Finsbury Park and Edgware stations. As part of their only partially completed Northern Heights plan, the London Underground started serving the station in 1941, using new platforms in tunnels beneath the surface station. The platforms of the surface station remain, but were last used in 1954; the section of the line through them to Finsbury Park was closed in 1970 and lifted by 1972. One of the original 1867 station buildings still exists and is in use as a private house. History Original station Highgate station was originally constructed by the Edgware, Highgate and Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent ceremonial counties of England, counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England. The Underground has its origins in the Metropolitan Railway, the world's first underground passenger railway. Opened on 10 January 1863, it is now part of the Circle line (London Underground), Circle, District line, District, Hammersmith & City line, Hammersmith & City and Metropolitan lines. The first line to operate underground electric locomotive, electric traction trains, the City & South London Railway in 1890, is now part of the Northern line. The network has expanded to 11 lines, and in 2020/21 was used for 296 million passenger journeys, making it List of metro systems, one of the world's busiest metro systems. The 11 lines collectively handle up to 5 million passenger journeys a day and serve 272 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Barnet Railway Station
High Barnet is a London Underground station, and former railway station, located in Chipping Barnet, North London. The station is the northern terminus of the High Barnet branch of the Northern line and is in Travelcard Zone 5. It is situated 10.2 miles (16.4 km) north north-west of Charing Cross. The next station south is Totteridge & Whetstone. Services Northern line trains are scheduled to arrive and depart every 3–9 minutes from the station's three southbound platforms, with trains operating to Morden via Bank or to Kennington or Morden via Charing Cross. On days when Night Tube service is not running, between about 00:00 and 01:00, departing trains run as far as East Finchley only, from where journeys to central London can be continued by night bus N20, which also serves High Barnet station itself. When trains are no longer required to run on the Northern line, they may be stabled on the sidings to the east of the station. Connections London Buses routes 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad Street Railway Station (England)
Broad Street was a major terminal station in the City of London, adjacent to Liverpool Street station. It served as the main terminus of the North London Railway (NLR) network, running from 1865 to 1986. During its lifetime, it catered for mainly local suburban services around London, and over time struggled to compete with other modes of transport, leading to its closure. The station was built as a joint venture by the NLR and the London and North Western Railway (LNWR) in order to have a station serving freight closer to the City. It was immediately successful for both goods and passenger services and saw a significant increase in NLR traffic. Usage peaked in the early 20th century, after which it suffered from competition of London trams,_buses,_and_particularly_the_London_Underground.html" ;"title=""type": ..., buses, and particularly the London Underground">"type": ..., buses, and particularly the London Underground network. Patronage gradually fell and services decreased, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moorgate Station
Moorgate is a central London railway terminus and connected London Underground station on Moorgate in the City of London. Main line railway services for Hertford, Welwyn Garden City, Stevenage and Letchworth are operated by Great Northern, while the Underground station is served by the Circle, Hammersmith & City, Metropolitan and Northern lines. The station was opened as Moorgate Street in 1865 by the Metropolitan Railway. In 1900, the City & South London Railway added the station to its network, and the Great Northern & City Railway began serving the station in 1904. In 1975, the Northern City Line platforms were the site of the Moorgate tube crash – at the time, the worst peacetime accident in the history of the London Underground – in which 43 people were killed. Thameslink branch services were withdrawn in the early 21st century, and in 2022 a new ticket hall was built connected to the newly opened Elizabeth line at , with through access to the rest of Liverpool Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And North Eastern Railway
The London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) was the second largest (after LMS) of the " Big Four" railway companies created by the Railways Act 1921 in Britain. It operated from 1 January 1923 until nationalisation on 1 January 1948. At that time, it was divided into the new British Railways' Eastern Region, North Eastern Region, and partially the Scottish Region. History The company was the second largest created by the Railways Act 1921. The principal constituents of the LNER were: * Great Eastern Railway * Great Central Railway * Great Northern Railway * Great North of Scotland Railway * Hull and Barnsley Railway * North British Railway * North Eastern Railway The total route mileage was . The North Eastern Railway had the largest route mileage of , whilst the Hull and Barnsley Railway was . It covered the area north and east of London. It included the East Coast Main Line from London to Edinburgh via York and Newcastle upon Tyne and the routes from Edinburgh to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Four (British Railway Companies)
"Big Four" was a name used to describe the four largest railway companies in the United Kingdom in the period 1923–1947. The name was coined by ''The Railway Magazine'' in its issue of February 1923: "The Big Four of the New Railway Era". The Big Four were: * Great Western Railway (GWR) * London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) * London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) * Southern Railway (SR) The companies were formed as a result of the Railways Act 1921, in a process known as "The Grouping" (of the railways), which came into effect on 1 January 1923. On 1 January 1948 the companies were nationalised to form British Rail, British Railways as a result of the Transport Act 1947. Characterisation The three larger companies relied heavily on freight (especially coal), as well as long-distance passenger traffic. The Southern Railway, in contrast, was predominantly a passenger railway, which, despite its small size, carried more than a quarter of the total UK passenger tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921 (c. 55), also known as the Grouping Act, was an Act of Parliament enacted by the British government and intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, by "grouping" them into four large companies dubbed the " Big Four". This was intended to move the railways away from internal competition, and retain some of the benefits which the country had derived from a government-controlled railway during and after the Great War of 1914–1918. The provisions of the Act took effect from the start of 1923. History The British railway system had been built up by more than a hundred railway companies, large and small, and often, particularly locally, in competition with each other. The parallel railways of the East Midlands and the rivalry between the South Eastern Railway and the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway at Hastings were two examples of such local competition. During the First World War the railways were under st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Platform
An island platform (also center platform, centre platform) is a station layout arrangement where a single platform is positioned between two tracks within a railway station, tram stop or transitway interchange. Island platforms are popular on twin-track routes due to pragmatic and cost reasons. They are also useful within larger stations where local and express services for the same direction of travel can be provided from opposite sides of the same platform thereby simplifying transfers between the two tracks. An alternative arrangement is to position side platforms on either side of the tracks. The historical use of island platforms depends greatly upon the location. In the United Kingdom the use of island platforms is relatively common when the railway line is in a cutting or raised on an embankment, as this makes it easier to provide access to the platform without walking across the tracks. Advantages and tradeoffs Island platforms are necessary for any station with many th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranley Gardens Railway Station
Cranley Gardens railway station was a station in the Muswell Hill area of north London. It was located between Highgate and Muswell Hill stations, at the junction of Muswell Hill Road and Cranley Gardens. Nothing remains of the station today and its site is now occupied by housing and a school. In the 1930s, plans were made to electrify the line and transfer the mainline service to London Underground's Northern line, but these were abandoned after the Second World War. The station closed for passengers in 1954 and for goods in 1957. History The branch line from the Great Northern Railway's (GNR's) station at Highgate to Alexandra Palace was built by the Muswell Hill Railway (MHR) and opened on 24 May 1873. Cranley Gardens station opened on 2 August 1902. In 1911, the line was taken over by the GNR. After the 1921 Railways Act created the ''Big Four'' railway companies, the line became part of the London & North Eastern Railway (LNER) from 1923. The LNER closed the station on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muswell Hill Railway Station
Muswell Hill railway station was in Muswell Hill in North London, just north of the junction of Muswell Hill and Muswell Hill Place. Nothing remains of the station and Muswell Hill Primary School now occupies its former site. In the 1930s, plans were made to electrify the line and transfer the mainline service to London Underground's Northern line, but these were abandoned after the Second World War. The station closed for passengers in 1954 and goods in 1956. History The Muswell Hill Railway (MHR) opened the station on 24 May 1873 as ''Alexandra Park (Muswell Hill)''. It was the intermediate station on the MHR's branch line from the Great Northern Railway's (GNR's) station at Highgate to Alexandra Palace. The line was constructed to bring passengers to Alexandra Palace and the branch line opened at the same time as the Palace. Following a fire at the Palace, the line was closed from 1 August 1873 to 1 May 1875 with the station being given its final name when reopened. The ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highgate Wood
Highgate Wood is a 28 hectare (70 acre) area of ancient woodland in North London, lying between East Finchley, Highgate and Muswell Hill. It was originally part of the ancient Forest of Middlesex which covered much of London, Hertfordshire and Essex and was mentioned in the Domesday Book. It lies in the London Borough of Haringey, but is owned and managed by the City of London Corporation. The London Borough of Haringey contains four ancient woods: Highgate Wood, Queen's Wood, Coldfall Wood and Bluebell Wood, London, Bluebell Wood. Highgate Wood is shown on the Ordnance Survey map of Middlesex in 1886 more or less in its present formation, but known by the name "Gravelpit Wood". Flora and fauna The flora and fauna in the wood have been managed to varying degrees by humans through the ages. Predominantly an oak, hornbeam and holly wood, Highgate Wood is also home to more than 50 other tree and shrub species which have self-seeded there. The wild service tree, a rare deciduous tree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muswell Hill Railway
The Edgware, Highgate and London Railway was a railway in North London. The railway was a precursor of parts of London Underground's Northern line and was, in the 1930s the core of an ambitious expansion plan for that line which was thwarted by the Second World War. Parts of the line were closed in the 1950s and have since been removed. Establishment The company was established by a private act of parliament passed on 3 June 1862. The route, measuring , ran through parts of rural Middlesex (now suburban north London) from Finsbury Park through Stroud Green, Crouch End, Highgate, Finchley and Mill Hill to Edgware. Additional acts in 1864 and 1866 granted powers to construct branch lines from Highgate to Muswell Hill and from Finchley to High Barnet respectively. The railway was sponsored by the larger Great Northern Railway (GNR), whose main line from King's Cross ran through Finsbury Park on its way to Potters Bar and the north. Before the line to Edgware was opened, it was p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |