|
HiPER
The High Power laser Energy Research facility (HiPER), is a proposed experimental laser-driven inertial confinement fusion (ICF) device undergoing preliminary design for possible construction in the European Union. , the effort appears to be inactive. HiPER was designed to study the "fast ignition" approach to generating nuclear fusion, which uses much smaller lasers than conventional ICF designs, yet produces fusion power outputs of about the same magnitude. This offers a total " fusion gain" that is much higher than devices like the National Ignition Facility (NIF), and a reduction in construction costs of about ten times. This opened a window for a small machine to be rapidly built that would reach ignition before NIF. HiPER and the Japanese FIREX designs intended to explore this approach. However, research into the fast ignition approach on smaller machines like the Omega laser in the US demonstrated a number of problems with the concept. Another alternative approach, ''sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HiPER Baseline Design
The High Power laser Energy Research facility (HiPER), is a proposed experimental laser-driven inertial confinement fusion (ICF) device undergoing preliminary design for possible construction in the European Union. , the effort appears to be inactive. HiPER was designed to study the "fast ignition" approach to generating nuclear fusion, which uses much smaller lasers than conventional ICF designs, yet produces fusion power outputs of about the same magnitude. This offers a total "fusion gain" that is much higher than devices like the National Ignition Facility (NIF), and a reduction in construction costs of about ten times. This opened a window for a small machine to be rapidly built that would reach ignition before NIF. HiPER and the Japanese FIREX designs intended to explore this approach. However, research into the fast ignition approach on smaller machines like the Omega laser in the US demonstrated a number of problems with the concept. Another alternative approach, ''sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
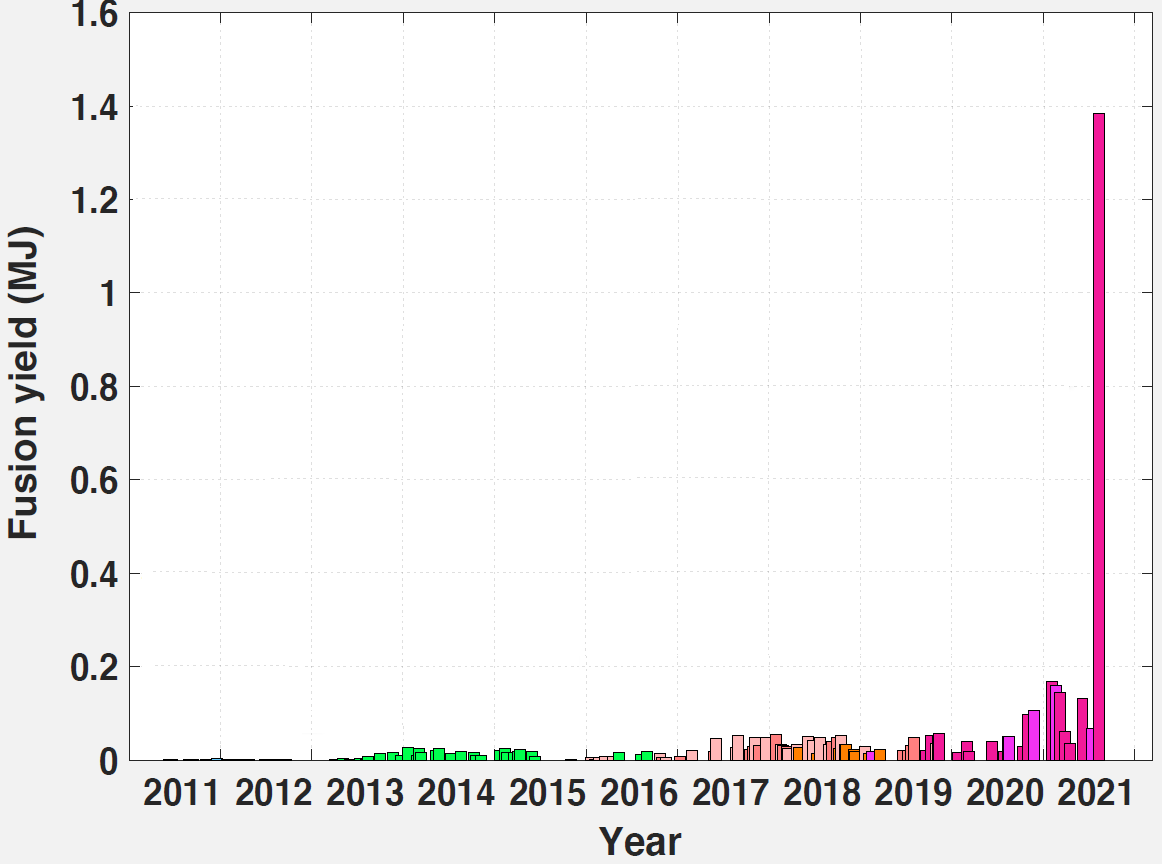
Inertial Confinement Fusion
Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) is a fusion energy process that initiates nuclear fusion reactions by compressing and heating targets filled with thermonuclear fuel. In modern machines, the targets are small spherical pellets about the size of a pinhead typically containing a mixture of about 10 milligrams of deuterium 2H and tritium 3H. To compress and heat the fuel, energy is deposited in the outer layer of the target using high-energy beams of photons, electrons or ions, although almost all ICF devices used lasers. The beams heat the outer layer, which explodes outward. This produces a reaction force against the remainder of the target, which accelerates it inwards and compresses the fuel. This process also creates shock waves that travel inward through the target. Sufficiently powerful shock waves can compress and heat the fuel at the center such that fusion occurs. ICF is one of two major branches of fusion energy research, the other is magnetic confinement fusion. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Confinement Fusion
Inertial confinement fusion (ICF) is a fusion energy process that initiates nuclear fusion reactions by compressing and heating targets filled with thermonuclear fuel. In modern machines, the targets are small spherical pellets about the size of a pinhead typically containing a mixture of about 10 milligrams of deuterium 2H and tritium 3H. To compress and heat the fuel, energy is deposited in the outer layer of the target using high-energy beams of photons, electrons or ions, although almost all ICF devices used lasers. The beams heat the outer layer, which explodes outward. This produces a reaction force against the remainder of the target, which accelerates it inwards and compresses the fuel. This process also creates shock waves that travel inward through the target. Sufficiently powerful shock waves can compress and heat the fuel at the center such that fusion occurs. ICF is one of two major branches of fusion energy research, the other is magnetic confinement fusion. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Ignition Facility
The National Ignition Facility (NIF) is a laser-based inertial confinement fusion (ICF) research device, located at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in Livermore, California, United States. NIF's mission is to achieve fusion ignition with high energy gain. It achieved the first scientific breakeven controlled fusion experiment on December 5, 2022, with an energy gain factor of 1.5. It supports nuclear weapon maintenance and design by studying the behavior of matter under the conditions found within nuclear explosions. NIF is the largest and most powerful ICF device built to date. The basic ICF concept is to squeeze a small amount of fuel to reach pressure and temperature necessary for fusion. NIF hosts the world's most energetic laser. The laser heats the outer layer of a small sphere. The energy is so intense that it causes the sphere to implode, squeezing the fuel inside. The implosion reaches a peak speed of , raising the fuel density from about that of water to abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusion Gain
A fusion energy gain factor, usually expressed with the symbol ''Q'', is the ratio of fusion power produced in a nuclear fusion reactor to the power required to maintain the plasma in steady state. The condition of ''Q'' = 1, when the power being released by the fusion reactions is equal to the required heating power, is referred to as breakeven, or in some sources, scientific breakeven. The energy given off by the fusion reactions may be captured within the fuel, leading to ''self-heating''. Most fusion reactions release at least some of their energy in a form that cannot be captured within the plasma, so a system at ''Q'' = 1 will cool without external heating. With typical fuels, self-heating in fusion reactors is not expected to match the external sources until at least ''Q'' ≈ 5. If ''Q'' increases past this point, increasing self-heating eventually removes the need for external heating. At this point the reaction becomes self-sustaining, a condition called combustion, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nanometer, nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 Hertz, PHz) to 400 nm (750 Hertz, THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight, and constitutes about 10% of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the Sun. It is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights. Although long-wavelength ultraviolet is not considered an ionizing radiation because its photons lack the energy to ionization, ionize atoms, it can cause chemical reactions and causes many substances to glow or fluorescence, fluoresce. Consequently, the chemical and biological effects of UV are greater than simple heating effects, and many practical applications of UV radiation derive from its interactions with organic molecules. Short-wave ultraviolet light damages DNA and sterilizes surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Frequency Multiplier
An optical frequency multiplier is a nonlinear optical device in which photons interacting with a nonlinear material are effectively "combined" to form new photons with greater energy, and thus higher frequency (and shorter wavelength). Two types of devices are currently common: ''frequency doublers,'' often based on lithium niobate (LN), lithium tantalate (LT), potassium titanyl phosphate (KTP) or lithium triborate (LBO), and ''frequency triplers'' typically made of potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP). Both are widely used in optical experiments that use lasers as a light source. Harmonic generation There are two processes that are commonly used to achieve the conversion: second-harmonic generation (''SHG'', also called frequency doubling), or sum-frequency generation which sums two non-similar frequencies. Direct third-harmonic generation (''THG'', also called frequency tripling) also exists and can be used to detect an interface between materials of different excitability. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family, and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have no known components or substructure. The electron's mass is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton. Quantum mechanical properties of the electron include an intrinsic angular momentum ( spin) of a half-integer value, expressed in units of the reduced Planck constant, . Being fermions, no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state, in accordance with the Pauli exclusion principle. Like all elementary particles, electrons exhibit properties of both particles and waves: They can collide with other particles and can be diffracted like light. The wave properties of electrons are easier to observe with experiments than those of other particles like neutrons and protons because electrons have a lower mass and hence a longer de Broglie wavele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenon Flash Tube
A flashtube (flashlamp) is an electric arc lamp designed to produce extremely intense, incoherent, full-spectrum white light for a very short time. A flashtube is a glass tube with an electrode at each end and is filled with a gas that, when triggered, ionizes and conducts a high-voltage pulse to make light. Flashtubes are used most in photography; they also are used in science, medicine, industry, and entertainment. Construction The lamp comprises a hermetically sealed glass tube, which is filled with a noble gas, usually xenon, and electrodes to carry electrical current to the gas. Additionally, a high voltage power source is necessary to energize the gas as a trigger event. A charged capacitor is usually used to supply energy for the flash, so as to allow very speedy delivery of very high electrical current when the lamp is triggered. Glass envelopes The glass envelope is most commonly a thin tube, often made of fused quartz, borosilicate or Pyrex, which may be straight, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around 1 millimeter (300 GHz) to the nominal red edge of the visible spectrum, around 700 nanometers (430 THz). Longer IR wavelengths (30 μm-100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation range. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is at infrared wavelengths. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, IR propagates energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit invisible heat; in 1681 the pioneering experimenter Edme Mariotte showed that glass, though transparent to sunlight, obstructed radiant heat. In 1800 the astronomer Sir William Herschel discovered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiva Laser
The Shiva laser was a powerful 20-beam infrared neodymium glass (silica glass) laser built at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in 1977 for the study of inertial confinement fusion (ICF) and long-scale-length laser-plasma interactions. Presumably, the device was named after the multi-armed form of the Hindu god Shiva, due to the laser's multi-beamed structure. Shiva was instrumental in demonstrating a particular problem in compressing targets with lasers, leading to a major new device being constructed to address these problems, the Nova laser. Background The basic idea of any ICF device is to rapidly heat the outer layers of a "target", normally a small plastic sphere containing a few milligrams of fusion fuel, typically a mix of deuterium and tritium. The heat burns the plastic into a plasma, which explodes off the surface. Due to Newton's Third Law, the remaining portion of the target is driven inwards, eventually collapsing into a small point of very high density. The ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spatial Filter
A spatial filter is an optical device which uses the principles of Fourier optics to alter the structure of a beam of light or other electromagnetic radiation, typically coherent laser light. Spatial filtering is commonly used to "clean up" the output of lasers, removing aberrations in the beam due to imperfect, dirty, or damaged optics, or due to variations in the laser gain medium itself. This filtering can be applied to transmit a pure transverse mode from a multimode laser while blocking other modes emitted from the optical resonator. The term "filtering" indicates that the desirable structural features of the original source pass through the filter, while the undesirable features are blocked. An apparatus which follows the filter effectively sees a higher-quality but lower-powered image of the source, instead of the actual source directly. An example of the use of spatial filter can be seen in advanced setup of micro-Raman spectroscopy. In spatial filtering, a lens is used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |