|
Heteropsammia
''Heteropsammia'' is a genus of apozooxanthellate corals that belong to the family Dendrophylliidae. Anatomy These corals consist of free-living, single polyps, of a diameter of around 2.5 cm. They form a symbiotic relationship with a sipunculid worm, '' Aspidosiphon corallicola''. The worm lives in a cavity situated on the under surface of the coral and it pulls the polip over sandy substrates. They also present a facultative symbiotic relationship with zooxanthellae of the ''Symbiodinium'' genus, as this link has been observed at shallow waters (under 40 m), but not at greater depths (where the corals live without the algae). ''Heteropsammia'' corals can sometimes establish symbiotic relationships with other marine species, such as hermit crabs, that live in the cavity where the endosymbiotic Sipunculid worm is usually located. Nutrition ''Heteropsammia'' corals (of the species ''Heteropsammia cochlea'') have been observed ingesting salps in Leuk Bay, Koh Tao, Gulf o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heteropsammia Moretonensis
''Heteropsammia'' is a genus of apozooxanthellate corals that belong to the family Dendrophylliidae. Anatomy These corals consist of free-living, single polyps, of a diameter of around 2.5 cm. They form a symbiotic relationship with a sipunculid worm, '' Aspidosiphon corallicola''. The worm lives in a cavity situated on the under surface of the coral and it pulls the polip over sandy substrates. They also present a facultative symbiotic relationship with zooxanthellae of the ''Symbiodinium'' genus, as this link has been observed at shallow waters (under 40 m), but not at greater depths (where the corals live without the algae). ''Heteropsammia'' corals can sometimes establish symbiotic relationships with other marine species, such as hermit crabs, that live in the cavity where the endosymbiotic Sipunculid worm is usually located. Nutrition ''Heteropsammia'' corals (of the species ''Heteropsammia cochlea'') have been observed ingesting salps in Leuk Bay, Koh Tao, Gulf o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heteropsammia Eupsammides
''Heteropsammia'' is a genus of apozooxanthellate corals that belong to the family Dendrophylliidae. Anatomy These corals consist of free-living, single polyps, of a diameter of around 2.5 cm. They form a symbiotic relationship with a sipunculid worm, '' Aspidosiphon corallicola''. The worm lives in a cavity situated on the under surface of the coral and it pulls the polip over sandy substrates. They also present a facultative symbiotic relationship with zooxanthellae of the ''Symbiodinium'' genus, as this link has been observed at shallow waters (under 40 m), but not at greater depths (where the corals live without the algae). ''Heteropsammia'' corals can sometimes establish symbiotic relationships with other marine species, such as hermit crabs, that live in the cavity where the endosymbiotic Sipunculid worm is usually located. Nutrition ''Heteropsammia'' corals (of the species ''Heteropsammia cochlea'') have been observed ingesting salps in Leuk Bay, Koh Tao, Gulf o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heteropsammia Cochlea
''Heteropsammia cochlea'', also known as walking dendro, is a species of small solitary coral in the family Dendrophylliidae that is native to the Indo-Pacific area. Description This small solitary free-living coral, not more than 2.5 cm across, is not fixed to the sea floor. It is composed of one or two corallites in the shape of a figure of eight when observed from top, making it easy to identify. The base in contact with the bottom is relatively circular, depending on the nature of the substrate it is either flat or slightly keeled. The base has an orifice that houses a commensal worm belonging to the family Aspidosiphonidae.LEON Virginie, PROUZET Anne, SCAPS Patrick, MITEL Cédric, in : DORIS, 21/3/2014 : Aspidosiphon muelleri Diesing, 1851, http://doris.ffessm.fr/fiche2.asp?fiche_numero=589 The overall color is yellowish, grayish or greenish. The polyp tentacles can be seen deployed, especially at night. Distribution & habitat The walking dendro is widespread througho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
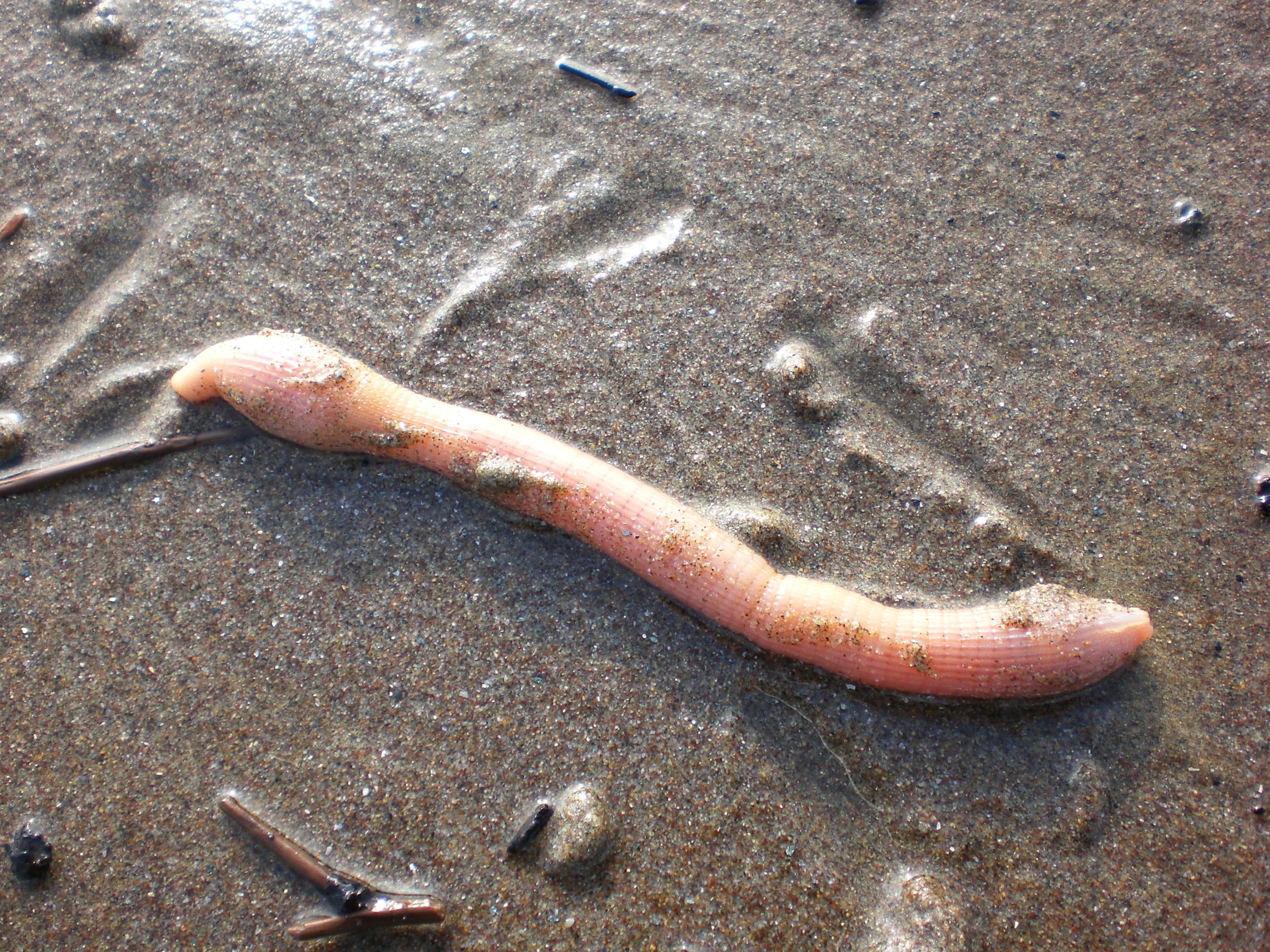
Aspidosiphon Corallicola
''Aspidosiphon muelleri'' is a species of unsegmented benthic marine worm in the phylum Sipuncula, the peanut worms. This worm is found in the eastern Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea and in various locations in the Indo-Pacific region at depths down to about . Description ''Aspidosiphon muelleri'' has a cylindrical trunk and a narrower, cylindrical introvert at the front end which can retract back into the trunk. The oral disc is at the tip of the introvert; this has a terminal mouth and a cluster of ten to twelve short tentacles arranged in a crescent surrounding a nuchal organ. The introvert bears rings of tiny hooks at the front, and larger, more irregularly-placed hooks at the rear. At the front of the trunk is an anal shield and this acts as an operculum when the introvert is retracted. At the posterior of the trunk is the caudal shield; both it and the anal shield are rough and chitinised, with radial grooves and edged by wart-like papillae. This worm can grow to a le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salp
A salp (plural salps, also known colloquially as “sea grape”) or salpa (plural salpae or salpas) is a barrel-shaped, planktic tunicate. It moves by contracting, thereby pumping water through its gelatinous body, one of the most efficient examples of jet propulsion in the animal kingdom. The salp strains the pumped water through its internal feeding filters, feeding on phytoplankton. Distribution Salps are common in equatorial, temperate, and cold seas, where they can be seen at the surface, singly or in long, stringy colonies. The most abundant concentrations of salps are in the Southern Ocean (near Antarctica), where they sometimes form enormous swarms, often in deep water, and are sometimes even more abundant than krill. Since 1910, while krill populations in the Southern Ocean have declined, salp populations appear to be increasing. Salps have been seen in increasing numbers along the coast of Washington. Life cycle Salps have a complex life cycle, with an obligatory a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diogenes Heteropsammicola
''Diogenes heteropsammicola'' is a species of hermit crab discovered during samplings between 2012 and 2016 in the shallow waters of the Japanese Amami Islands. This ''D. heteropsammicola'' is strongly associated with the walking corals. This hermit crab species is unique due to the discovery that they use living, growing coral as a shell. The live in the inside of the coral and vary from other types of hermits. Crustaceans of this type commonly replace their shell as the organism grows in size, but ''D. heteropsammicola'' are the first of their kind to use solitary corals as a shell form. ''Heteropsammia'' and ''Heterocyathus'' are the two solitary corals that this hermit species has been observed as occupying. These two coral species are also used as a home by symbiotic sipunculans of the genus '' Aspidosiphon'', which normally occupy the corals that the were previously occupied by crabs. The discoverers of this species are Momoko Igawa and Makoto Kato of Kyoto University , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendrophylliidae
Dendrophylliidae is a family of stony corals. Most (but not all) members are azooxanthellate and thus have to capture food with their tentacles instead of relying on photosynthesis to produce their food. The World Register of Marine Species includes these genera in the family: * '' Astroides'' Quoy & Gaimard, 1827 * ''Balanophyllia'' Wood, 1844 * '' Balanopsammia'' Ocana & Brito, 2013 * '' Bathypsammia'' Marenzeller, 1907 * '' Cladopsammia'' Lacaze-Duthiers, 1897 * '' Dendrophyllia'' de Blainville, 1830 * '' Dichopsammia'' Song, 1994 * '' Duncanopsammia'' Wells, 1936 * '' Eguchipsammia'' Cairns, 1994 * ''Enallopsammia'' Sismonda, 1871 * '' Endopachys'' Milne Edwards & Haime, 1848 * '' Endopsammia'' Milne Edwards & Haime, 1848 * ''Heteropsammia ''Heteropsammia'' is a genus of apozooxanthellate corals that belong to the family Dendrophylliidae. Anatomy These corals consist of free-living, single polyps, of a diameter of around 2.5 cm. They form a symbiotic relationship w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sipuncula
The Sipuncula or Sipunculida (common names sipunculid worms or peanut worms) is a class containing about 162 species of unsegmented marine annelid worms. The name ''Sipuncula'' is from the genus name ''Sipunculus'', and comes from the Latin ''siphunculus'' meaning a "small tube". Sipuncula was once considered a phylum, but was demoted to a class of Annelida, based on recent molecular work. Sipunculans vary in size but most species are under in length. The body is divided into an unsegmented, bulbous trunk and a narrower, anterior section, called the "introvert", which can be retracted into the trunk. The mouth is at the tip of the introvert and is surrounded in most groups by a ring of short tentacles. With no hard parts, the body is flexible and mobile. Although found in a range of habitats throughout the world's oceans, the majority of species live in shallow water habitats, burrowing under the surface of sandy and muddy substrates. Others live under stones, in rock crevic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoologische Mededelingen
''Zoologische Mededelingen'' was a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal publishing papers and monographs on animal systematics. The publisher was the National Museum of Natural History Naturalis in the Netherlands. The first issue appeared in 1915, as the official journal of Naturalis' predecessor, the Rijks Museum van Natuurlijke Historie. Earlier, the museum published ''Muséum d'Histoire Naturelle des Pays-Bas'' (volumes I-XIV, 1862-1908) and ''Notes from the Leyden Museum'' (volumes I-XXXVI, 1879-1914), which mainly covered the fauna of the Netherlands and the former Dutch colonies. ''Zoologische Mededelingen'' was indexed in ''The Zoological Record'' and ''BIOSIS''. A complete backlist of published volumes is presented on the institutional repository of Naturalis. The last article was published in 2014 and the journal was merged into the ''European Journal of Taxonomy The ''European Journal of Taxonomy'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal for descrip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
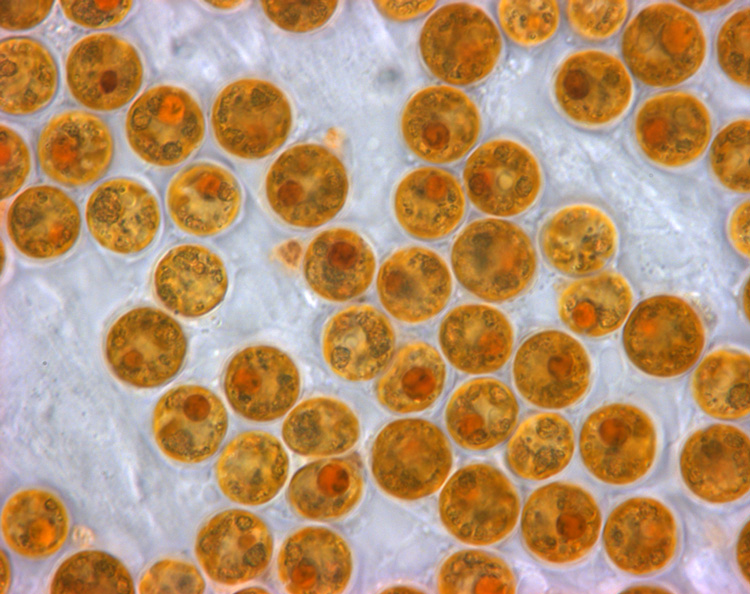
Zooxanthella
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''Symbiodinium'', but some are known from the genus ''Amphidinium'', and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. The true ''Zooxanthella'' K.brandt is a mutualist of the radiolarian ''Collozoum inerme'' (Joh.Müll., 1856) and systematically placed in Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae. Zooxanthellae are photosynthetic organisms, which contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c, as well as the dinoflagellate pigments peridinin and diadinoxanthin. These provide the yellowish and brownish colours typical of many of the host species. During the day, they provide their host with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbiodinium
: ''This is about the genus sometimes called Zoox. For the company, see Zoox (company)'' ''Symbiodinium'' is a genus of dinoflagellates that encompasses the largest and most prevalent group of endosymbiotic dinoflagellates known. These unicellular microalgae commonly reside in the endoderm of tropical cnidarians such as corals, sea anemones, and jellyfish, where the products of their photosynthetic processing are exchanged in the host for inorganic molecules. They are also harbored by various species of demosponges, flatworms, mollusks such as the giant clams, foraminifera ( soritids), and some ciliates. Generally, these dinoflagellates enter the host cell through phagocytosis, persist as intracellular symbionts, reproduce, and disperse to the environment. The exception is in most mollusks, where these symbionts are intercellular (between the cells). Cnidarians that are associated with ''Symbiodinium'' occur mostly in warm oligotrophic (nutrient-poor), marine environments where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |