|
High Virgo
The High Virgo, also known as Weapons System 199C (WS-199C), was a prototype air-launched ballistic missile (ALBM) jointly developed by Lockheed and the Convair division of General Dynamics during the late 1950s. The missile proved moderately successful and aided in the development of the later GAM-87 Skybolt ALBM. It was also used in early tests of anti-satellite weapons. Design and development As part of the WS-199 project to develop new strategic weapons for the United States Air Force's Strategic Air Command, the Lockheed Corporation and the Convair division of General Dynamics proposed the development of an air-launched ballistic missile, to be carried by the Convair B-58 Hustler supersonic medium bomber.Parsch 2005 In early 1958 the two companies were awarded a contract for development of the weapon, designated WS-199C and given the code-name "High Virgo". While the project was intended to be strictly a research-and-development exercise, it was planned that the weapon woul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air-launched Ballistic Missile
An air-launched ballistic missile or ALBM is a ballistic missile launched from an aircraft. An ALBM allows the launch aircraft to stand off at long distances from its target, keeping it well outside the range of defensive weapons like anti-aircraft missiles and interceptor aircraft. Historically, once launched the missile was essentially immune to interception due to a lack of capable anti-ballistic missiles, with those few that did exist being limited to known static positions. This combination of features allowed a strategic bomber to present a credible deterrent second-strike option in an era when improving anti-aircraft defences appeared to be rendering conventional bombers obsolete. However, by the 1990's surface-to-air missile technology had innovated to the point of allowing the interception of such weapons (especially in their terminal phase) from road mobile systems, albeit at a lower PoK. By the early 21st century capable, dedicated, ABM systems from several nations had b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiokol
Thiokol (variously Thiokol Chemical Corporation(/Company), Morton Thiokol Inc., Cordant Technologies Inc., Thiokol Propulsion, AIC Group, ATK Thiokol, ATK Launch Systems Group; finally Orbital ATK before becoming part of Northrop Grumman) was an American corporation concerned initially with rubber and related chemicals, and later with rocket and missile propulsion systems. Its name is a portmanteau of the Greek words for sulfur (θεῖον ''"theion"'') and glue (κόλλα ''"kolla"''), an allusion to the company's initial product, Thiokol polymer. The Thiokol Chemical Company was founded in 1929. Its initial business was a range of synthetic rubber and polymer sealants. Thiokol was a major supplier of liquid polymer sealants during World War II. When scientists at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory discovered that Thiokol's polymers made ideal binders for solid rocket fuels, Thiokol moved into the new field, opening laboratories at Elkton, Maryland, and later production facilitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bold Orion
The Bold Orion missile, also known as Weapons System 199B (WS-199B), was a prototype air-launched ballistic missile (ALBM) developed by Martin Aircraft during the 1950s. Developed in both one- and two-stage designs, the missile was moderately successful in testing, and helped pave the way for development of the GAM-87 Skybolt ALBM. In addition, the Bold Orion was used in early anti-satellite weapons testing, performing the first interception of a satellite by a missile. Design and development The Bold Orion missile was developed as part of Weapons System 199, initiated by the United States Air Force (USAF) in response to the U.S. Navy's Polaris program, with funding authorised by the United States Congress in 1957.Yengst 2010, p.37. The purpose of WS-199 was the development of technology that would be used in new strategic weapons for the USAF's Strategic Air Command, not to deliver operational weapons; a primary emphasis was on proving the feasibility of an air-launched ballist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha Draco
The Alpha Draco missile, also known as Weapons System 199D (WS-199D), was an experimental ballistic missile developed by McDonnell Aircraft in the late 1950s to investigate the aerodynamic physics of the boost-glide reentry trajectory. Three test flights were conducted in 1959, of which two were successful. Design and development As part of the WS-199 project to develop new strategic weapons for the United States Air Force's Strategic Air Command, McDonnell Aircraft developed the Alpha Draco missile between 1957 and 1959, under a contract to launch three vehicles to determine the feasibility of the boost-glide reentry vehicle (BGRV) concept.Brulle 2008, p. 89. The purpose of the rocket was to establish whether a strategic missile using the "boost-glide" principle of propulsion could be practically used.Parsch 2005. The idea had been proposed by Walter Dornberger, who had moved to McDonnell after working for a short time at Bell Aircraft. Dornberger had originally worked on the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
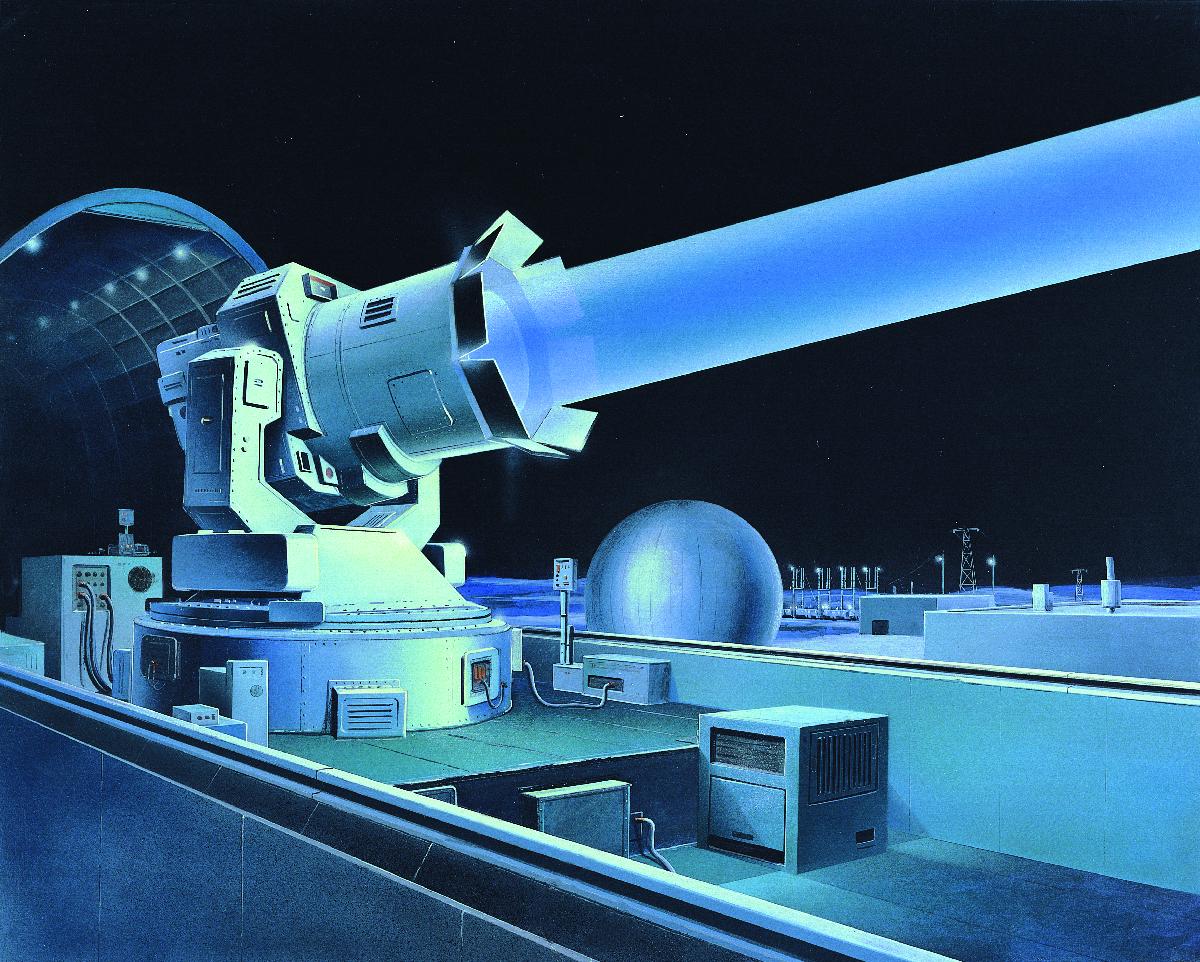
Terra-3
Terra-3 (Russian language, Russian: терра–3) was a Soviet laser testing centre, located on the Sary Shagan anti-ballistic missile (ABM) testing range in the Karaganda Region of Kazakhstan. It was originally built to test missile defense concepts, but these attempts were dropped after the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty was signed. The site later hosted two modest devices used primarily for experiments in space tracking. Several other laser test sites were also active during this period. During the 1980s, officials within the United States Department of Defense (DoD) suggested it was the site of a prototypical anti-satellite weapon system."Soviets could have laser able to blind US satellites" ''Gadsden Times'', 10 April 1984 The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apogee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. For example, the apsides of the Earth are called the aphelion and perihelion. General description There are two apsides in any elliptic orbit. The name for each apsis is created from the prefixes ''ap-'', ''apo-'' (), or ''peri-'' (), each referring to the farthest and closest point to the primary body the affixing necessary suffix that describes the primary body in the orbit. In this case, the suffix for Earth is ''-gee'', so the apsides' names are ''apogee'' and ''perigee''. For the Sun, its suffix is ''-helion'', so the names are ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion''. According to Newton's laws of motion, all periodic orbits are ellipses. The barycenter of the two bodies may lie well within the bigger body—e.g., the Earth–Moon barycenter is about 75% of the way from Earth's center to its surface. If, compared to the larger mass, the smaller mass is negligible (e.g., f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMR DZ
The Eastern Range (ER) is an American rocket range (Spaceport) that supports missile and rocket launches from the two major launch heads located at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station and the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida. The range has also supported Ariane launches from the Guiana Space Centre as well as launches from the Wallops Flight Facility and other lead ranges. The range also uses instrumentation operated by NASA at Wallops and KSC. The range can support launches between 37° and 114° azimuth. The headquarters of the range is now the 45th Space Wing at Patrick Space Force Base. History The history of the Eastern Range began on 18 October 1940, with the activation of the Banana River Naval Air Station which supported antisubmarine sea-patrol planes during World War II. The station was deactivated and put into a caretaker status on 1 September 1947. Launches of captured German V-2 rockets had been ongoing since the end of World War II at White Sands P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telemetry
Telemetry is the in situ data collection, collection of measurements or other data at remote points and their automatic data transmission, transmission to receiving equipment (telecommunication) for monitoring. The word is derived from the Greek language, Greek roots ''tele'', "remote", and ''metron'', "measure". Systems that need external instructions and data to operate require the counterpart of telemetry, telecommand. Although the term commonly refers to wireless data transfer mechanisms (e.g., using radio, ultrasonic, or Infrared#Communications, infrared systems), it also encompasses data transferred over other media such as a telephone or computer network, optical link or other wired communications like power line carriers. Many modern telemetry systems take advantage of the low cost and ubiquity of GSM networks by using SMS to receive and transmit telemetry data. A ''telemeter'' is a physical device used in telemetry. It consists of a sensor, a transmission path, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorer 5
Explorer 5 was a United States satellite with a mass of . It was the last of the original series of Explorer satellites built, designed, and operated by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Background Explorer 5 was similar in all respects to Explorer 4 and was designed with the same basic science objectives, to make the first detailed measurements of charged particles (protons and electrons) trapped in the terrestrial radiation belts and to observe the effects of the Project Argus A-bomb detonations. Spacecraft and subsystems Explorer 5 was a long, diameter cylinder and nosecone that comprised the fourth stage of the Jupiter-C launch vehicle. The on-orbit mass (after fuel burnout) was . The spacecraft body was made of stainless AISI-410 steel, thick. The surface was sandblasted, no aluminum oxide striping was used as on earlier Explorer satellites. The base of the cylinder held the Sergeant solid-fuel rocket motor. The Mallory mercury batteries for the low power transmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Explorer 4
Explorer 4 was an American satellite launched on 26 July 1958. It was instrumented by Dr. James van Allen's group. The Department of Defense's Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) had initially planned two satellites for the purposes of studying the Van Allen radiation belts and the effects of nuclear explosions upon these belts (and the Earth's magnetosphere in general), however Explorer 4 was the only such satellite launched as the other, Explorer 5, suffered launch failure. Explorer 4 was a cylindrically shaped satellite instrumented to make the first detailed measurements of charged particles (protons and electrons) trapped in the terrestrial radiation belts. Juno I launch vehicle The launch vehicle was a Juno I, a variant of the three-stage Jupiter-C with an added fourth propulsive stage, which in this case was the Explorer 4. The first stage was an upgraded Redstone liquid-fueled rocket. The second stage comprised a cluster of eleven Sergeant solid-fuel rocket mot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missile Guidance
Missile guidance refers to a variety of methods of guiding a missile or a guided bomb to its intended target. The missile's target accuracy is a critical factor for its effectiveness. Guidance systems improve missile accuracy by improving its Probability of Guidance (Pg). These guidance technologies can generally be divided up into a number of categories, with the broadest categories being "active", "passive", and "preset" guidance. Missiles and guided bombs generally use similar types of guidance system, the difference between the two being that missiles are powered by an onboard engine, whereas guided bombs rely on the speed and height of the launch aircraft for propulsion. History The concept of unmanned guidance originated at least as early as World War I, with the idea of remotely guiding an airplane bomb onto a target, such as the systems developed for the R.F.C. World War I Drone Weapons, first powered drones by Archibald Low (The Father of Radio Guidance). In World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruciform Tail
__NOTOC__ The cruciform tail is an aircraft empennage configuration which, when viewed from the aircraft's front or rear, looks much like a cross. The usual arrangement is to have the horizontal stabilizer intersect the vertical tail somewhere near the middle, and above the top of the fuselage. The design is often used to locate the horizontal stabilizer away from jet exhaust, propeller and wing wake, as well as to provide undisturbed airflow to the rudder. Prominent examples of aircraft with cruciform tails include the Avro Canada CF-100 Canuck, the British Aerospace Jetstream 31, the Fairchild Swearingen Metroliner, and the Rockwell B-1 Lancer. See also * Pelikan tail * T-tail * Twin tail * V-tail The V-tail or ''Vee-tail'' (sometimes called a butterfly tail or Rudlicki's V-tailGudmundsson S. (2013). "General Aviation Aircraft Design: Applied Methods and Procedures" (Reprint). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 489. , 9780123973290) of an aircraft ... References {{Aircraft com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)

.jpg)
