|
Henry Benson (soldier)
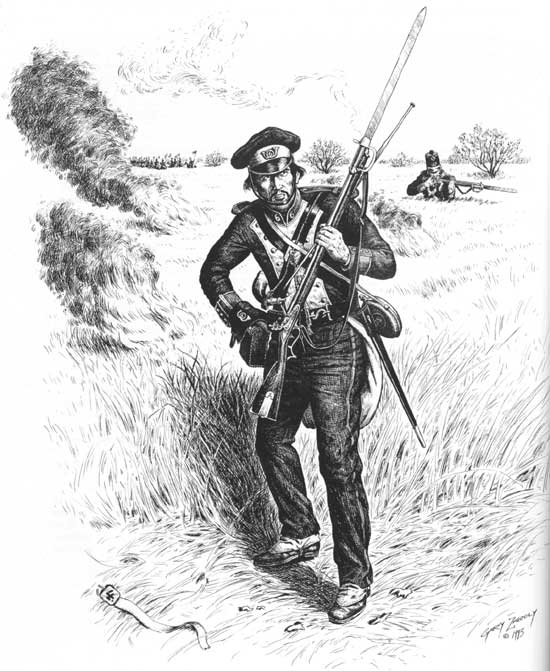
Henry Benson (November 20, 1824 – August 11, 1862) was a career United States Army artillery officer who served in the Mexican–American War, Third Seminole War, and American Civil War with the 2nd U.S. Artillery. He sustained mortal wounds on August 5, 1862, during an engagement at Malvern Hill near the end of the Peninsula Campaign, and died several days later on August 11 while being transported north aboard the steamer ''S.R. Spaulding.'' Early life Henry Benson was born in Belleville, New Jersey. He enlisted in the United States Army on June 6, 1845, at Fort Hamilton, New York. He served in the Mexican-American War with Major James Duncan's Battery A, 2nd U.S. Artillery, where he was frequently breveted for "good qualities" from the rank of private in 1845 through the rank of second lieutenant on June 28, 1848, later made permanent after the war on January 26, 1849. Benson was present with Battery A at the battles of Palo Alto, Resaca de la Palma, Monterrey, Ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belleville, New Jersey
Belleville (French: "Belle ville" meaning "Beautiful city / town") is a township in Essex County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2020 United States Census, the township's population was 38,222, reflecting an increase of 6.4% from the 2010 Census population of 35,926, an increase that follows a decline of 2 (0.0%) from the 35,928 counted in the 2000 Census. History Originally known as "Second River" or "Washington", the inhabitants renamed the settlement "Belleville" in 1797. Belleville was originally incorporated as a township by an act of the New Jersey Legislature on April 8, 1839, from portions of Bloomfield. Portions of the township were taken to create Woodside Township (March 24, 1869, now defunct) and Franklin Township (February 18, 1874, now known as Nutley). The independent municipality of Belleville city was created within the township on March 27, 1874, and was dissolved on February 22, 1876. On November 16, 1910, Belleville was reincorporated as a to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Duncan (United States Army Officer)
James Duncan (September 29, 1811 – July 3, 1849) became a hero of the Mexican–American War for his capable command of an artillery battery at several important battles. He was a graduate of United States Military Academy in 1834 and served in the Seminole Wars. In 1848, he became involved in a post-war squabble between several general officers, though it did not harm his prospects. After his exploits in the Mexican–American War, he was appointed Inspector general of the US Army. A promising career was cut short when he died of yellow fever on an inspection tour of Mobile, Alabama in 1849. Early career James Duncan was born on September 29, 1811, at Philipstown, New York. He became a cadet at the United States Military Academy at West Point, New York on January 1, 1831, and graduated on July 1, 1834, as a brevet second lieutenant in the 2nd Artillery Regiment. He was posted to the garrison of Savannah, Georgia in 1834–35. He became a full second lieutenant on November 17, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
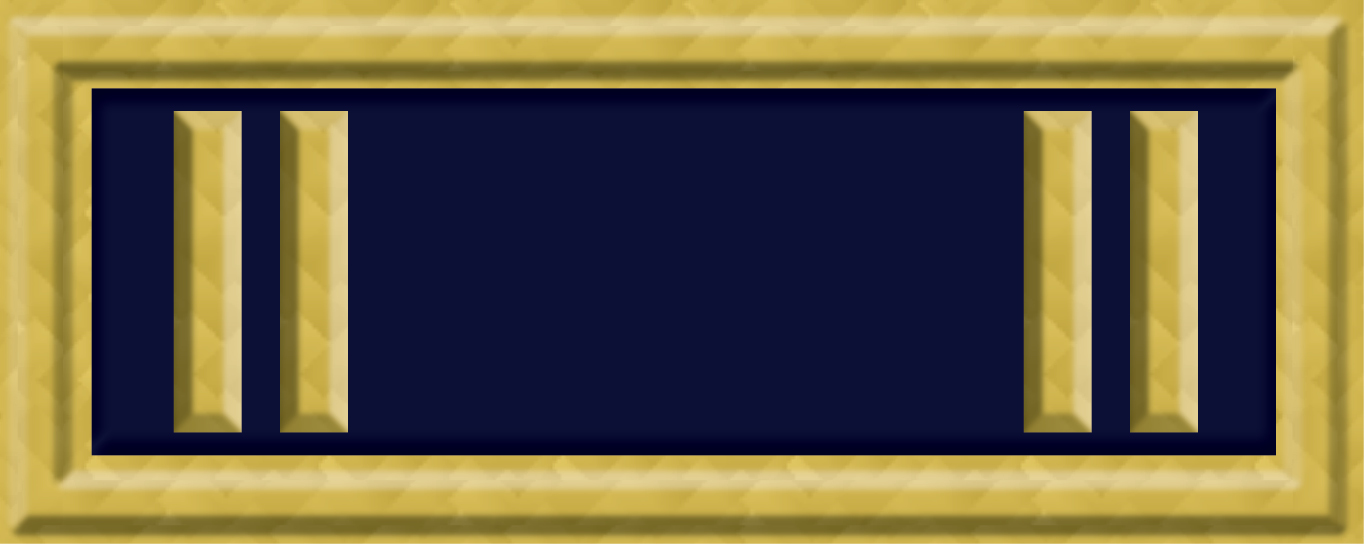
First Lieutenant
First lieutenant is a commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces; in some forces, it is an appointment. The rank of lieutenant has different meanings in different military formations, but in most forces it is sub-divided into a senior (first lieutenant) and junior (second lieutenant) rank. The NATO equivalent rank for land force officers is OF-1 rank. In navies, while certain rank insignia may carry the name lieutenant, the term may also be used to relate to a particular post or duty, rather than a rank. Indonesia In Indonesia, "first lieutenant" is known as ''Letnan Satu'' (''Lettu''), Indonesian National Armed Forces uses this rank across all three of its services. It is just above the rank of second lieutenant and just below the rank of captain. Israel In the Israel Defense Forces, the rank above second lieutenant is simply lieutenant. The rank of (קצין מקצועי אקדמאי (קמ"א (''katsín miktsoí akademai'' or "kama"), a professional aca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
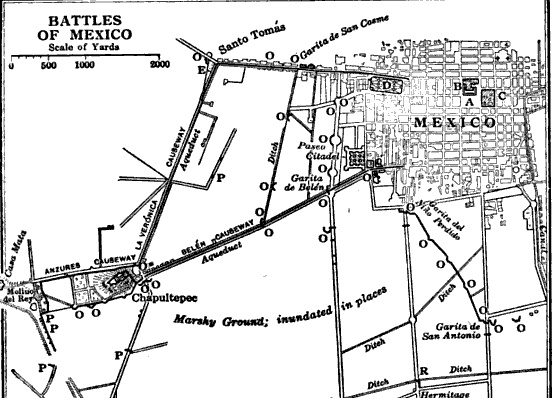
Battle Of Chapultepec
The Battle of Chapultepec was a battle between American forces and Mexican forces holding the strategically located Chapultepec Castle just outside Mexico City, fought 13 September 1847 during the Mexican–American War. The building, sitting atop a hill, was an important position for the defense of the city. The battle was part of the campaign to take Mexico City, for which General Winfield Scott's U.S. Army totaled 7,200 men. General Antonio López de Santa Anna, known for vicious attacks against Native Mexican American tribes, had formed an army of approximately 25,000 men. Mexican forces, including military cadets of the Military Academy, defended the position at Chapultepec against 2,000 U.S. forces. The Mexicans' loss opened the way for the Americans to take the center of Mexico City. In Mexican history, the battle is cast as the story of the brave deaths of six cadets, the Niños Héroes, who leapt to their deaths rather than be taken captive, with one wrapping himself ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
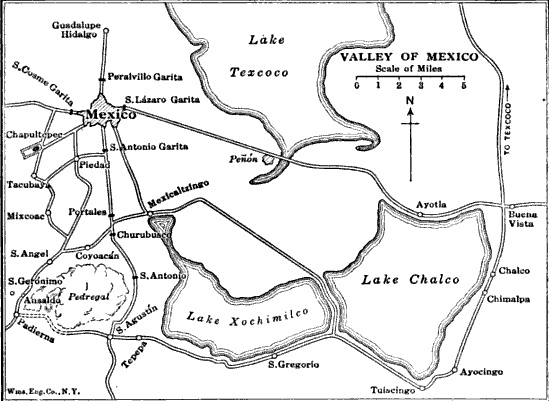
Battle For Mexico City
The Battle for Mexico City refers to the series of engagements from September 8 to September 15, 1847, in the general vicinity of Mexico City during the Mexican–American War. Included are major actions at the battles of Molino del Rey and Chapultepec, culminating with the fall of Mexico City. The U.S. Army under Winfield Scott won a major victory that ended the war. Background The major objective of American operations in central Mexico had been the capture of Mexico City. After capturing the port of Veracruz in March, General Winfield Scott was able to secure a base and move inland and defeat a large Mexican force at the Battle of Cerro Gordo. After routing the Mexicans at the Battle of Churubusco, Scott's army was less than eight kilometers (five miles) away from its objective of Mexico City. Battles Molino del Rey On September 8, the fight for Mexico City began. General Scott believed that a cannon foundry was located at the Molino del Rey, known as the ''King's Mill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Jackson Hunt
Henry Jackson Hunt (September 14, 1819 – February 11, 1889) was Chief of Artillery in the Army of the Potomac during the American Civil War. Considered by his contemporaries the greatest artillery tactician and strategist of the war, he was a master of the science of gunnery and rewrote the manual on the organization and use of artillery in early modern armies. His courage and tactics affected the outcome of some of the most significant battles in the war, including Malvern Hill, Antietam, Fredericksburg, and most notably at Gettysburg, where his operational decisions regarding strategic cannon placement and conservation of ammunition for the Confederate main assault, contributed greatly to the defeat of Pickett's Charge. Early life and family Hunt was born in the frontier outpost of Detroit to Samuel Wellington Hunt, an Army infantry officer who entered West Point in 1814 and died in 1829. He was named after his uncle, Henry Jackson Hunt, who was the second mayor of Detroi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Churubusco
The Battle of Churubusco took place on August 20, 1847, while Santa Anna's army was in retreat from the Battle of Contreras or Battle of Padierna during the Mexican–American War. It was the battle where the San Patricio Battalion, made up largely of US deserters, made their last stand against U.S. forces. The U.S. Army was victorious, outnumbering more than two-to-one the defending Mexican troops. After the battle, the U.S. Army was only 5 miles (8 km) away from Mexico City. 50 Saint Patrick's Battalion members were officially executed by the U.S. Army, all but two by hanging. Collectively, this was the largest mass execution in United States history. Background Following their defeats at Contreras, Antonio López de Santa Anna ordered Major General Nicolás Bravo Rueda with the Army of the Center, to retreat from San Antonio to Churubusco.Bauer, K.J., 1974, ''The Mexican War, 1846-1848'', New York:Macmillan, Santa Anna also ordered Major General Manuel Rincón to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
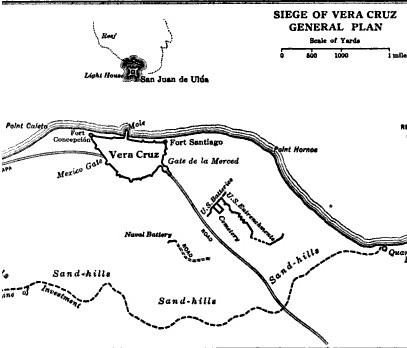
Siege Of Veracruz
The Battle of Veracruz was a 20-day siege of the key Mexican beachhead seaport of Veracruz during the Mexican–American War. Lasting from March 9–29, 1847, it began with the first large-scale amphibious assault conducted by United States military forces, and ended with the surrender and occupation of the city. U.S. forces then marched inland to Mexico City. Background After the battles of Monterrey and Buena Vista, much of Zachary Taylor's Army of Occupation was transferred to the command of Major General Winfield Scott in support of the upcoming campaign. That campaign, determined by Scott and other Washington officials, would be a Veracruz landing and an advance inland.Bauer, K.J., 1974, ''The Mexican War, 1846–1848'', New York: Macmillan, Mexican military intelligence knew in advance of U.S. plans to attack Veracruz, but internal government turmoil left them powerless to send crucial reinforcements before the American assault commenced. Opposing forces Mexican de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Monterrey
In the Battle of Monterrey (September 21–24, 1846) during the Mexican–American War, General Pedro de Ampudia and the Mexican Army of the North was defeated by the Army of Occupation, a force of United States Regulars, Volunteers and Texas Rangers under the command of General Zachary Taylor. The hard-fought urban combat led to heavy casualties on both sides. The battle ended with both sides negotiating a two-month armistice and the Mexican forces being allowed to make an orderly evacuation in return for the surrender of the city. Background Following the Battle of Resaca de la Palma, Taylor crossed the Rio Grande on 18 May, while in early June, Mariano Arista turned over command of what remained of his army, 2,638 men, to Francisco Mejia, who led them to Monterrey.Bauer, K.J., 1974, ''The Mexican War, 1846–1848'', New York: Macmillan, On 8 June, United States Secretary of War William L. Marcy ordered Taylor to continue command of operations in northern Mexico, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Resaca De La Palma
The Battle of Resaca de la Palma was one of the early engagements of the Mexican–American War, where the United States Army under General Zachary Taylor engaged the retreating forces of the Mexican ''Ejército del Norte'' ("Army of the North") under General Mariano Arista on May 9, 1846. The United States emerged victorious and forced the Mexicans out of Texas. Background Following the Mexican defeat at the Battle of Palo Alto the previous day, Arista on the morning of May 9 moved his forces to a more defensible position along a resaca, known as Resaca de Guerrero to the Mexicans but as Resaca de la Palma to the Americans. Recalling his experiences at the Siege of Fort Texas, he positioned his forces along the twelve foot deep and two hundred foot wide resaca, three miles from the Rio Grande, by 10 a.m. Arista placed most of his infantry in the ravine, thickly forested on either side, to negate the effectiveness of Taylor's artillery, with the 6th and 10th Infantry, Sappers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Palo Alto
The Battle of Palo Alto ( es, Batalla de Palo Alto) was the first major battle of the Mexican–American War and was fought on May 8, 1846, on disputed ground five miles (8 km) from the modern-day city of Brownsville, Texas. A force of some 3,700 Mexican troops – most of the ''Army of The North'' – led by General Mariano Arista engaged a force of approximately 2,300 United States troops – the Army of Occupation led by General Zachary Taylor. On April 30, following the Thornton Affair, Mexican General Mariano Arista's troops began to cross the Rio Grande. On May 3, the troops began to besiege the American outpost at Fort Texas. Taylor marched his Army of Occupation south to relieve the siege. Arista, upon learning of his approach, diverted many of his units away from the siege to meet Taylor's force. The battle took place on May 8, three days before the formal declaration of war on Mexico by the United States. Arista ordered two cavalry charges, first against the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |