|
High-conductance State
The term high-conductance state describes a particular state of neurons in specific states of the brain, such as for example during wakefulness, attentive states, or even during some anesthetized states. In individual neurons, the high-conductance state is formally defined by the fact that the total synaptic conductance received by the neuron is larger than its natural resting (or leak) conductance, so in a sense the neuron is "driven" by its inputs rather than being dominated by its intrinsic activity. High-conductance states have been well characterized experimentally, but they also have motivated numerous theoretical studies, in particular in relation to the considerable amount of "noise" present in such states. It is believed that this "synaptic noise" has determinant properties on neuronal processing, and even may confer several computational advantages to neurons (see details in the articlHigh-Conductance Statein Scholarpedia). The term high-conductance state is also used t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. Non-animals like plants and fungi do not have nerve cells. Neurons are typically classified into three types based on their function. Sensory neurons respond to stimuli such as touch, sound, or light that affect the cells of the sensory organs, and they send signals to the spinal cord or brain. Motor neurons receive signals from the brain and spinal cord to control everything from muscle contractions to glandular output. Interneurons connect neurons to other neurons within the same region of the brain or spinal cord. When multiple neurons are connected together, they form what is called a neural circuit. A typical neuron consists of a cell body (soma), dendrites, and a single axon. The soma is a compact structure, and the axon and dend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wakefulness
Wakefulness is a daily recurring Human brain, brain state and state of consciousness in which an individual is conscious and engages in coherent cognition, cognitive and behavioral responses to the external world. Being awake is the opposite of being asleep, in which most external inputs to the brain are excluded from neural processing. Effects upon the brain The longer the brain has been awake, the greater the synchronous firing rates of cerebral cortex neurons. After sustained periods of sleep, both the speed and synchronicity of the neurons firing are shown to decrease. Another effect of wakefulness is the reduction of glycogen held in the astrocytes, which supply energy to the neurons. Studies have shown that one of sleep's underlying functions is to replenish this glycogen energy source. Maintenance by the brain Wakefulness is produced by a complex interaction between multiple neurotransmitter systems arising in the brainstem and ascending through the midbrain, hypothalam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise cause severe or intolerable pain in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. * Regional and local anesthesia, which blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapse
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell. Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses from one neuron to another. Neurons are specialized to pass signals to individual target cells, and synapses are the means by which they do so. At a synapse, the plasma membrane of the signal-passing neuron (the ''presynaptic'' neuron) comes into close apposition with the membrane of the target (''postsynaptic'') cell. Both the presynaptic and postsynaptic sites contain extensive arrays of molecular machinery that link the two membranes together and carry out the signaling process. In many synapses, the presynaptic part is located on an axon and the postsynaptic part is located on a dendrite or soma. Astrocytes also exchange information with the synaptic neurons, responding to synaptic activity and, in turn, regulating neurotransmission. Syna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Noise
Synaptic noise refers to the constant bombardment of synaptic activity in neurons. This occurs in the background of a cell when potentials are produced without the nerve stimulation of an action potential, and are due to the inherently random nature of synapses. These random potentials have similar time courses as excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs), yet they lead to variable neuronal responses. The variability is due to differences in the discharge times of action potentials. Causes Many types of noise exist in cells. First, there is intrinsic noise and extrinsic, or synaptic, noise. Within each category there are two further divisions of noise – voltage noise or temporal noise. Intrinsic voltage noise is due to random changes in the membrane potential of a cell, and intrinsic temporal noise is caused by variations in spike generation timing. The following sections give explanations about the causes of synaptic noise. Quanta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scholarpedia
''Scholarpedia'' is an English-language wiki-based online encyclopedia with features commonly associated with open-access online academic journals, which aims to have quality content in science and medicine. ''Scholarpedia'' articles are written by invited or approved expert authors and are subject to peer review. ''Scholarpedia'' lists the real names and affiliations of all authors, curators and editors involved in an article: however, the peer review process (which can suggest changes or additions, and has to be satisfied before an article can appear) is anonymous. ''Scholarpedia'' articles are stored in an online repository, and can be cited as conventional journal articles (''Scholarpedia'' has the ISSN number ). ''Scholarpedia''s citation system includes support for revision numbers. The project was created in February 2006 by Eugene M. Izhikevich, while he was a researcher at the Neurosciences Institute, San Diego, California. Izhikevich is also the encyclopedia's editor-i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
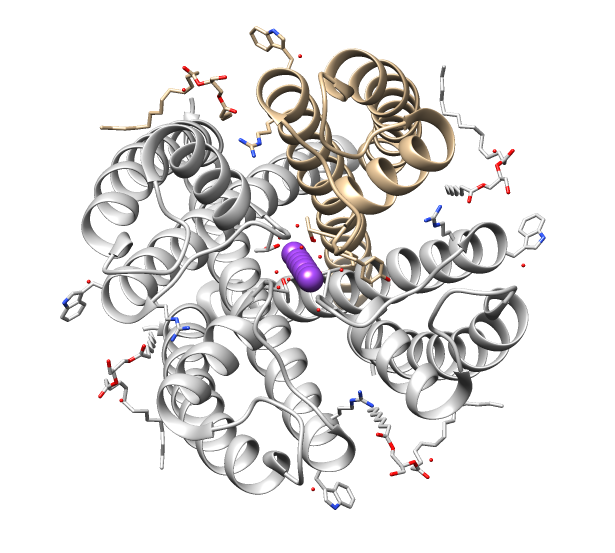
Ion Channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion transporter proteins: #The rate of ion transport through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |