|
Herbert Cozens-Hardy, 1st Baron Cozens-Hardy
Herbert Hardy Cozens-Hardy, 1st Baron Cozens-Hardy, (1838–1920) was a British politician and judge who served as Master of the Rolls from 1907 until 1918. Early life and career Cozens-Hardy was born in Letheringsett, Norfolk in 1838, the second son of William Hardy Cozens-Hardy, a former Norwich solicitor, and Sarah, ''née'' Theobald, daughter of Thomas Theobald, textile manufacturer. His grandmother was the diarist Mary Hardy. His family were Methodists, a connection which proved to be useful in his career at the bar. Cozens-Hardy was educated at Amersham School and University College, London, where he matriculated in 1858 and gained the LLB in 1863, later becoming a fellow of University College. He was called to the bar at Lincoln's Inn in 1862, and read in the chambers of Thomas Lewin and James Dickinson. Cozens-Hardy acquired a large junior practice at the Chancery bar, and became Queen's Counsel in 1882. It was then the practice of Chancery Queen's Counsels t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Right Honourable
''The Right Honourable'' ( abbreviation: ''Rt Hon.'' or variations) is an honorific style traditionally applied to certain persons and collective bodies in the United Kingdom, the former British Empire and the Commonwealth of Nations. The term is predominantly used today as a style associated with the holding of certain senior public offices in the United Kingdom, Canada, New Zealand, and to a lesser extent, Australia. ''Right'' in this context is an adverb meaning 'very' or 'fully'. Grammatically, ''The Right Honourable'' is an adjectival phrase which gives information about a person. As such, it is not considered correct to apply it in direct address, nor to use it on its own as a title in place of a name; but rather it is used in the third person along with a name or noun to be modified. ''Right'' may be abbreviated to ''Rt'', and ''Honourable'' to ''Hon.'', or both. ''The'' is sometimes dropped in written abbreviated form, but is always pronounced. Countries with common or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lincoln's Inn
The Honourable Society of Lincoln's Inn is one of the four Inns of Court in London to which barristers of England and Wales belong and where they are called to the Bar. (The other three are Middle Temple, Inner Temple and Gray's Inn.) Lincoln's Inn, along with the three other Inns of Court, is recognised as being one of the world's most prestigious professional bodies of judges and lawyers. Lincoln's Inn is situated in Holborn, in the London Borough of Camden, just on the border with the City of London and the City of Westminster, and across the road from London School of Economics and Political Science, Royal Courts of Justice and King's College London's Maughan Library. The nearest tube station is Holborn tube station or Chancery Lane. Lincoln's Inn is the largest Inn, covering . It is believed to be named after Henry de Lacy, 3rd Earl of Lincoln. History During the 12th and early 13th centuries, the law was taught in the City of London, primarily by the clergy. Then two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Ewart Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone ( ; 29 December 1809 – 19 May 1898) was a British statesman and Liberal politician. In a career lasting over 60 years, he served for 12 years as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, spread over four non-consecutive terms (the most of any British prime minister) beginning in 1868 and ending in 1894. He also served as Chancellor of the Exchequer four times, serving over 12 years. Gladstone was born in Liverpool to Scottish parents. He first entered the House of Commons in 1832, beginning his political career as a High Tory, a grouping which became the Conservative Party under Robert Peel in 1834. Gladstone served as a minister in both of Peel's governments, and in 1846 joined the breakaway Peelite faction, which eventually merged into the new Liberal Party in 1859. He was chancellor under Lord Aberdeen (1852–1855), Lord Palmerston (1859–1865) and Lord Russell (1865–1866). Gladstone's own political doctrine—which emphasised equalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rule Against Perpetuities
The rule against perpetuities is a legal rule in the American common law that prevents people from using legal instruments (usually a deed or a will) to exert control over the ownership of private property for a time long beyond the lives of people living at the time the instrument was written. Specifically, the rule forbids a person from creating future interests (traditionally contingent remainders and executory interests) in property that would vest beyond 21 years after the lifetimes of those living at the time of creation of the interest, often expressed as a “life in being plus twenty-one years”. In essence, the rule prevents a person from putting qualifications and criteria in a deed or a will that would continue to affect the ownership of property long after he or she has died, a concept often referred to as control by the "dead hand" or "''mortmain''". The basic elements of the rule against perpetuities originated in England in the 17th century and were "crystallize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortmain
Mortmain () is the perpetual, inalienable ownership of real estate by a corporation or legal institution; the term is usually used in the context of its prohibition. Historically, the land owner usually would be the religious office of a church; today, insofar as mortmain prohibitions against perpetual ownership still exist, it refers most often to modern companies and charitable trusts. The term ''mortmain'' is derived from Mediaeval Latin ''mortua manus'', literally "dead hand", through Old French ''morte main'' (in modern French, ''mainmorte''). History During the Middle Ages in Western European countries such as England, the Roman Catholic Church acquired a substantial amount of real estate. As the Church and religious orders were each recognised as a legal person separate from the office holder who administered the Church land (such as the abbot or the bishop), the land would not escheat on the death of the holder, or pass by inheritance, as the Church and the religious o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Acts Of The Parliament Of The United Kingdom, 1860–1879
This is an ''incomplete'' list of Acts of the Parliament of the United Kingdom for the years 1860–1879. Note that the first parliament of the United Kingdom was held in 1801; parliaments between 1707 and 1800 were either parliaments of Great Britain or of Ireland). For Acts passed up until 1707 see List of Acts of the Parliament of England and List of Acts of the Parliament of Scotland. For Acts passed from 1707 to 1800 see List of Acts of the Parliament of Great Britain. See also the List of Acts of the Parliament of Ireland. For Acts of the devolved parliaments and assemblies in the United Kingdom, see the List of Acts of the Scottish Parliament, the List of Acts of the Northern Ireland Assembly, and the List of Acts and Measures of the National Assembly for Wales; see also the List of Acts of the Parliament of Northern Ireland. The number shown after each Act's title is its chapter number. Acts passed before 1963 are cited using this number, preceded by the year(s) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
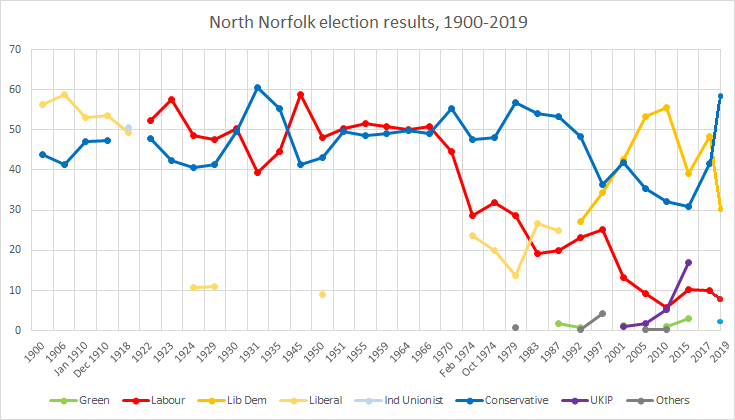
North Norfolk (UK Parliament Constituency)
North Norfolk is a List of United Kingdom Parliament constituencies, constituency represented in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK Parliament since 2019 United Kingdom general election, 2019 by Duncan Baker, a Conservative Party (UK), Conservative. Constituency profile The seat covers a long stretch of the Norfolk coast including the seaside towns of Cromer, Wells-next-the-Sea and Sheringham. History The North Division of Norfolk was first created by the Reform Act 1867 as one of three two-member divisions of the Parliamentary County of Norfolk. Under the Redistribution of Seats Act 1885, the three two-member county divisions were replaced with six single-member divisions. The second version of this constituency was one of the single-member seats. It has remained as a single-member seat since then, being designated as a County Constituency from the 1950 United Kingdom general election, 1950 general electi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Member Of Parliament (United Kingdom)
In the United Kingdom, a member of Parliament (MP) is an individual elected to serve in the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Electoral system All 650 members of the UK House of Commons are elected using the first-past-the-post voting system in single member constituencies across the whole of the United Kingdom, where each constituency has its own single representative. Elections All MP positions become simultaneously vacant for elections held on a five-year cycle, or when a snap election is called. The Fixed-term Parliaments Act 2011 set out that ordinary general elections are held on the first Thursday in May, every five years. The Act was repealed in 2022. With approval from Parliament, both the 2017 and 2019 general elections were held earlier than the schedule set by the Act. If a vacancy arises at another time, due to death or resignation, then a constituency vacancy may be filled by a by-election. Under the Representation of the People Act 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberal Party (UK)
The Liberal Party was one of the two Major party, major List of political parties in the United Kingdom, political parties in the United Kingdom, along with the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party, in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Beginning as an alliance of Whigs (British political party), Whigs, free trade–supporting Peelites and reformist Radicals (UK), Radicals in the 1850s, by the end of the 19th century it had formed four governments under William Ewart Gladstone, William Gladstone. Despite being divided over the issue of Irish Home Rule Movement, Irish Home Rule, the party returned to government in 1905 and won a landslide victory in the 1906 United Kingdom general election, 1906 general election. Under Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, prime ministers Henry Campbell-Bannerman (1905–1908) and H. H. Asquith (1908–1916), the Liberal Party passed Liberal welfare reforms, reforms that created a basic welfare state. Although Asquith was the Leader of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Council Of The Bar
The General Council of the Bar, commonly known as the Bar Council, is the representative body for barristers in England and Wales. Established in 1894, the Bar Council is the 'approved regulator' of barristers, but discharges its regulatory function to the independent Bar Standards Board. As the lead representative body for barristers in England and Wales, the Bar Council’s work is devoted to ensuring the Bar’s voice is heard, efficiently and effectively, and with the interests of the Bar (and the public interest) as its focus. History The General Council of the Bar was created in 1894 to deal with breaches of a barrister's professional etiquette, something that had previously been handled by the judiciary. Along with the Inns of Court it formed the Senate of the Inns of Court and the Bar in 1974, a union that was broken up on 1 January 1987 following a report by Lord Rawlinson. The Courts and Legal Services Act 1990 designated the Bar Council as the professional body for ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ford North
Sir Ford North (10 January 1830 – 12 October 1913), was an English lawyer and judge. Biography North was born in Liverpool. He was the eldest son of John North, a solicitor, and Ellen Haworth. In 1857, he married Elizabeth William Mann."Obituary," ''The Straits Times'', 14 October 1913, p. 9. North was educated at Winchester College and then University College, Oxford. He began his legal studies at the Inner Temple in 1853, and was called to the Bar in 1856. Practising as a barrister, he was named Queen's Counsel in 1877, and was elected a bencher in 1881. He was appointed a judge of the High Court of Justice in 1881, and was knighted. North was sworn in before the Lord Chancellor, Lord Selborne, at his country residence, Blackmoor, Petersfield. Justice North sat originally in the Queen’s Bench Division of the High Court, where he presided over the blasphemy trial of George William Foote; when he sentenced Foote to a lengthy term of imprisonment, Foote responded "My Lord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Appeal (England And Wales)
The Court of Appeal (formally "His Majesty's Court of Appeal in England", commonly cited as "CA", "EWCA" or "CoA") is the highest court within the Senior Courts of England and Wales, and second in the legal system of England and Wales only to the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom. The Court of Appeal was created in 1875, and today comprises 39 Lord Justices of Appeal and Lady Justices of Appeal. The court has two divisions, Criminal and Civil, led by the Lord Chief Justice and the Master of the Rolls and Records of the Chancery of England respectively. Criminal appeals are heard in the Criminal Division, and civil appeals in the Civil Division. The Criminal Division hears appeals from the Crown Court, while the Civil Division hears appeals from the County Court, High Court of Justice and Family Court. Permission to appeal is normally required from either the lower court or the Court of Appeal itself; and with permission, further appeal may lie to the Supreme Court. The C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(cropped).jpg)


.png)