|
Henry Samuel Chapman
Henry Samuel Chapman (21 July 1803 – 27 December 1881) was an Australian and New Zealand judge, colonial secretary, attorney-general, journalist and politician. Early life Chapman was born at Kennington, London, the son of Henry Chapman, English civil servant, and his wife Ann, daughter of Rev. Thomas Hart Davies. Chapman was educated privately at Bromley, Kent. In 1818, he entered a bank, then in 1823 emigrated to Quebec, Canada where he went into business as a commission merchant. In 1833 he started the first Canadian daily newspapers, the radical ''Montreal Daily Advertiser'', in association with Samuel Revans. In 1835, Chapman returned to England as a salaried intermediary between the Legislative Assembly of Lower Canada and its friends in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom. Chapman remained in England for some time and took up the study of law, being admitted to the bar of the Middle Temple in 1840. Five years earlier he had published ''The Act for the Regulation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kennington
Kennington is a district in south London, England. It is mainly within the London Borough of Lambeth, running along the boundary with the London Borough of Southwark, a boundary which can be discerned from the early medieval period between the Lambeth and St George's parishes of those boroughs respectively. It is located south of Charing Cross in Inner London and is identified as a local centre in the London Plan. It was a royal manor in the parish of Lambeth (parish), St Mary, Lambeth in the Surrey, county of Surrey and was the administrative centre of the parish from 1853. Proximity to central London was key to the development of the area as a residential suburb and it was Metropolis Management Act 1855, incorporated into the metropolitan area of London in 1855. Kennington is the location of three significant London landmarks: the Oval cricket ground, the Imperial War Museum, and Kennington Park. Its population at the United Kingdom Census 2011 was 15,106. Kennington is serve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawhia
Kawhia Harbour (Maori: ''Kāwhia'') is one of three large natural inlets in the Tasman Sea coast of the Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. It is located to the south of Raglan Harbour, Ruapuke and Aotea Harbour, 40 kilometres southwest of Hamilton. Kawhia is part of the Ōtorohanga District Council and is in the King Country. It has a high-tide area of and a low-tide area of . Te Motu Island is located in the harbour. The settlement of Kawhia is located on the northern coast of the inlet, and was an important port in early colonial New Zealand. The area of Kawhia comprises and is the town block that was owned by the New Zealand Government. The government bought it from the Europeans in 1880 "not from the original Māori owners, but from a European who claimed ownership in payment of money owed by another European". History and culture Early history The Kawhia Harbour is the southernmost location where kauri trees historically grew. Kawhia is known in Māori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John O'Shanassy
Sir John O'Shanassy, KCMG (18 February 1818 – 5 May 1883), was an Irish-Australian politician who served as the 2nd Premier of Victoria. O'Shanassy was born near Thurles in County Tipperary, Ireland, the son of a surveyor, and came to the Port Phillip District (later Victoria) in 1839. He went into business in Melbourne as a draper, and by 1846 he was rich enough to be elected to the Melbourne City Council and to become the founding chairman of the Colonial Bank of Australasia. By the 1850s he was a major landowner and one of the wealthiest men in the colony. He also became a recognised leader of the large Irish Catholic community. Biography O'Shanassy was elected to the inaugural Victorian Legislative Council for City of Melbourne in 1851. When Victoria gained responsible government in 1856, he was elected to the Legislative Assembly for both Melbourne and Kilmore districts, he decided to represent the latter resulting in a by-election for Melbourne. In 1868 he returned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attorney-General Of Victoria (Australia)
The Attorney-General of Victoria, in formal contexts also Attorney-General or Attorney General for Victoria, is a minister in the Government of Victoria, Australia. The Attorney-General is a senior minister in the state government and the First Law Officer of the State. The current Attorney-General of Victoria has, since December 2020, been Jaclyn Symes of the Australian Labor Party. The Attorney-General is one of the ministers who administer parts of the Victorian Department of Justice and Community Safety, with responsibility for the state's courts and tribunals. Bill Slater served as Attorney-General of Victoria 6 separate times and Arthur Rylah holds the record for the longest term of 11 years and 334 days. List of attorneys-general of Victoria See also * Justice ministry * Politics of Victoria References {{Victorian ministries Victoria Attorney-General of Victoria The Attorney-General of Victoria, in formal contexts also Attorney-General or Attorney Ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral District Of St Kilda
The Electoral district of St Kilda was one of the inaugural electoral districts of the Victorian Legislative Assembly, abolished on 2 October 1992. St Kilda was one of the initial districts created in the first Victorian Legislative Assembly, 1856. It included an area south of the Yarra River and the then villages of St Kilda and Elsternwick. Members for St Kilda Two members initially, one after the redistribution of 1889. Election results See also * Parliaments of the Australian states and territories * List of members of the Victorian Legislative Assembly {{{Use dmy dates, date=June 2015 {{Use Australian English, date=June 2015 The following are lists of members of the Victorian Legislative Assembly: * Members of the Victorian Legislative Assembly, 1856–1859 * Members of the Victorian Legislative ... References * Former electoral districts of Victoria (Australia) 1856 establishments in Australia 1992 disestablishments in Australia Constituencies establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral District Of South Bourke, Evelyn And Mornington
''For the lower house seats in the Victorian Legislative Assembly, see South Bourke 1856–1889, or Evelyn and Mornington 1856–1859.'' The Electoral district of South Bourke, Evelyn and Mornington was one of the sixteen electoral districts of the original unicameral Victorian Legislative Council of 1851 to 1856. From 1856 onwards, the Victorian parliament consisted of two houses, the Victorian Legislative Council (upper house, consisting of Provinces) and the Victorian Legislative Assembly (lower house). Members of South Bourke, Evelyn and Mornington One member originally, two from the expanded Council of 1853.Sweetman p.109 Miller went on to represent Central Province in the Legislative Council from November 1856. Dane later represented the Electoral district of Warrnambool in the Victorian Legislative Assembly from November 1864. Chapman later represented the Electoral district of St Kilda in the Victorian Legislative Assembly from January 1858 and Electoral distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian Legislative Council
The Victorian Legislative Council (VLC) is the upper house of the bicameral Parliament of Victoria, Australia, the lower house being the Legislative Assembly. Both houses sit at Parliament House in Spring Street, Melbourne. The Legislative Council serves as a house of review, in a similar fashion to its federal counterpart, the Australian Senate. Although, it is possible for legislation to be first introduced in the Council, most bills receive their first hearing in the Legislative Assembly. The presiding officer of the chamber is the President of the Legislative Council. The Council presently comprises 40 members serving four-year terms from eight electoral regions each with five members. With each region electing 5 members using the single transferable vote, the quota in each region for election, after distribution of preferences, is 16.7% (one-sixth). Ballot papers for elections for the Legislative Council have above and below the line voting. Voting above the line requir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Denison
Sir William Thomas Denison (3 May 1804 – 19 January 1871) was Lieutenant Governor of Van Diemen's Land from 1847 to 1855, Governor of New South Wales from 1855 to 1861, and Governor of Madras from 1861 to 1866. According to Percival Serle, Denison was a man of high character and a good administrator. In his early days in Tasmania he spoke too frankly about the colonists in communications which he regarded as confidential, and this accentuated the feeling against him as a representative of the colonial office during the anti-transportation and responsible government movements. He showed great interest in the life of the colony, and helped to foster education, science and trade, during the period when Tasmania was developing into a prosperous colony. In New South Wales his task was easier, and he had no difficulty in coping adequately with the problems that arose during the early days of responsible government in Australia. Early life Denison was the third son of John De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
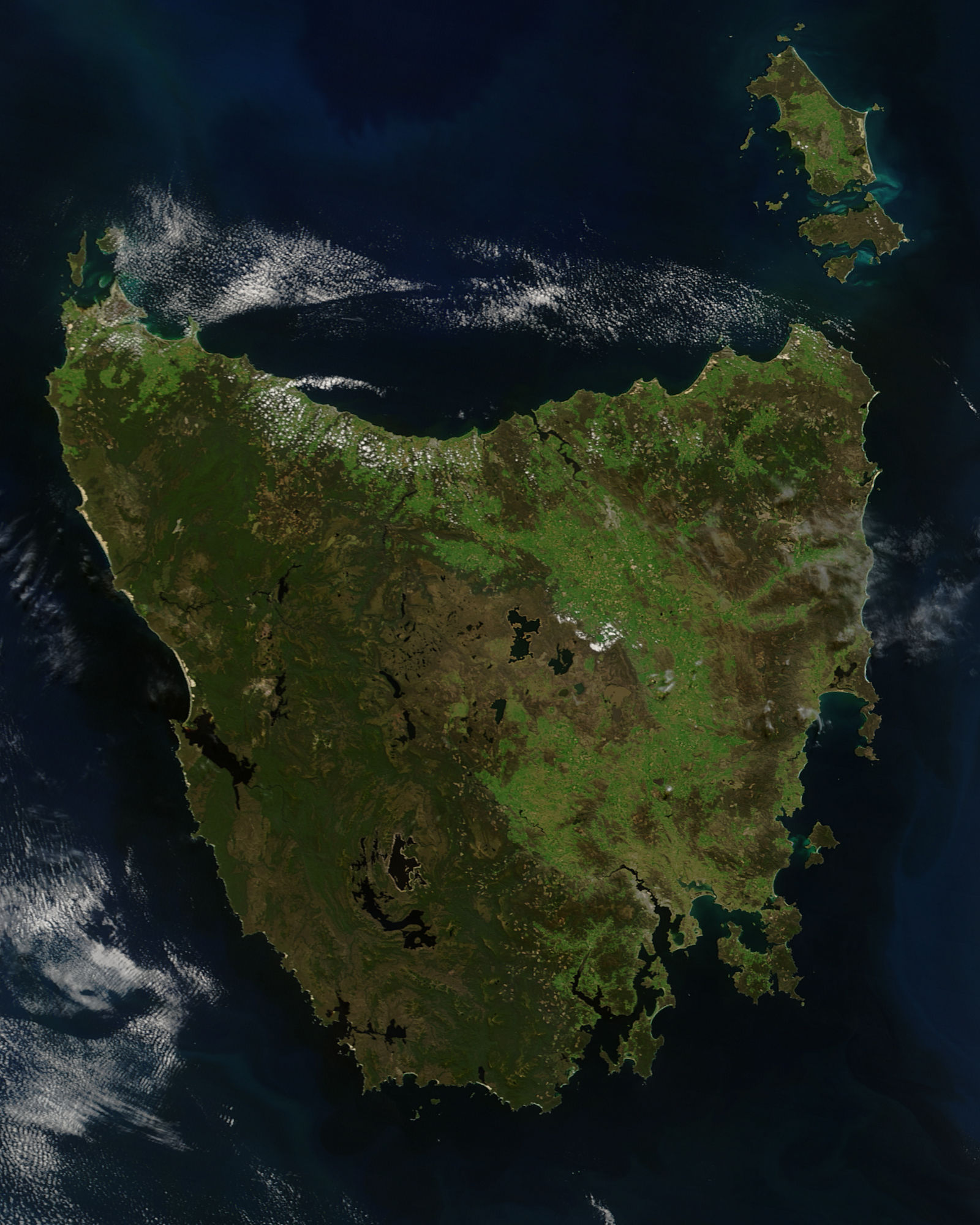
Tasmania
) , nickname = , image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Tasmania , established_title2 = Federation , established_date2 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Abel Tasman , demonym = , capital = Hobart , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 29 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania used by the British during the European exploration of Australia in the 19th century. A British settlement was established in Van Diemen's Land in 1803 before it became a separate colony in 1825. Its penal colonies became notorious destinations for the transportation of convicts due to the harsh environment, isolation and reputation for being inescapable. Macquarie Harbour and Port Arthur are among the most well-known penal settlements on the island. With the passing of the Australian Constitutions Act 1850, Van Diemen's Land (along with New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, and Western Australia) was granted responsible self-government with its own elected representative and parliament. On 1 January 1856, the colony of Van Diemen's Land was officially changed to Tasmania. The last penal settlement was closed in Tasmania in 1877. Toponym The island was named in honour of Anthony van Die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R V Symonds
''R v Symonds'' ''(The Queen v Symonds)'' incorporated the concept of aboriginal title into New Zealand law and upheld the government's pre-emptive right of purchase to Māori land deriving from the common law and expressed in the Treaty of Waitangi. Although the Native Lands Act 1862 waived Crown pre-emption, the notion of aboriginal title has been revived in the 20th century to deal with Māori property rights. Background Faced with a "virtually bankrupt colonial administration" Governor Robert FitzRoy had in 1843 waived the Crown's right of pre-emption to purchase Māori land, allowing settlers to directly buy land from Māori if they held certificates waiving the Crown's right. Under what became known as the "penny-an-acre" proclamation, 90,000 acres were bought by settlers. When Governor George Grey took office in 1845, he decided to take a test case, with a claimant seeking a writ of scire facias to "justify his refusal to award Crown grants over land to persons whose cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |