|
Henophidia
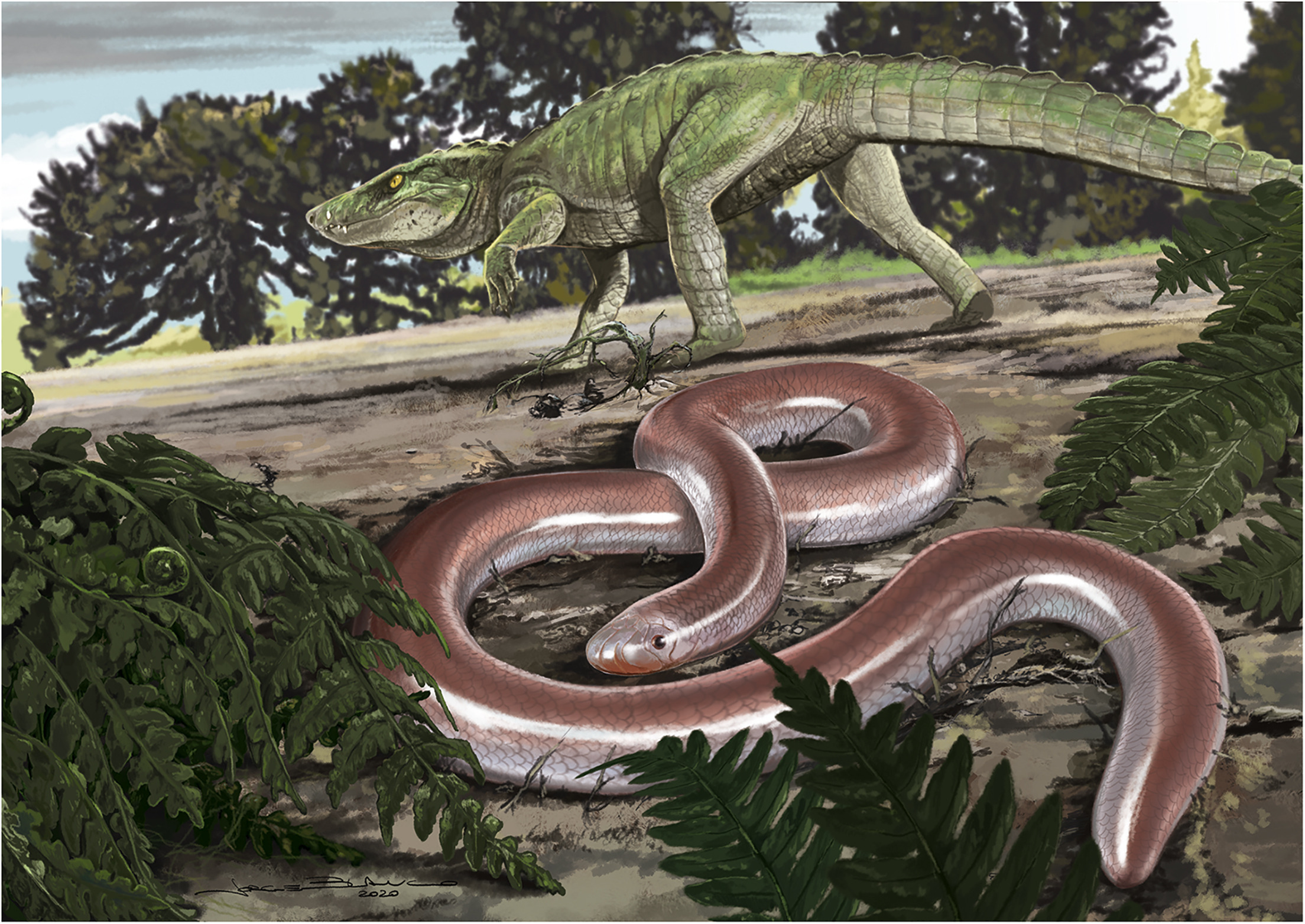
Henophidia is a former superfamily of the suborder Serpentes (snakes) that contains boas, pythons and numerous other less-well-known snakes. Snakes once considered to belong to superfamily Henophidia include two families now considered Amerophidia (Aniliidae – red pipe snakes, and Tropidophiidae – dwarf "boas" or thunder snakes), three families now considered Uropeltoidea (Cylindrophiidae – Asian pipe snakes, Anomochilidae – dwarf pipe snakes, and Uropeltidae – shield-tailed snakes and short-tailed snakes), three families now considered Pythonoidea (Pythonidae – pythons, Loxocemidae – Mexican burrowing snake, and Xenopeltidae – sunbeam snakes), at least one family now considered Booidea (Boidae – boas ncluding sand boas and many other lineages often called boas, mostly now considered subfamilies of Boidaeref name="Reynolds14"/>), and Bolyeriidae – Round Island splitjaw snakes. Because these snakes do not form a monophyletic group they can no longer be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake
Snakes are elongated, Limbless vertebrate, limbless, carnivore, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other Squamata, squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping Scale (zoology), scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads (cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most have only one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs about twenty-five times independently via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, altho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caenophidia
The Caenophidia are a derived clade of alethinophidian snakes, which contains over 80% of all the extant species of snakes. The largest family is Colubridae, but it also includes at least seven other families, at least four of which were once classified as "Colubridae" before molecular phylogenetics helped us understand their relationships. It has been found to be monophyletic. Although the Caenophidia previously was held to exclude Acrochordidae, researchers have recognized that acrochordids share several traits with the other caenophidians. Hence Caenophidia is usually considered to comprise Acrochordidae plus more the more derived snakes classified as Colubroidea. Recent molecular studies have also found the families Xenophidiidae and Bolyeriidae to be closely related to caenophidians, forming the sister group to Caenophidia rather than being part of Henophidia. Below is a phylogeny of the Caenophidia based on analyses from several studies: References Alethino ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python Bivittatus
The Burmese python (''Python bivittatus'') is one of the largest species of snakes. It is native to a large area of Southeast Asia and is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List. Until 2009, it was considered a subspecies of the Indian python, but is now recognized as a distinct species. It is an invasive species in Florida as a result of the pet trade. Description The Burmese python is a dark-colored non-venomous snake with many brown blotches bordered by black down the back. In the wild, Burmese pythons typically grow to , while specimens of more than are unconfirmed. This species is sexually dimorphic in size; females average only slightly longer, but are considerably heavier and bulkier than the males. For example, length-weight comparisons in captive Burmese pythons for individual females have shown: at length, a specimen weighed , a specimen of just over weighed , a specimen of weighed , and a specimen of weighed . In comparison, length-weight comparisons for males ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loxocemidae
:''Common names: Mexican python, Mexican burrowing python, Mexican burrowing snake.'' ''Loxocemus bicolor'',the sole member of the monotypic family Loxocemidae, is a species of python-like snake found in Mexico and Central America. No subspecies are currently recognized. Analyses of DNA show that ''Loxocemus'' is most closely related to the true pythons and the sunbeam snakes. Description Adults grow to a maximum of in length. On average this snake grows to roughly . The body is stout and very muscular. The snout is shovel-shaped, with a narrow head and small eyes to facilitate burrowing. It has been observed that both male and females have various scent glands on their bodies that secrete fatty acids and alcohols to deter nuisance arthropods, such as ants or other burrowing insects. The species is described as terrestrial and semi- fossorial, which makes them hard to observe and study. The color pattern is usually dark with patches of white scales, although occasionally after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primitive (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, a primitive (or ancestral) character, trait, or feature of a lineage or taxon is one that is inherited from the common ancestor of a clade (or clade group) and has undergone little change since. Conversely, a trait that appears ''within'' the clade group (that is, is present in any subgroup within the clade but not all) is called advanced or derived. A clade is a group of organisms that consists of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants. A primitive trait is the original condition of that trait in the common ancestor; advanced indicates a notable change from the original condition. These terms in biology contain no judgement about the sophistication, superiority, value or adaptiveness of the named trait. "Primitive" in biology means only that the character appeared first in the common ancestor of a clade group and has been passed on largely intact to more recent members of the clade. "Advanced" means the character has evolved within a later subgroup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, basal is the direction of the ''base'' (or root) of a phylogenetic tree#Rooted tree, rooted phylogenetic tree or cladogram. The term may be more strictly applied only to nodes adjacent to the root, or more loosely applied to nodes regarded as being close to the root. Note that extant taxa that lie on branches connecting directly to the root are not more closely related to the root than any other extant taxa. While there must always be two or more equally "basal" clades sprouting from the root of every cladogram, those clades may differ widely in taxonomic rank, Phylogenetic diversity, species diversity, or both. If ''C'' is a basal clade within ''D'' that has the lowest rank of all basal clades within ''D'', ''C'' may be described as ''the'' basal taxon of that rank within ''D''. The concept of a 'key innovation' implies some degree of correlation between evolutionary innovation and cladogenesis, diversification. However, such a correlation does not make a given ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scolecophidia
The Scolecophidia, commonly known as blind snakes or thread snakes, are an infraorder of snakes. They range in length from . All are fossorial (adapted for burrowing). Five families and 39 genera are recognized. The Scolecophidia infraorder is most likely paraphyletic. Taxonomy The infraorder name Scolecophidia derives from the two Ancient Greek words or σκώληκος (, genitive ), meaning "earthworm", and (), meaning "snake". It refers to their shape and fossorial lifestyle. Families Evolution Despite only having fossils as early as the Cretaceous, Scolecophidia itself likely originated in the Middle Jurassic, with Anomalepididae, Leptotyphlopidae, and Typhlopoidea diverging from one another during the Late Jurassic. Within Typhlopoidea, Gerrhopilidae likely diverged from the Xenotyphlopidae-Typhlopidae clade during the Early Cretaceous, and Xenotyphlopidae and Typhlopidae likely diverged from one another during the Late Cretaceous. Scolecophidians are believed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyly
In cladistics for a group of organisms, monophyly is the condition of being a clade—that is, a group of taxa composed only of a common ancestor (or more precisely an ancestral population) and all of its lineal descendants. Monophyletic groups are typically characterised by shared derived characteristics ( synapomorphies), which distinguish organisms in the clade from other organisms. An equivalent term is holophyly. The word "mono-phyly" means "one-tribe" in Greek. Monophyly is contrasted with paraphyly and polyphyly as shown in the second diagram. A ''paraphyletic group'' consists of all of the descendants of a common ancestor minus one or more monophyletic groups. A '' polyphyletic group'' is characterized by convergent features or habits of scientific interest (for example, night-active primates, fruit trees, aquatic insects). The features by which a polyphyletic group is differentiated from others are not inherited from a common ancestor. These definitions have taken ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolyeriidae
:''Common names: Mauritius snakes, Round Island boas, splitjaw snakes.'' The Bolyeriidae are a family of snakes native to Mauritius and a few islands around it, especially Round Island. They also used to be found on the island of Mauritius, but were extirpated there due to human influence and foraging pigs in particular. These snakes used to be placed in the Boidae, but are now classed as a separate family. Two monotypic genera are recognized, but only a single species is extant. Bolyeriidae appear to be most closely related to the Asian genus '' Xenophidion''. Geographic range Found in Mauritius. Genera ) Type genus In biological taxonomy, the type genus is the genus which defines a biological family and the root of the family name. Zoological nomenclature According to the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature, "The name-bearing type of a nominal .... Both of these monotypic genera once inhabited Mauritius and/or a number of islands around it. However, ''Bol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boidae
The Boidae, commonly known as boas or boids, are a family of nonvenomous snakes primarily found in the Americas, as well as Africa, Europe, Asia, and some Pacific Islands. Boas include some of the world's largest snakes, with the green anaconda of South America being the heaviest and second-longest snake known; in general, adults are medium to large in size, with females usually larger than the males. Five subfamilies, comprising 12 genera and 49 species, are currently recognized. The Old Tupi name for such snakes was mbói, which figures in the etymology of names such as ''jibóia'' and ''boitatá'' (the Brazilian name for the mythical giant anaconda). Description Like the pythons, boas have elongated supratemporal bones. The quadrate bones are also elongated, but not as much, while both are capable of moving freely so when they swing sideways to their maximum extent, the distance between the hinges of the lower jaw is greatly increased.Parker HW, Grandison AGC. 1977. Snakes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Booidea
The Booidea, also known as booid snakes, are a superfamily of snakes that contains boas (family Boidae) and other closely related boa-like snakes (but not pythons, which are in a separate superfamily called Pythonoidea). As of 2017, Booidea contains 61 species, including the eponymous neotropical ''Boa constrictor'', anacondas (genus ''Eunectes''), and smaller tree and rainbow boas ('' Corallus'', '' Epicrates'', and ''Chilabothrus'') as well as several genera of booid snakes from various locations around the world: bevel-nosed boas or keel-scaled boas (''Candoia'') from New Guinea and Melanesia, Old World sand boas (''Eryx'') from Northeast Africa, the Middle East, and Southwest Asia, rubber boas (''Charina'') and rosy boas (''Lichanura'') from North America, neotropical dwarf boas ('' Ungaliophis'') and the Oaxacan dwarf boa (''Exiliboa'') from Central America, Madagascan boas or Malagasy boas (''Acrantophis'' and ''Sanzinia'') from Madagascar, and the Calabar python (''Calabaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenopeltidae
''Xenopeltis'', the sunbeam snakes, are the sole genus of the monotypic family Xenopeltidae, the species of which are found in Southeast Asia. Sunbeam snakes are known for their highly iridescent scales. Two species are recognized, each one with no subspecies. Studies of DNA suggest that the xenopeltids are most closely related to the Mexican burrowing python ('' Loxocemus bicolor'') and to the true pythons of Pythonidae. Description Adults can grow up to in length.Burnie D, Wilson DE. 2001. ''Animal''. London: Dorling Kindersley. 624 pp. . The head scales are made up of large plates much like those of the Colubridae, while the ventral scales are only slightly reduced. Pelvic vestiges are not present. The dorsal color pattern is a reddish-brown, brown, or blackish color. The belly is an unpatterned whitish-gray.Mehrtens JM. 1987. ''Living Snakes of the World in Color''. New York: Sterling Publishers. 480 pp. . The scales are highly iridescent. Geographic range They are found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |