|
Henryk Sławik
Henryk Sławik (16 July 1894 – 23 August 1944) was a Polish politician in the interwar period, social worker, activist, and diplomat, who during World War II helped save over 30,000 Polish refugees, including 5,000 Polish Jews in Budapest, Hungary, by giving them false Polish passports with Catholic designation. He was executed with some of his fellow Polish activists on order of Reichsführer SS in concentration camp Gusen on 23 August 1944. Life Henryk Sławik was born 16 July 1894 in ''Timmendorf'' (now Szeroka, a part of Jastrzębie-Zdrój), into an impoverished Polish Silesian family as one of its 5 children. He was sent by his mother to an academic secondary school. After graduation, Sławik left his hometown for Pszczyna where he was drafted to the army during World War I. Released from internment in 1918, he joined the Polish Socialist Party in Upper Silesia and went to Warsaw for additional training. He took active part in the Silesian Plebiscite as one of its or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szeroka
Szeroka (german: Timmendorf) is a sołectwo of Jastrzębie-Zdrój, Silesian Voivodeship, southern Poland. It was an independent village but became administratively part of Jastrzębie-Zdrój in 1975. It has na area of 1026.64 ha and on December 31, 2012 it had 2,325 inhabitants. History The village was first mentioned in a Latin document of Diocese of Wrocław called ''Liber fundationis episcopatus Vratislaviensis'' from around 1305 as ''item in Syroka et in Gogolow debent esse LIII) mansi''. The creation of the village was a part of a larger settlement campaign taking place in the late 13th century on the territory of what would later be known as Upper Silesia. In 1321 appears the German name of the village, ''Tymendorf'', which eventually evolved into ''Timmendorf''. A Catholic parish was established in the early years of the village. It was mentioned in the register of Peter's Pence payment from 1447 among the parishes of Żory Deanery as ''Tunsdorff''. Politically the vill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies located around the world. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The bishopric of Rome, known as the Holy See, is the central governing authority of the church. The administrative body of the Holy See, the Roman Curia, has its principal offices in Vatican City, a small enclave of the Italian city of Rome, of which the pope is head of state. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kraków Army
Kraków Army ( pl, Armia Kraków) was one of the Polish armies which took part in the Polish Defensive War of 1939. It was officially created on March 23, 1939 as the main pivot of Polish defence. It was commanded by Gen. Antoni Szylling. Originally, Kraków Army was to be made of seven infantry divisions, two cavalry brigades and one mountain brigade. On September 1, 1939, General Szylling had the force which consisted of five infantry divisions, two cavalry brigades and one brigade of mountain infantry. Altogether, the army was made of 59 battalions, 29 squadrons, 352 cannons, 90 tanks, two armoured trains and 44 planes. These forces were not enough to halt German advance, especially in the area north of Częstochowa, where Kraków Army connected with Łódź Army. Main thrust of Wehrmacht panzer units was directed there, and this area was defended only by the Polish 7th I.D., which was destroyed in the early days of September 1939, opening the way towards central Poland. Creati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
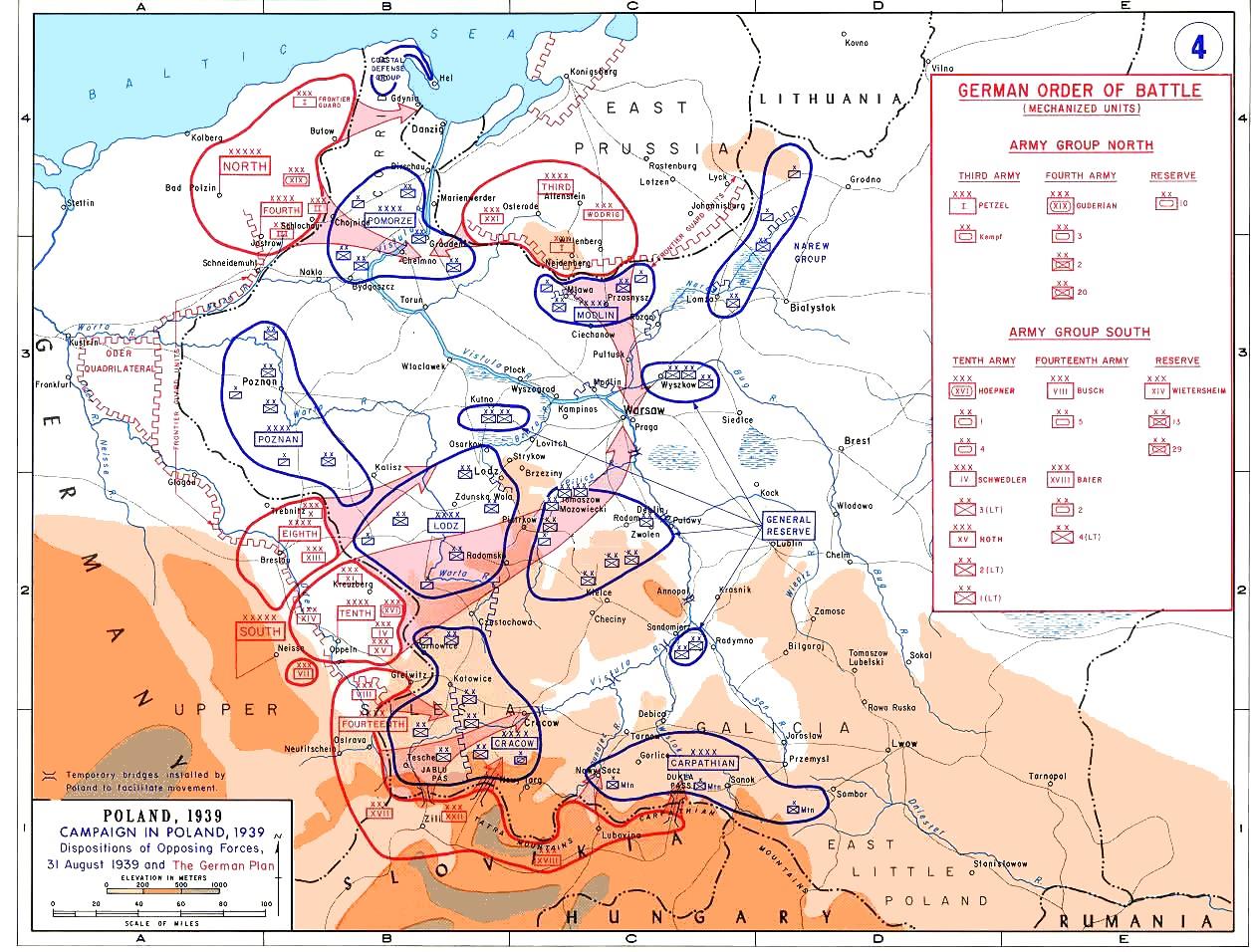
Invasion Of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week after the signing of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact between Germany and the Soviet Union, and one day after the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union had approved the pact. The Soviets invaded Poland on 17 September. The campaign ended on 6 October with Germany and the Soviet Union dividing and annexing the whole of Poland under the terms of the German–Soviet Frontier Treaty. The invasion is also known in Poland as the September campaign ( pl, kampania wrześniowa) or 1939 defensive war ( pl, wojna obronna 1939 roku, links=no) and known in Germany as the Poland campaign (german: Überfall auf Polen, Polenfeldzug). German forces invaded Poland from the north, south, and west the morning after the Gleiwitz incident. Slovak military forces ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zagłębie Dąbrowskie
Zagłębie in Polish means coalfield. It can refer to: *Górnośląskie Zagłębie Węglowe, a mining region *Zagłębie Dąbrowskie, a mining region *Zagłębie Sosnowiec, an association football club *Zagłębie Lubin, an association football club *Zagłębie Wałbrzych, an association football club *Zagłębie Steelers, a Polish club of American football *KH Zagłębie Sosnowiec KH Zagłębie Sosnowiec is an ice hockey team from Sosnowiec, Poland Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . ... an ice hockey club * MKS Zagłębie Lubin, a women's handball team {{disamb, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanacja
Sanation ( pl, Sanacja, ) was a Polish political movement that was created in the interwar period, prior to Józef Piłsudski's May 1926 ''Coup d'État'', and came to power in the wake of that coup. In 1928 its political activists would go on to form the Nonpartisan Bloc for Cooperation with the Government (BBWR). The Sanation movement took its name from Piłsudski's aspirations for a moral "sanation" (healing) of the Polish body politic. The movement functioned integrally until his death in 1935. Following Piłsudski's death, Sanation split into several competing factions, including "the Castle" (President Ignacy Mościcki and his partisans)."''Sanacja''," ''Encyklopedia Polski'', p. 601. Sanation, which advocated authoritarian rule, rested on a circle of Piłsudski's close associates, including Walery Sławek, Aleksander Prystor, Kazimierz Świtalski, Janusz Jędrzejewicz, Adam Koc, Józef Beck, Tadeusz Hołówko, Bogusław Miedziński, and Edward Rydz-Śmigły. It preac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Editor-in-chief
An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The highest-ranking editor of a publication may also be titled editor, managing editor, or executive editor, but where these titles are held while someone else is editor-in-chief, the editor-in-chief outranks the others. Description The editor-in-chief heads all departments of the organization and is held accountable for delegating tasks to staff members and managing them. The term is often used at newspapers, magazines, yearbooks, and television news programs. The editor-in-chief is commonly the link between the publisher or proprietor and the editorial staff. The term is also applied to academic journals, where the editor-in-chief gives the ultimate decision whether a submitted manuscript will be published. This decision is made by the editor-in-chief after seeking input from reviewers selected on the basis of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesian Plebiscite
The Upper Silesia plebiscite was a plebiscite mandated by the Versailles Treaty and carried out on 20 March 1921 to determine ownership of the province of Upper Silesia between Weimar Germany and Poland. The region was ethnically mixed with both Germans and Poles; according to prewar statistics, ethnic Poles formed 60 percent of the population. Under the previous rule by the German Empire, Poles claimed they had faced discrimination, making them effectively second class citizens. The period of the plebiscite campaign and inter- Allied occupation was marked by violence. There were three Polish uprisings, and German volunteer paramilitary units came to the region as well. The area was policed by French, British, and Italian troops, and overseen by an Inter-Allied Commission. The Allies planned a partition of the region, but a Polish insurgency took control of over half the area. The Germans responded with volunteer paramilitary units from all over Germany, which fought the Polis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( pl, Górny Śląsk; szl, Gůrny Ślůnsk, Gōrny Ślōnsk; cs, Horní Slezsko; german: Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ; la, Silesia Superior) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. Since the 9th century, Upper Silesia has been part of (chronologically) Greater Moravia, the Duchy of Bohemia, the Piast Kingdom of Poland, again of the Lands of the Bohemian Crown and the Holy Roman Empire, as well as of the Habsburg monarchy from 1526. In 1742 the greater part of Upper Silesia was annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia, and in 1871 it became part of the German Empire. After the First World War the region was divided between Poland (East Upper Silesia) and Germany (West Upper Silesia). After the Second World War, West Upper Silesia also became Polish as the result of the Potsdam Conference. Geography Upper Silesia is situated on the upper Oder River, north o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Socialist Party
The Polish Socialist Party ( pl, Polska Partia Socjalistyczna, PPS) is a socialist political party in Poland. It was one of the most important parties in Poland from its inception in 1892 until its merger with the communist Polish Workers' Party to form the Polish United Workers' Party in 1948. Józef Piłsudski, founder of the Second Polish Republic, belonged to and later led the PPS in the early 20th century. The party was re-established in 1987, near the end of the Polish People's Republic. However, it remained in the margins of Polish politics until 2019, when it was able to win a seat in the Senate of Poland. History The PPS was founded in Paris in 1892 (see the Great Emigration). In 1893 the party called Social Democracy of the Kingdom of Poland and Lithuania, (SDKPiL), emerged from the PPS, with the PPS being more nationalist and oriented towards Polish independence, and the SDKPiL being more revolutionary and communist. In November 1892 the leading personalities of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pszczyna
Pszczyna (german: Pleß, cs, Pština) is a town in southern Poland with 25,823 inhabitants (2019), and a seat of a local gmina (commune). It is situated in the Silesian Voivodeship, and was a part of the Katowice Voivodeship from 1975 until administrative reforms in 1998. Etymology There are several different theories of the origins of the name ''Pszczyna''. Ezechiel Zivier (1868–1925) hypothesized that the land was first owned by Pleszko (alternatively Leszko, or possibly Leszek, Duke of Racibórz). Polish scholar Aleksander Brückner in turn explained the name based on its old spelling ''Plszczyna'', from the ancient Polish word ''pło'' or ''pleso'' meaning a lake, making ''Plszczyna'' a place by a lake. Brückner's derivation, suggesting a marshy lakeside, based on Proto-Slavic ''plszczyna'', is generally accepted in literature. Yet another explanation has been put forward by Prof. Jan Miodek of Wrocław University, who derives the town's name from the name of a nearby ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gymnasium (school)
''Gymnasium'' (and variations of the word) is a term in various European languages for a secondary school that prepares students for higher education at a university. It is comparable to the US English term '' preparatory high school''. Before the 20th century, the gymnasium system was a widespread feature of educational systems throughout many European countries. The word (), from Greek () 'naked' or 'nude', was first used in Ancient Greece, in the sense of a place for both physical and intellectual education of young men. The latter meaning of a place of intellectual education persisted in many European languages (including Albanian, Bulgarian, Estonian, Greek, German, Hungarian, the Scandinavian languages, Dutch, Polish, Czech, Serbo-Croatian, Macedonian, Slovak, Slovenian and Russian), whereas in other languages, like English (''gymnasium'', ''gym'') and Spanish (''gimnasio''), the former meaning of a place for physical education was retained. School structure Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

.jpg)