|
Heron's Formula
In geometry, Heron's formula (or Hero's formula) gives the area of a triangle in terms of the three side lengths , , . If s = \tfrac12(a + b + c) is the semiperimeter of the triangle, the area is, :A = \sqrt. It is named after first-century engineer Heron of Alexandria (or Hero) who proved it in his work ''Metrica'', though it was probably known centuries earlier. Example Let be the triangle with sides , and . This triangle’s semiperimeter is :s=\frac=\frac=16 and so the area is : \begin A &= \sqrt = \sqrt\\ &= \sqrt = \sqrt = 24. \end In this example, the side lengths and area are integers, making it a Heronian triangle. However, Heron's formula works equally well in cases where one or more of the side lengths are not integers. Alternate expressions Heron's formula can also be written in terms of just the side lengths instead of using the semiperimeter, in several ways, :\begin A &=\tfrac\sqrt \\ mu&=\tfrac\sqrt \\ mu&=\tfrac\sqrt \\ mu&=\tfrac\sqrt \\ mu&=\tf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle With Notations 2 Without Points
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC. In Euclidean geometry, any three points, when non-collinear, determine a unique triangle and simultaneously, a unique plane (i.e. a two-dimensional Euclidean space). In other words, there is only one plane that contains that triangle, and every triangle is contained in some plane. If the entire geometry is only the Euclidean plane, there is only one plane and all triangles are contained in it; however, in higher-dimensional Euclidean spaces, this is no longer true. This article is about triangles in Euclidean geometry, and in particular, the Euclidean plane, except where otherwise noted. Types of triangle The terminology for categorizing triangles is more than two thousand years old, having been defined on the very first page of Euclid's Elements. The names used for modern classification are eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics that studies relationships between side lengths and angles of triangles. The field emerged in the Hellenistic world during the 3rd century BC from applications of geometry to astronomical studies. The Greeks focused on the calculation of chords, while mathematicians in India created the earliest-known tables of values for trigonometric ratios (also called trigonometric functions) such as sine. Throughout history, trigonometry has been applied in areas such as geodesy, surveying, celestial mechanics, and navigation. Trigonometry is known for its many identities. These trigonometric identities are commonly used for rewriting trigonometrical expressions with the aim to simplify an expression, to find a more useful form of an expression, or to solve an equation. History Sumerian astronomers studied angle measure, using a division of circles into 360 degrees. They, and later the Babylonians, studied the ratios of the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Cotangents
In trigonometry, the law of cotangentsThe Universal Encyclopaedia of Mathematics, Pan Reference Books, 1976, page 530. English version George Allen and Unwin, 1964. Translated from the German version Meyers Rechenduden, 1960. is a relationship among the lengths of the sides of a triangle and the cotangents of the halves of the three angles. This is also known as the Cot Theorem. Just as three quantities whose equality is expressed by the law of sines are equal to the diameter of the circumscribed circle of the triangle (or to its reciprocal, depending on how the law is expressed), so also the law of cotangents relates the radius of the inscribed circle of a triangle (the inradius) to its sides and angles. Statement Using the usual notations for a triangle (see the figure at the upper right), where , , are the lengths of the three sides, , , are the vertices opposite those three respective sides, , , are the corresponding angles at those vertices, is the semi-perimeter, that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incircle
In geometry, the incircle or inscribed circle of a triangle is the largest circle that can be contained in the triangle; it touches (is tangent to) the three sides. The center of the incircle is a triangle center called the triangle's incenter. An excircle or escribed circle of the triangle is a circle lying outside the triangle, tangent to one of its sides and tangent to the extensions of the other two. Every triangle has three distinct excircles, each tangent to one of the triangle's sides. The center of the incircle, called the incenter, can be found as the intersection of the three internal angle bisectors. The center of an excircle is the intersection of the internal bisector of one angle (at vertex , for example) and the external bisectors of the other two. The center of this excircle is called the excenter relative to the vertex , or the excenter of . Because the internal bisector of an angle is perpendicular to its external bisector, it follows that the center of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Difference Of Squares
In mathematics, the difference of two squares is a squared (multiplied by itself) number subtracted from another squared number. Every difference of squares may be factored according to the identity :a^2-b^2 = (a+b)(a-b) in elementary algebra. Proof The proof of the factorization identity is straightforward. Starting from the left-hand side, apply the distributive law to get :(a+b)(a-b) = a^2+ba-ab-b^2 By the commutative law, the middle two terms cancel: :ba - ab = 0 leaving :(a+b)(a-b) = a^2-b^2 The resulting identity is one of the most commonly used in mathematics. Among many uses, it gives a simple proof of the AM–GM inequality in two variables. The proof holds in any commutative ring. Conversely, if this identity holds in a ring ''R'' for all pairs of elements ''a'' and ''b'', then ''R'' is commutative. To see this, apply the distributive law to the right-hand side of the equation and get :a^2 + ba - ab - b^2. For this to be equal to a^2 - b^2, we must have :ba - ab = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
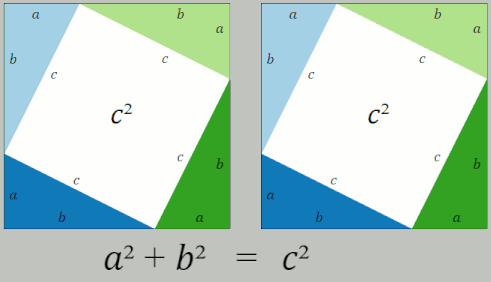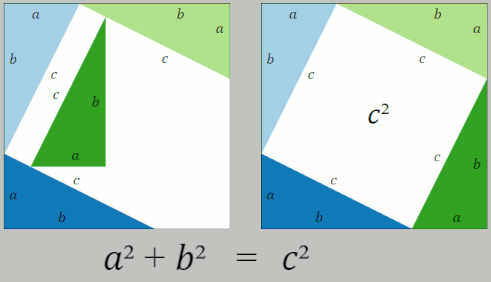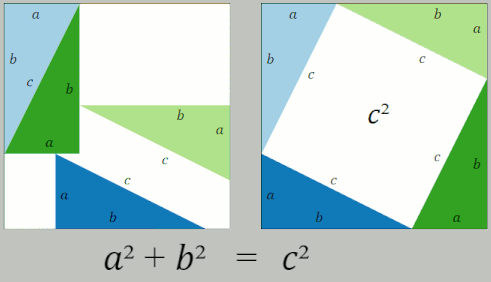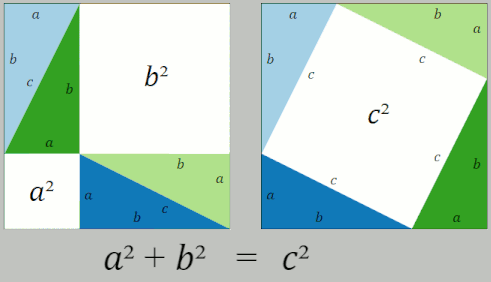
Pythagorean Theorem
In mathematics, the Pythagorean theorem or Pythagoras' theorem is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry between the three sides of a right triangle. It states that the area of the square whose side is the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides. This theorem can be written as an equation relating the lengths of the sides ''a'', ''b'' and the hypotenuse ''c'', often called the Pythagorean equation: :a^2 + b^2 = c^2 , The theorem is named for the Greek philosopher Pythagoras, born around 570 BC. The theorem has been proven numerous times by many different methods – possibly the most for any mathematical theorem. The proofs are diverse, including both geometric proofs and algebraic proofs, with some dating back thousands of years. When Euclidean space is represented by a Cartesian coordinate system in analytic geometry, Euclidean distance satisfies the Pythagorean relation: the squared dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle With Notations 3
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC. In Euclidean geometry, any three points, when non-collinear, determine a unique triangle and simultaneously, a unique plane (i.e. a two-dimensional Euclidean space). In other words, there is only one plane that contains that triangle, and every triangle is contained in some plane. If the entire geometry is only the Euclidean plane, there is only one plane and all triangles are contained in it; however, in higher-dimensional Euclidean spaces, this is no longer true. This article is about triangles in Euclidean geometry, and in particular, the Euclidean plane, except where otherwise noted. Types of triangle The terminology for categorizing triangles is more than two thousand years old, having been defined on the very first page of Euclid's Elements. The names used for modern classification are eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude (triangle)
In geometry, an altitude of a triangle is a line segment through a vertex and perpendicular to (i.e., forming a right angle with) a line containing the base (the side opposite the vertex). This line containing the opposite side is called the ''extended base'' of the altitude. The intersection of the extended base and the altitude is called the ''foot'' of the altitude. The length of the altitude, often simply called "the altitude", is the distance between the extended base and the vertex. The process of drawing the altitude from the vertex to the foot is known as ''dropping the altitude'' at that vertex. It is a special case of orthogonal projection. Altitudes can be used in the computation of the area of a triangle: one half of the product of an altitude's length and its base's length equals the triangle's area. Thus, the longest altitude is perpendicular to the shortest side of the triangle. The altitudes are also related to the sides of the triangle through the trigonometr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Cosines
In trigonometry, the law of cosines (also known as the cosine formula, cosine rule, or al-Kashi's theorem) relates the lengths of the sides of a triangle to the cosine of one of its angles. Using notation as in Fig. 1, the law of cosines states :c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab\cos\gamma, where denotes the angle contained between sides of lengths and and opposite the side of length . For the same figure, the other two relations are analogous: :a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc\cos\alpha, :b^2=a^2+c^2-2ac\cos\beta. The law of cosines generalizes the Pythagorean theorem, which holds only for right triangles: if the angle is a right angle (of measure 90 degrees, or radians), then , and thus the law of cosines reduces to the Pythagorean theorem: :c^2 = a^2 + b^2. The law of cosines is useful for computing the third side of a triangle when two sides and their enclosed angle are known. History Though the notion of the cosine was not yet developed in his time, Euclid's '' Elements'', dating back to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle is the figure formed by two rays, called the '' sides'' of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the '' vertex'' of the angle. Angles formed by two rays lie in the plane that contains the rays. Angles are also formed by the intersection of two planes. These are called dihedral angles. Two intersecting curves may also define an angle, which is the angle of the rays lying tangent to the respective curves at their point of intersection. ''Angle'' is also used to designate the measure of an angle or of a rotation. This measure is the ratio of the length of a circular arc to its radius. In the case of a geometric angle, the arc is centered at the vertex and delimited by the sides. In the case of a rotation, the arc is centered at the center of the rotation and delimited by any other point and its image by the rotation. History and etymology The word ''angle'' comes from the Latin word ''angulus'', meaning "corner"; cognate words are the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebra
Algebra () is one of the broad areas of mathematics. Roughly speaking, algebra is the study of mathematical symbols and the rules for manipulating these symbols in formulas; it is a unifying thread of almost all of mathematics. Elementary algebra deals with the manipulation of variables (commonly represented by Roman letters) as if they were numbers and is therefore essential in all applications of mathematics. Abstract algebra is the name given, mostly in education, to the study of algebraic structures such as groups, rings, and fields (the term is no more in common use outside educational context). Linear algebra, which deals with linear equations and linear mappings, is used for modern presentations of geometry, and has many practical applications (in weather forecasting, for example). There are many areas of mathematics that belong to algebra, some having "algebra" in their name, such as commutative algebra, and some not, such as Galois theory. The word ''alge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |