|
Heptatoma
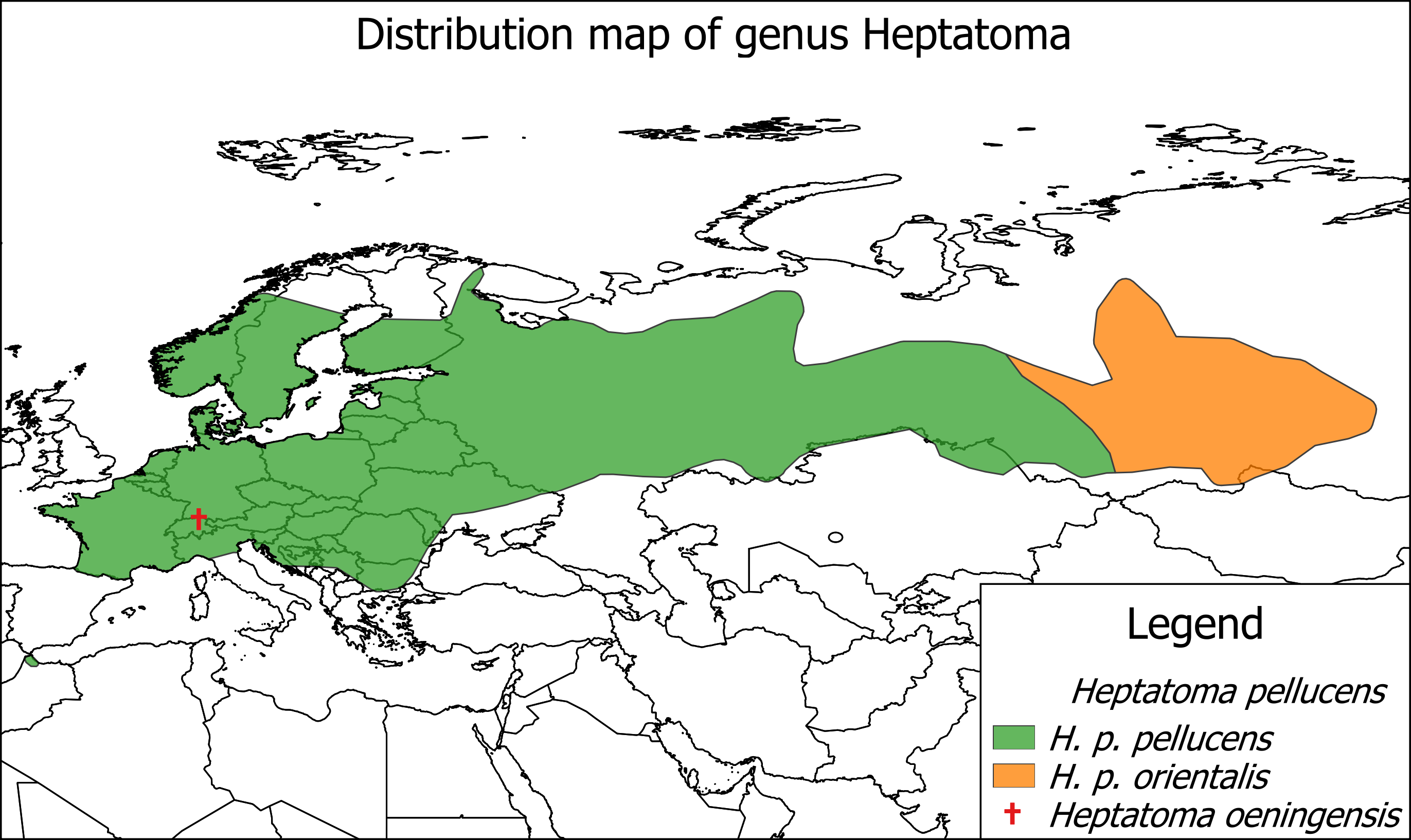
''Heptatoma'' is a genus of European flies belonging to the subfamily Tabaninae. This is effectively a monotypic genus, containing the extant species '' Heptatoma pellucens'' (Fabricius, 1776): of which there are two subspecies (as shown above). The locality of the extinct species ŌĆĀ''Heptatoma oeningensis'' (Heer, 1865) is also shown. Species *'' Heptatoma oeningensis'' (Heer, 1864) *'' Heptatoma pellucens'' (Fabricius Fabricius ( la, smith, german: Schmied, Schmidt) is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *people from the Ancient Roman gens Fabricia: **Gaius Fabricius Luscinus, the first of the Fabricii to move to Rome * Johann Goldsmid (1587ŌĆ ..., 1777) References External links * {{Taxonbar, from=Q18109524, from2=Q1308039 Tabanidae Diptera of Europe Brachycera genera Taxa named by Johann Wilhelm Meigen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heptatoma Pellucens
''Heptatoma'' is a genus of European flies belonging to the subfamily Tabaninae. This is effectively a monotypic genus, containing the extant species '' Heptatoma pellucens'' (Fabricius, 1776): of which there are two subspecies (as shown above). The locality of the extinct species ŌĆĀ''Heptatoma oeningensis'' (Heer, 1865) is also shown. Species *'' Heptatoma oeningensis'' (Heer, 1864) *'' Heptatoma pellucens'' (Fabricius Fabricius ( la, smith, german: Schmied, Schmidt) is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *people from the Ancient Roman gens Fabricia: **Gaius Fabricius Luscinus, the first of the Fabricii to move to Rome * Johann Goldsmid (1587ŌĆ ..., 1777) References External links * {{Taxonbar, from=Q18109524, from2=Q1308039 Tabanidae Diptera of Europe Brachycera genera Taxa named by Johann Wilhelm Meigen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heptatoma Distribution
''Heptatoma'' is a genus of European flies belonging to the subfamily Tabaninae. This is effectively a monotypic genus, containing the extant species ''Heptatoma pellucens'' (Fabricius, 1776): of which there are two subspecies (as shown above). The locality of the extinct species ŌĆĀ''Heptatoma oeningensis'' (Heer, 1865) is also shown. Species *'' Heptatoma oeningensis'' (Heer, 1864) *''Heptatoma pellucens'' (Fabricius Fabricius ( la, smith, german: Schmied, Schmidt) is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *people from the Ancient Roman gens Fabricia: **Gaius Fabricius Luscinus, the first of the Fabricii to move to Rome * Johann Goldsmid (1587ŌĆ ..., 1777) References External links * {{Taxonbar, from=Q18109524, from2=Q1308039 Tabanidae Diptera of Europe Brachycera genera Taxa named by Johann Wilhelm Meigen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heptatoma Oeningensis
''Heptatoma'' is a genus of European flies belonging to the subfamily Tabaninae. This is effectively a monotypic genus, containing the extant species ''Heptatoma pellucens'' (Fabricius, 1776): of which there are two subspecies (as shown above). The locality of the extinct species ŌĆĀ''Heptatoma oeningensis'' (Heer, 1865) is also shown. Species *'' Heptatoma oeningensis'' (Heer, 1864) *''Heptatoma pellucens'' (Fabricius Fabricius ( la, smith, german: Schmied, Schmidt) is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: *people from the Ancient Roman gens Fabricia: **Gaius Fabricius Luscinus, the first of the Fabricii to move to Rome * Johann Goldsmid (1587ŌĆ ..., 1777) References External links * {{Taxonbar, from=Q18109524, from2=Q1308039 Tabanidae Diptera of Europe Brachycera genera Taxa named by Johann Wilhelm Meigen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabaninae
Tabaninae is a subfamily of horse flies in the family Horse-fly, Tabanidae. There are more than 3000 described species in Tabaninae. Tribes and genera Diachlorini *''Acanthocera'' Pierre-Justin-Marie Macquart, Macquart, 1834 *''Acellomyia'' Gonzalez, 1999 *''Anacimas'' G├╝nther Enderlein, Enderlein, 1923 *''Anaerythrops'' Barretto, 1948 *''Atelozella'' Joseph Charles Bequaert, Bequaert, 1930 *''Atelozomyia'' Dias, 1987 *''Bartolomeudiasiella'' Dias, 1987 *''Bolbodimyia'' Jacques-Marie-Frangile Bigot, Bigot, 1892 *''Buestanmyia'' Gonz├Īlez, 2021 *''Catachlorops'' Adolfo Lutz, Lutz, 1909 *''Chalybosoma'' Harold Oldroyd, Oldroyd, 1949 *''Chasmia'' G├╝nther Enderlein, Enderlein, 1922 *''Chlorotabanus'' Adolfo Lutz, Lutz, 1909 *''Cretotabanus'' Graham Fairchild, Fairchild, 1969 *''Cryptotylus'' Adolfo Lutz, Lutz, 1909 *''Cydistomorpha'' Trojan, 1994 *''Cydistomyia'' Taylor, 1919 *''Dasybasis'' Pierre-Justin-Marie Macquart, Macquart, 1847 *''Dasychela'' G├╝nther Enderlein, Enderlein, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Wilhelm Meigen
Johann Wilhelm Meigen (3 May 1764 ŌĆō 11 July 1845) was a German entomologist famous for his pioneering work on Diptera. Life Early years Meigen was born in Solingen, the fifth of eight children of Johann Clemens Meigen and Sibylla Margaretha Bick. His parents, though not poor, were not wealthy either. They ran a small shop in Solingen. His paternal grandparents, however, owned an estate and hamlet with twenty houses. Adding to the rental income, Meigen's grandfather was a farmer and a guild mastercutler in Solingen. Two years after Meigen was born, his grandparents died and his parents moved to the family estate. This was already heavily indebted by the Seven Years' War, then bad crops and rash speculations forced the sale of the farm and the family moved back to Solingen. Meigen attended the town school but only for a short time. He had learned to read and write on his grandfather's estate and he read widely at home as well as taking an interest in natural history. A lodge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flies
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek ╬┤╬╣- ''di-'' "two", and ŽĆŽä╬ĄŽüŽī╬Į ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced mechanosensory organs known as halteres, which act as high-speed sensors of rotational movement and allow dipterans to perform advanced aerobatics. Diptera is a large order containing an estimated 1,000,000 species including horse-flies, crane flies, hoverflies and others, although only about 125,000 species have been described. Flies have a mobile head, with a pair of large compound eyes, and mouthparts designed for piercing and sucking (mosquitoes, black flies and robber flies), or for lapping and sucking in the other groups. Their wing arrangement gives them great maneuverability in flight, and claws and pads on their feet enable them to cling to smooth surfaces. Flies undergo complete metamorphosis; the eggs are often laid on the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Genus
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda.' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extant Taxon
Neontology is a part of biology that, in contrast to paleontology, deals with living (or, more generally, '' recent'') organisms. It is the study of extant taxa (singular: extant taxon): taxa (such as species, genera and families) with members still alive, as opposed to (all) being extinct. For example: * The moose (''Alces alces'') is an extant species, and the dodo (''Raphus cucullatus'') is an extinct species. * In the group of molluscs known as the cephalopods, there were approximately 600 extant species and 7,500 extinct species. A taxon can be classified as extinct if it is broadly agreed or certified that no members of the group are still alive. Conversely, an extinct taxon can be reclassified as extant if there are new discoveries of living species ("Lazarus species"), or if previously-known extant species are reclassified as members of the taxon. Most biologists, zoologists, and botanists are in practice neontologists, and the term neontologist is used large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johan Christian Fabricius
Johan Christian Fabricius (7 January 1745 ŌĆō 3 March 1808) was a Danish zoologist, specialising in "Insecta", which at that time included all arthropods: insects, arachnids, crustaceans and others. He was a student of Carl Linnaeus, and is considered one of the most important entomologists of the 18th century, having named nearly 10,000 species of animals, and established the basis for the modern insect classification. Biography Johan Christian Fabricius was born on 7 January 1745 at T├Ėnder in the Duchy of Schleswig, where his father was a doctor. He studied at the gymnasium at Altona and entered the University of Copenhagen in 1762. Later the same year he travelled together with his friend and relative Johan Zo├½ga to Uppsala, where he studied under Carl Linnaeus for two years. On his return, he started work on his , which was finally published in 1775. Throughout this time, he remained dependent on subsidies from his father, who worked as a consultant at Frederiks Hospita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabanidae
Horse-flies or horseflies are true flies in the family Tabanidae in the insect order Diptera. They are often large and agile in flight, and only the female horseflies bite animals, including humans, to obtain blood. They prefer to fly in sunlight, avoiding dark and shady areas, and are inactive at night. They are found all over the world except for some islands and the polar regions (Hawaii, Greenland, Iceland). Both horse-flies and botflies (Oestridae) are sometimes referred to as gadflies. Adult horse-flies feed on nectar and plant exudates; the males have weak mouthparts and only the females bite animals to obtain enough protein from blood to produce eggs. The mouthparts of females are formed into a stout stabbing organ with two pairs of sharp cutting blades, and a spongelike part used to lap up the blood that flows from the wound. The larvae are predaceous and grow in semiaquatic habitats. Female horse-flies can transfer blood-borne diseases from one animal to anoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diptera Of Europe
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek ╬┤╬╣- ''di-'' "two", and ŽĆŽä╬ĄŽüŽī╬Į ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced mechanosensory organs known as halteres, which act as high-speed sensors of rotational movement and allow dipterans to perform advanced aerobatics. Diptera is a large order containing an estimated 1,000,000 species including horse-flies, crane flies, hoverflies and others, although only about 125,000 species have been described. Flies have a mobile head, with a pair of large compound eyes, and mouthparts designed for piercing and sucking (mosquitoes, black flies and robber flies), or for lapping and sucking in the other groups. Their wing arrangement gives them great maneuverability in flight, and claws and pads on their feet enable them to cling to smooth surfaces. Flies undergo complete metamorphosis; the eggs are often laid on the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(10144905255).jpg)
.jpg)
