|
Hepatitis C Virus-associated Diseases
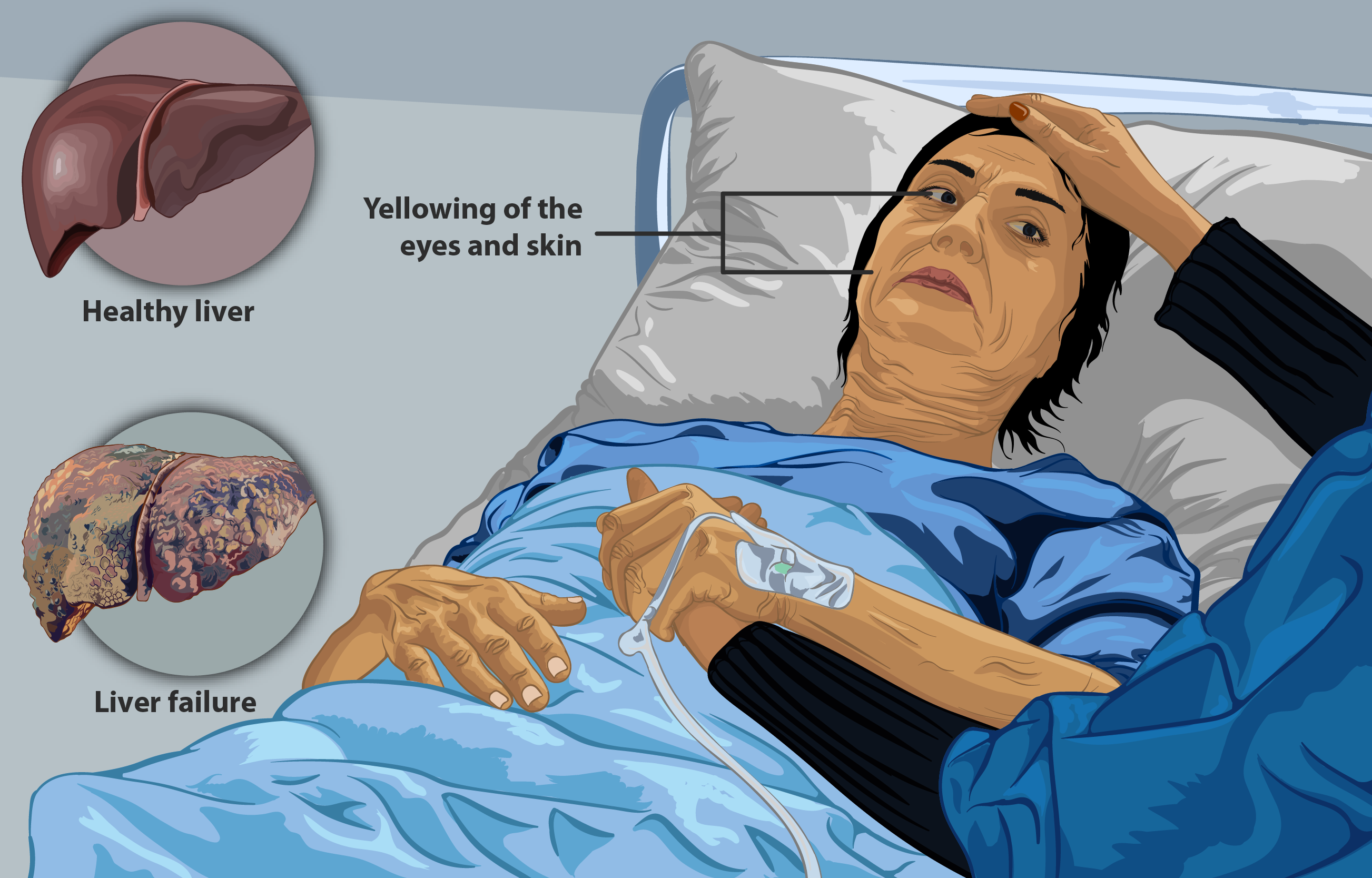
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver tissue. Some people or animals with hepatitis have no symptoms, whereas others develop yellow discoloration of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), poor appetite, vomiting, tiredness, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Hepatitis is '' acute'' if it resolves within six months, and '' chronic'' if it lasts longer than six months. Acute hepatitis can resolve on its own, progress to chronic hepatitis, or (rarely) result in acute liver failure. Chronic hepatitis may progress to scarring of the liver ( cirrhosis), liver failure, and liver cancer. Hepatitis is most commonly caused by the virus '' hepatovirus A'', '' B'', '' C'', '' D'', and '' E''. Other viruses can also cause liver inflammation, including cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus, and yellow fever virus. Other common causes of hepatitis include heavy alcohol use, certain medications, toxins, other infections, autoimmune diseases, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcoholic hepatitis is hepatitis (inflammation of the liver) due to excessive intake of alcohol. Patients typically have a history of at least 10 years of heavy alcohol intake, typically 8-10 drinks per day. It is usually found in association with fatty liver, an early stage of alcoholic liver disease, and may contribute to the progression of fibrosis, leading to cirrhosis. Symptoms may present acutely after a large amount of alcoholic intake in a short time period, or after years of excess alcohol intake. Signs and symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), ascites (fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity), fatigue and hepatic encephalopathy (brain dysfunction due to liver failure). Mild cases are self-limiting, but severe cases have a high risk of death. Severe cases may be treated with glucocorticoids. The condition often comes on suddenly and may progress in severity very rapidly. Signs and symptoms Alcoholic hepatitis is charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue (medicine)
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve after rest or sleep, or occurs independently of physical or mental exertion, it may be a symptom of a medical condition that may become severe or progressive. Fatigue can be a feature of a mental disorder such as depression; may be associated with conditions of chronic pain such as fibromyalgia; it may also feature in conditions of chronic low-level inflammation, and be a disease-related symptom in many other conditions. Fatigue often has no known cause, and is recognised as being very complex in nature. Fatigability describes a susceptibility to fatigue. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of cognitive activity which impairs cognitive abil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (''CMV'') (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order ''Herpesvirales'', in the family ''Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily ''Betaherpesvirinae''. Humans and other primates serve as natural hosts. The 11 species in this genus include ''human betaherpesvirus 5'' (HCMV, human cytomegalovirus, HHV-5), which is the species that infects humans. Diseases associated with HHV-5 include mononucleosis and pneumonia. In the medical literature, most mentions of CMV without further specification refer implicitly to human CMV. Human CMV is the most studied of all cytomegaloviruses. MX2/MXB was identified as a restriction factor for herpesviruses, which acts at a very early stage of the replication cycle and MX2/MXB restriction of herpesvirus requires GTPase activity. Taxonomy Within the ''Herpesviridae'', CMV belongs to the ''Betaherpesvirinae'' subfamily, which also includes the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is liver inflammation due to a viral infection. It may present in acute form as a recent infection with relatively rapid onset, or in chronic form. The most common causes of viral hepatitis are the five unrelated hepatotropic viruses hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E. Other viruses can also cause liver inflammation, including cytomegalovirus, Epstein–Barr virus, and yellow fever. There also have been scores of recorded cases of viral hepatitis caused by herpes simplex virus. Mode Of Transmission Viral hepatitis is either transmitted through contaminated food or water (A, E) or via blood and body fluids (B, C). The viruses transmitted through water and food are mostly self-limited, resulting in acute illness with full resolution. The blood borne viruses (B, C) can cause both acute and chronic liver disease and can be transmitted from mother to child during birth, through contact with body fluids during sex, unsafe injections and through unscreened blood transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis E Virus
The hepatitis E virus (HEV) is the causative agent of hepatitis E. It is of the species ''Orthohepevirus A.'' Globally, approximately 939 million corresponding to 1 in 8 individuals have ever experienced HEV infection. About 15–110 million individuals have recent or ongoing HEV infection. The virus particle was first seen in 1983, but was only molecularly cloned in 1989. Genome and proteome ''Orthohepevirus A'' can be classified into eight different genotypes from different geographical regions: genotype 1 (Asia), genotype 2 (Africa and Mexico), genotype 3 (Europe and North America), genotype 4 (Asia); genotypes 5 and 6 have been detected in Asian wild boar and genotypes 7 and 8 in camels.Schlauder, G. G. & Mushahwar, I. K. (2001) Genetic heterogeneity of hepatitis E virus. J Med Virol 65, 282–92 The viral genome is a single strand of positive-sense RNA that is about 7200 bases in length. The three open-reading frames (ORF1, ORF2 and ORF3) encode for three proteins (O1, O2, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis D Virus
Hepatitis D is a type of viral hepatitis caused by the hepatitis delta virus (HDV). HDV is one of five known hepatitis viruses: hepatitis A, A, hepatitis B, B, hepatitis C, C, D, and hepatitis E, E. HDV is considered to be a Satellite (biology), satellite (a type of subviral agent) because it can propagate only in the presence of the hepatitis B, hepatitis B virus (HBV). Transmission of HDV can occur either via simultaneous infection with HBV (coinfection) or superimposed on chronic hepatitis B or hepatitis B carrier state (superinfection). HDV infecting a person with chronic hepatitis B (superinfection) is considered the most serious type of viral hepatitis due to its severity of complications. These complications include a greater likelihood of experiencing liver failure in acute infections and a rapid progression to liver cirrhosis, with an increased risk of developing liver cancer in chronic infections. In combination with hepatitis B virus, hepatitis D has the highest fatality ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis C Virus
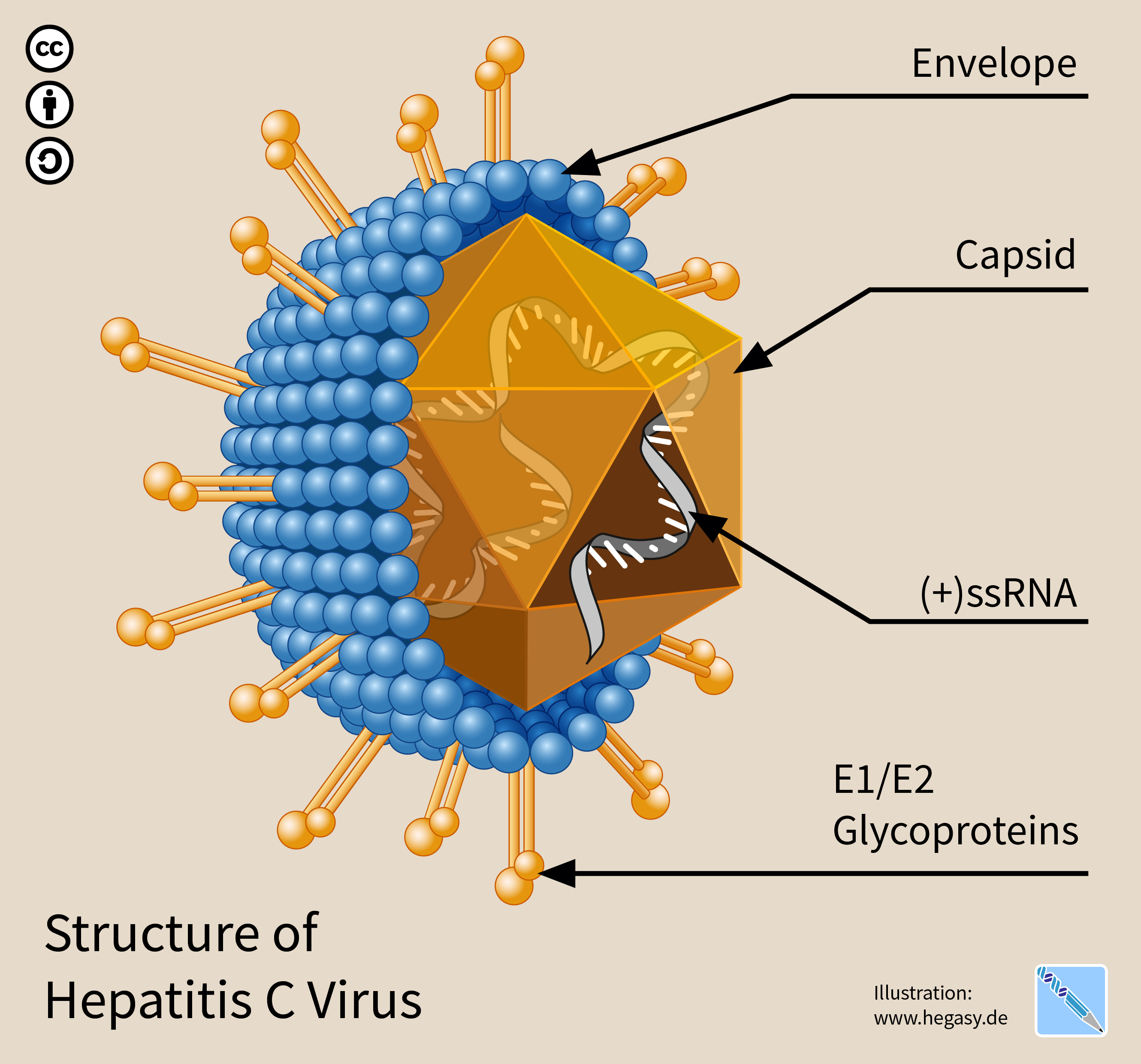
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer ( hepatocellular carcinoma, abbreviated HCC) and lymphomas in humans. Taxonomy The hepatitis C virus belongs to the genus ''Hepacivirus'', a member of the family ''Flaviviridae''. Before 2011, it was considered to be the only member of this genus. However a member of this genus has been discovered in dogs: canine hepacivirus. There is also at least one virus in this genus that infects horses. Several additional viruses in the genus have been described in bats and rodents. Structure The hepatitis C virus particle consists of a lipid membrane envelope that is 55 to 65 nm in diameter. Two viral envelope glycoproteins, E1 and E2, are embedded in the lipid envelope. They take part in viral attachment and entry into the cell. Within the envel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis B Virus
''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus ''Orthohepadnavirus'' and a member of the ''Hepadnaviridae'' family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B. Disease Despite there being a vaccine to prevent Hepatitis B, HBV remains a global health problem. Hepatitis B can be acute and later become chronic, leading to other diseases and health conditions. In addition to causing hepatitis, infection with HBV can lead to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. It has also been suggested that it may increase the risk of pancreatic cancer. Roles in disease Viral infection by ''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) causes many hepatocyte changes due to the direct action of a protein encoded by the virus, HBx, and to indirect changes due to a large increase in intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) after infection. HBx appears to dysregulate a number of cellular pathways. HBx causes dysregulation in part by binding to genomic DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatovirus A
Hepatitis A is an infectious disease of the liver caused by ''Hepatovirus A'' (HAV); it is a type of viral hepatitis. Many cases have few or no symptoms, especially in the young. The time between infection and symptoms, in those who develop them, is 2–6 weeks. When symptoms occur, they typically last 8 weeks and may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, jaundice, fever, and abdominal pain. Around 10–15% of people experience a recurrence of symptoms during the 6 months after the initial infection. Acute liver failure may rarely occur, with this being more common in the elderly. It is usually spread by eating food or drinking water contaminated with infected feces. Undercooked or raw shellfish are relatively common sources. It may also be spread through close contact with an infectious person. While children often do not have symptoms when infected, they are still able to infect others. After a single infection, a person is immune for the rest of his or her life. Diagnosis requir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Liver Failure
Acute liver failure is the appearance of severe complications rapidly after the first signs (such as jaundice) of liver disease, and indicates that the liver has sustained severe damage (loss of function of 80–90% of liver cells). The complications are hepatic encephalopathy and impaired protein synthesis (as measured by the levels of serum albumin and the prothrombin time in the blood). The 1993 classification defines ''hyperacute'' as within 1 week, ''acute'' as 8–28 days, and ''subacute'' as 4–12 weeks; both the speed with which the disease develops and the underlying cause strongly affect outcomes. Signs and symptoms The main features of acute liver failure are rapid-onset jaundice, weakness, and eventually, changes in mental status that can begin as mild confusion but progress to coma, known as hepatic encephalopathy. Encephalopathy and cerebral edema In ALF, hepatic encephalopathy leads to cerebral edema, coma, brain herniation, and eventually death. Detection of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-limiting (biology)
In biology, a self-limiting organism or colony of organisms limits its own growth by its actions. For example, a single organism may have a maximum size determined by genetics, or a colony of organisms may release waste which is ultimately toxic to the colony once it exceeds a certain population. In some cases, the self-limiting nature of a colony may be advantageous to the continued survival of the colony, such as in the case of parasites. If their numbers became too high, they would kill the host, and thus themselves. In other cases, self-limitation restricts the viability of predators, thus ensuring the long-term survival of rare species. In medicine Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ..., the term may imply that a condition would run its course without the need of ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Condition
A chronic condition is a health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term ''chronic'' is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months. Common chronic diseases include diabetes, functional gastrointestinal disorder, eczema, arthritis, asthma, cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Lyme disease, autoimmune diseases, genetic disorders and some viral diseases such as hepatitis C and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. An illness which is lifelong because it ends in death is a terminal illness. It is possible and not unexpected for an illness to change in definition from terminal to chronic. Diabetes and HIV for example were once terminal yet are now considered chronic due to the availability of insulin for diabetics and daily drug treatment for individuals with HIV which allow these individuals to live while managing symptoms. In medicine, ''chronic'' conditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |