|
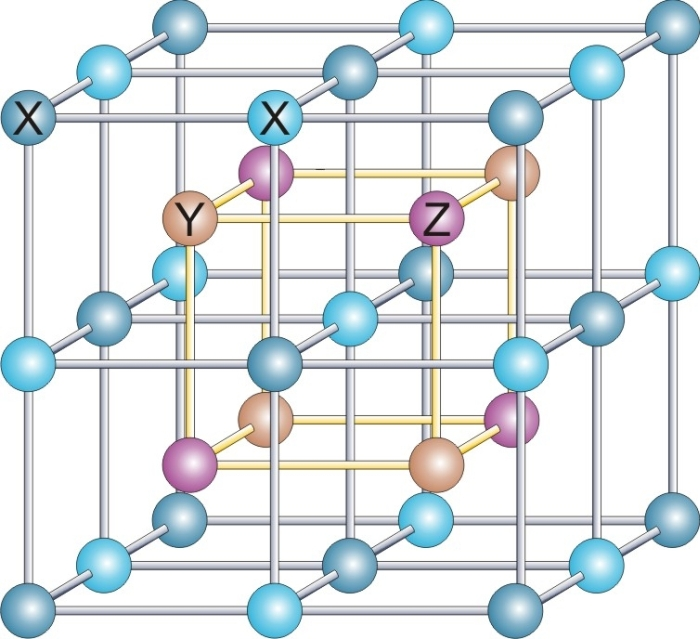
Heusler Compound
Heusler compounds are magnetic intermetallics with face-centered cubic crystal structure and a composition of XYZ (half-Heuslers) or X2YZ (full-Heuslers), where X and Y are transition metals and Z is in the p-block. The term derives from the name of Germany, German mining engineer and chemist Friedrich Heusler, who studied such a compound (Cu2MnAl) in 1903. Many of these compounds exhibit properties relevant to spintronics, such as magnetoresistance, variations of the Hall effect, ferromagnetism, ferro-, antiferromagnetism, antiferro-, and ferrimagnetism, Half-metal, half- and semimetallicity, semiconductivity with spin filter ability, superconductivity, Topological insulator, topological band structure and are actively studied as Thermoelectric materials. Their magnetism results from a double-exchange mechanism between neighboring magnetic ions. Manganese, which sits at the body centers of the cubic structure, was the magnetic ion in the first Heusler compound discovered. (See the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heusler Alloy - Structure
Heusler is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Andreas Heusler (1865–1940), Swiss medievalist * Friedrich Heusler (1866–1947), German mining engineer and chemist ** Heusler compound See also * Heusler, Indiana Heusler is an unincorporated community in Marrs Township, Posey County, in the U.S. state of Indiana Indiana () is a U.S. state in the Midwestern United States. It is the 38th-largest by area and the 17th-most populous of the 50 States ... {{surname German-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Half-metal
A half-metal is any substance that acts as a conductor to electrons of one spin orientation, but as an insulator or semiconductor to those of the opposite orientation. Although all half-metals are ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic), most ferromagnets are not half-metals. Many of the known examples of half-metals are oxides, sulfides, or Heusler alloys. In half-metals, the valence band for one spin orientation is partially filled while there is a gap in the density of states for the other spin orientation. This results in conducting behavior for only electrons in the first spin orientation. In some half-metals, the majority spin channel is the conducting one while in others the minority channel is. Half-metals were first described in 1983, as an explanation for the electrical properties of Mn-based Heusler alloys. Some notable half-metals are chromium(IV) oxide, magnetite, and lanthanum strontium manganite (LSMO), as well as chromium arsenide. Half-metals have attracted some i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent; as a rubber additive; and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese was first isolated in 1774. It is familiar in the laboratory in the form of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strukturbericht Type
In crystallography, a Strukturbericht designation or Strukturbericht type is a system of detailed crystal structure classification by analogy to another known structure. The designations were intended to be comprehensive but are mainly used as supplement to space group crystal structures designations, especially historically. Each Strukturbericht designation is described by a single space group, but the designation includes additional information about the positions of the individual atoms, rather than just the symmetry of the crystal structure. While Strukturbericht symbols exist for many of the earliest observed and most common crystal structures, the system is not comprehensive, and is no longer being updated. Modern databases such as Inorganic Crystal Structure Database index thousands of structure types directly by the prototype compound (i.e. "the NaCl structure" instead of "the B1 structure"). These are essentially equivalent to the old Stukturbericht designations. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. In its metallic state, iron is rare in the Earth's crust, limited mainly to deposition by meteorites. Iron ores, by contrast, are among the most abundant in the Earth's crust, although extracting usable metal from them requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching or higher, about higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BCE and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys, in some regions, only around 1200 BCE. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere. Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth's outer and inner cores. Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classified as an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bethe–Slater Curve
The Bethe–Slater curve is a heuristic explanation for why certain metals are ferromagnetic and others are antiferromagnetic. It assumes a Heisenberg model of magnetism, and explains the differences in exchange energy of transition metals as due to the ratio of the interatomic distance ''a'' to the radius ''r'' of the ''3d'' electron shell In chemistry and atomic physics, an electron shell may be thought of as an orbit followed by electrons around an atom's nucleus. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the "1 shell" (also called the "K shell"), followed by the "2 shell" (or .... When the magnetically important ''3d'' electrons of adjacent atoms are relatively close to each other, the exchange interaction, J_, is negative, but when they are further away, the exchange interaction becomes positive, before slowly dropping off. The idea of relating exchange energy to inter-atomic distance was first proposed by John C. Slater in 1930, and illustrated as a curve on a gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy uses, particularly in stainless steels. It improves strength, workability, and resistance to wear. Manganese oxide is used as an oxidising agent; as a rubber additive; and in glass making, fertilisers, and ceramics. Manganese sulfate can be used as a fungicide. Manganese is also an essential human dietary element, important in macronutrient metabolism, bone formation, and free radical defense systems. It is a critical component in dozens of proteins and enzymes. It is found mostly in the bones, but also the liver, kidneys, and brain. In the human brain, the manganese is bound to manganese metalloproteins, most notably glutamine synthetase in astrocytes. Manganese was first isolated in 1774. It is familiar in the laboratory in the form of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double-exchange Mechanism
The double-exchange mechanism is a type of a magnetic exchange that may arise between ions in different oxidation states. First proposed by Clarence Zener, this theory predicts the relative ease with which an electron may be exchanged between two species and has important implications for whether materials are ferromagnetic, antiferromagnetic, or exhibit spiral magnetism. For example, consider the 180 degree interaction of Mn- O-Mn in which the Mn "eg" orbitals are directly interacting with the O "2p" orbitals, and one of the Mn ions has more electrons than the other. In the ground state, electrons on each Mn ion are aligned according to the Hund's rule: If O gives up its spin-up electron to Mn4+, its vacant orbital can then be filled by an electron from Mn3+. At the end of the process, an electron has moved between the neighboring metal ions, retaining its spin. The double-exchange predicts that this electron movement from one species to another will be facilitated more easily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoelectric Materials
Thermoelectric materials show the thermoelectric effect in a strong or convenient form. The ''thermoelectric effect'' refers to phenomena by which either a temperature difference creates an electric potential or an electric current creates a temperature difference. These phenomena are known more specifically as the Seebeck effect (creating a voltage from temperature difference), Peltier effect (driving heat flow with an electric current), and Thomson effect (reversible heating or cooling within a conductor when there is both an electric current and a temperature gradient). While all materials have a nonzero thermoelectric effect, in most materials it is too small to be useful. However, low-cost materials that have a sufficiently strong thermoelectric effect (and other required properties) are also considered for applications including power generation and refrigeration. The most commonly used thermoelectric material is based on bismuth telluride (). Thermoelectric materials are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
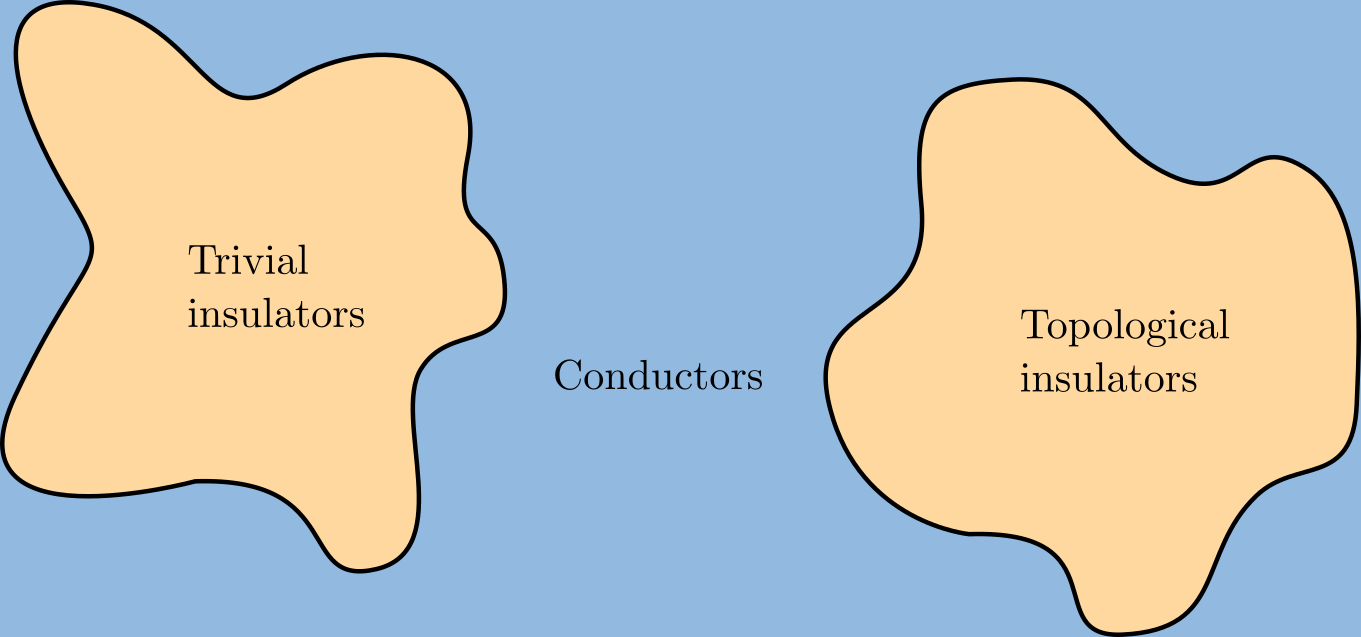
Topological Insulator
A topological insulator is a material whose interior behaves as an electrical insulator while its surface behaves as an electrical conductor, meaning that electrons can only move along the surface of the material. A topological insulator is an insulator for the same reason a "trivial" (ordinary) insulator is: there exists an energy gap between the valence and conduction bands of the material. But in a topological insulator, these bands are, in an informal sense, "twisted", relative to a trivial insulator. The topological insulator cannot be continuously transformed into a trivial one without untwisting the bands, which closes the band gap and creates a conducting state. Thus, due to the continuity of the underlying field, the border of a topological insulator with a trivial insulator (including vacuum, which is topologically trivial) is forced to support a conducting state. Since this results from a global property of the topological insulator's band structure, local (symmetry- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |