|
Helecs Vehicles
Helecs was a marque of British battery-electric road vehicles, produced initially by the electrical engineers Hindle Smart Co Ltd of Ardwick, Manchester from 1948 onwards. One of their first vehicles was a collaboration with Jensen Motors for a tractor unit, used primarily for railway deliveries, and they then produced a number of vehicles which were aimed at the dairy industry and bodied as milk floats for retail milk delivery. They had some success with exports to Canada, and two independent companies bearing the Helecs Vehicles name were set up, in 1952 and 1955. All of the companies became insolvent in 1956. One of the vehicles for which they built the chassis is on public display at The Transport Museum, Wythall. History Hindle Smart and Co. Ltd. was an electrical engineering company initially based at 20 Wilmslow Road Withington, south Manchester, and then in the late 1940s in Ardwick, at 27a New Bank Street. It was formed by Mr Noel Hindle and Mr Robert Eric Smart around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Transport Museum, Wythall
The Transport Museum, Wythall is a transport museum just outside Birmingham, at Chapel Lane, Wythall, Worcestershire, England. The museum was originally run by the charity The Birmingham and Midland Motor Omnibus Trust (BaMMOT). BaMMOT was formed in 1977 and the museum site was acquired in February 1978. The museum has three halls, presenting a significant collection of preserved buses and coaches, including Midland Red and Birmingham City Transport vehicles, a collection of battery electric vehicles such as milk floats, and a Tilling-Stevens Tilling-Stevens was a British manufacturer of buses and other commercial vehicles, based in Maidstone, Kent. Originally established in 1897, it became a specialist in petrol-electric vehicles. It continued as an independent manufacturer until ... petrol-electric bus. In 2016 the Trust became a CIO charity called Transport Museum Wythall (TMW), registered numbe1167872 It is also home to the Elmdon Model Engineering Society (EMES) who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Railways
British Railways (BR), which from 1965 traded as British Rail, was a state-owned company that operated most of the overground rail transport in Great Britain from 1948 to 1997. It was formed from the nationalisation of the Big Four British railway companies, and was privatised in stages between 1994 and 1997. Originally a trading brand of the Railway Executive of the British Transport Commission, it became an independent statutory corporation in January 1963, when it was formally renamed the British Railways Board. The period of nationalisation saw sweeping changes in the railway. A process of dieselisation and electrification took place, and by 1968 steam locomotives had been entirely replaced by diesel and electric traction, except for the Vale of Rheidol Railway (a narrow-gauge tourist line). Passengers replaced freight as the main source of business, and one-third of the network was closed by the Beeching cuts of the 1960s in an effort to reduce rail subsidies. On privatis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
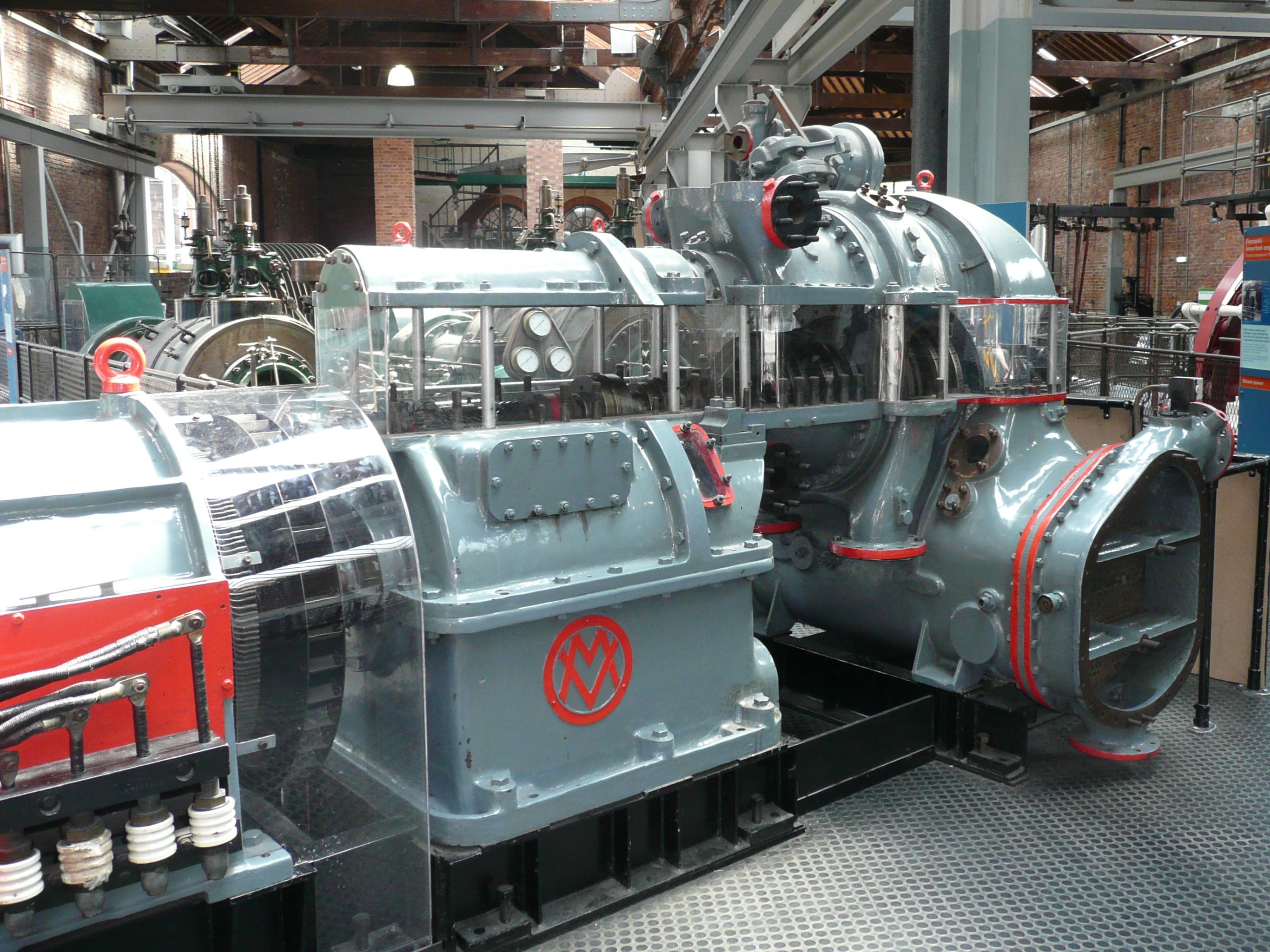
Metropolitan Vickers
Metropolitan-Vickers, Metrovick, or Metrovicks, was a British heavy electrical engineering company of the early-to-mid 20th century formerly known as British Westinghouse. Highly diversified, it was particularly well known for its industrial electrical equipment such as generators, steam turbines, switchgear, transformers, electronics and railway traction equipment. Metrovick holds a place in history as the builders of the first commercial transistor computer, the Metrovick 950, and the first British axial-flow jet engine, the Metropolitan-Vickers F.2. Its factory in Trafford Park, Manchester, was for most of the 20th century one of the biggest and most important heavy engineering facilities in Britain and the world. History Metrovick started as a way to separate the existing British Westinghouse Electrical and Manufacturing Company factories from United States control, which had proven to be a hindrance to gaining government contracts during the First World War. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olympia, London
Olympia London, sometimes referred to as the Olympia Exhibition Centre, is an exhibition centre, event space and conference centre in West Kensington, in the London Borough of Hammersmith and Fulham, London, England. A range of international trade and consumer exhibitions, conferences and sporting events are staged at the venue. There is an adjacent railway station at Kensington (Olympia) which is both a London Overground station, and a London Underground station. The direct District Line spur to the station only runs on weekends. Background The complex first opened in 1886. The Grand Hall and Pillar Hall were completed in 1885. The National Hall annexe was completed in 1923, and in 1930 the Empire Hall was added. After World War II, the West London exhibition hall was in single ownership with the larger nearby Earls Court Exhibition Centre. The latter was built in the 1930s as a rival to Olympia. In 2008, ownership of the two venues passed from P&O to Capco Plc whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Motors
Guy Motors was a Wolverhampton-based vehicle manufacturer that produced cars, lorries, buses and trolleybuses. The company was founded by Sydney S. Guy (1885–1971) who was born in Kings Heath, Birmingham. Guy Motors operated out of its Fallings Park factory from 1914 to 1982, playing an important role in the development of the British motor industry. History Foundation and the First World War Sydney S. Guy registered Guy Motors Limited on Saturday 30 May 1914, the same day he departed his position as works manager at the Wolverhampton company, Sunbeam. A factory was built on the site at Fallings Park, Wolverhampton. and by September 1914 production was underway on the newly designed 30 cwt lorry. This employed a much lighter form of pressed steel frame, unlike the more commonly used heavy rolled steel channel frames of the time. This made the vehicle able to cross difficult terrain and a 14-seat post bus built based on the design was used for crossing the Scottish Highlands. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunbeam Commercial Vehicles
Sunbeam Commercial Vehicles was a commercial vehicle manufacturing offshoot of the Wolverhampton based Sunbeam Motor Car Company when it was a subsidiary of S T D Motors Limited. Sunbeam had always made ambulances on modified Sunbeam car chassis. S T D Motors chose to enter the large commercial vehicle market in the late 1920s, and once established they made petrol and diesel buses and electrically powered trolleybuses and milk floats. Commercial Vehicles became a separate department of Sunbeam in 1931. Ownership switched from S T D Motors to Rootes Securities in mid-1935, and later that year their Karrier trolleybus designs were added to Sunbeam production lines. In 1946 J. Brockhouse and Co of West Bromwich bought Sunbeam but in September 1948 sold the trolleybus part of the business to Guy Motors. In the early 1950s the amalgamated Sunbeam, Karrier and Guy trolleybus operation was the largest in Britain and possibly the world. In 1954 Sunbeam Commercial Vehicles moved withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Motor
''Commercial Motor'' is a weekly magazine serving the road transport industry in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1905 by Edmund Dangerfield, it is notable for having been "the first journal to be devoted exclusively to the commercial vehicle engaged in the conveyance of goods or in passenger carrying". Originally named ''The Commercial Motor'', the title was shortened to ''Commercial Motor'' for the first issue of 1966. The publication is commonly referred to as 'CM' by its readers and editorial staff. ''Commercial Motor'' was initially published by Temple Press and since 2011 it has been published by Road Transport Media. Launch ''The Commercial Motor'' was launched in March 1905 by Temple Press. In the leader of the first issue it described itself as a "missionary and educative medium". For the first issue on 16 March, 20,000 copies were issued "in Britain and other countries, with the hope that the normal weekly circulation would be at least 5,000". Composition The content ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jensen Interceptor (1950)
The Jensen Interceptor made its debut in 1950 as the second car made by Jensen Motors after World War II. The car was based on Austin components with a body built by Jensen and styled by Eric Neale. The straight-six engine and transmission came from the Austin Sheerline and the chassis was a lengthened version of the one used on the Austin A70 with a modified version of the independent coil sprung suspension. Production continued through 1957. Jensen later reused the name for a second-generation Jensen Interceptor which debuted in 1966 and was revived several times after that. History The two door Interceptor first appeared as a convertible bodied in a mix of aluminium and steel on a wood frame. The entire front section hinged forwards to give access to the engine. The wrap around rear window was made of rigid plastic (Perspex) and was arranged to drop down into a well for stowage when the top was lowered. In 1952 a hardtop version with fabric-covered roof was launched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinky Toys
Dinky Toys was the brand name for a range of die-cast toy, die-cast zamak zinc alloy scale model model car, vehicles produced by British toy company Meccano Ltd. They were made in England from 1934 to 1979, at a factory in Binns Road in Liverpool. Dinky Toys were among the most popular die-cast vehicles ever made – pre-dating other popular die-cast marques, including Corgi Toys, Corgi, Matchbox (brand), Matchbox and Mattel's Hot Wheels. Vehicles commercialised under the "Dinky" name include model car, cars, model commercial vehicle, trucks, model aircraft, aircraft, model military vehicle, military, model ship, ships. Pre-war history Frank Hornby established Meccano Ltd. in 1908 to make metal construction sets. The company later moved into model railways, with its O scale, O gauge clockwork trains appearing in 1920. In the early 1930s, Meccano made many types of tinplate and other metal cars, such as its Morgan and Birmingham Small Arms Company, BSA three-wheelers, mostl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Warwick
The University of Warwick ( ; abbreviated as ''Warw.'' in post-nominal letters) is a public research university on the outskirts of Coventry between the West Midlands (county), West Midlands and Warwickshire, England. The university was founded in 1965 as part of a government initiative to expand higher education. The Warwick Business School was established in 1967, the Warwick Law School in 1968, WMG, University of Warwick, Warwick Manufacturing Group (WMG) in 1980, and Warwick Medical School in 2000. Warwick incorporated Coventry College of Education in 1979 and Horticulture Research International in 2004. Warwick is primarily based on a campus on the outskirts of Coventry, with a satellite campus in Wellesbourne and a central London base at the Shard. It is organised into three faculties—Arts, Science Engineering and Medicine, and Social Sciences—within which there are 32 departments. As of 2021, Warwick has around 29,534 full-time students and 2,691 academic and research ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasgow
Glasgow ( ; sco, Glesca or ; gd, Glaschu ) is the most populous city in Scotland and the fourth-most populous city in the United Kingdom, as well as being the 27th largest city by population in Europe. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 635,640. Straddling the border between historic Lanarkshire and Renfrewshire, the city now forms the Glasgow City Council area, one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, and is governed by Glasgow City Council. It is situated on the River Clyde in the country's West Central Lowlands. Glasgow has the largest economy in Scotland and the third-highest GDP per capita of any city in the UK. Glasgow's major cultural institutions – the Burrell Collection, Kelvingrove Art Gallery and Museum, the Royal Conservatoire of Scotland, the Royal Scottish National Orchestra, Scottish Ballet and Scottish Opera – enjoy international reputations. The city was the European Capital of Culture in 1990 and is notable for its architecture, cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
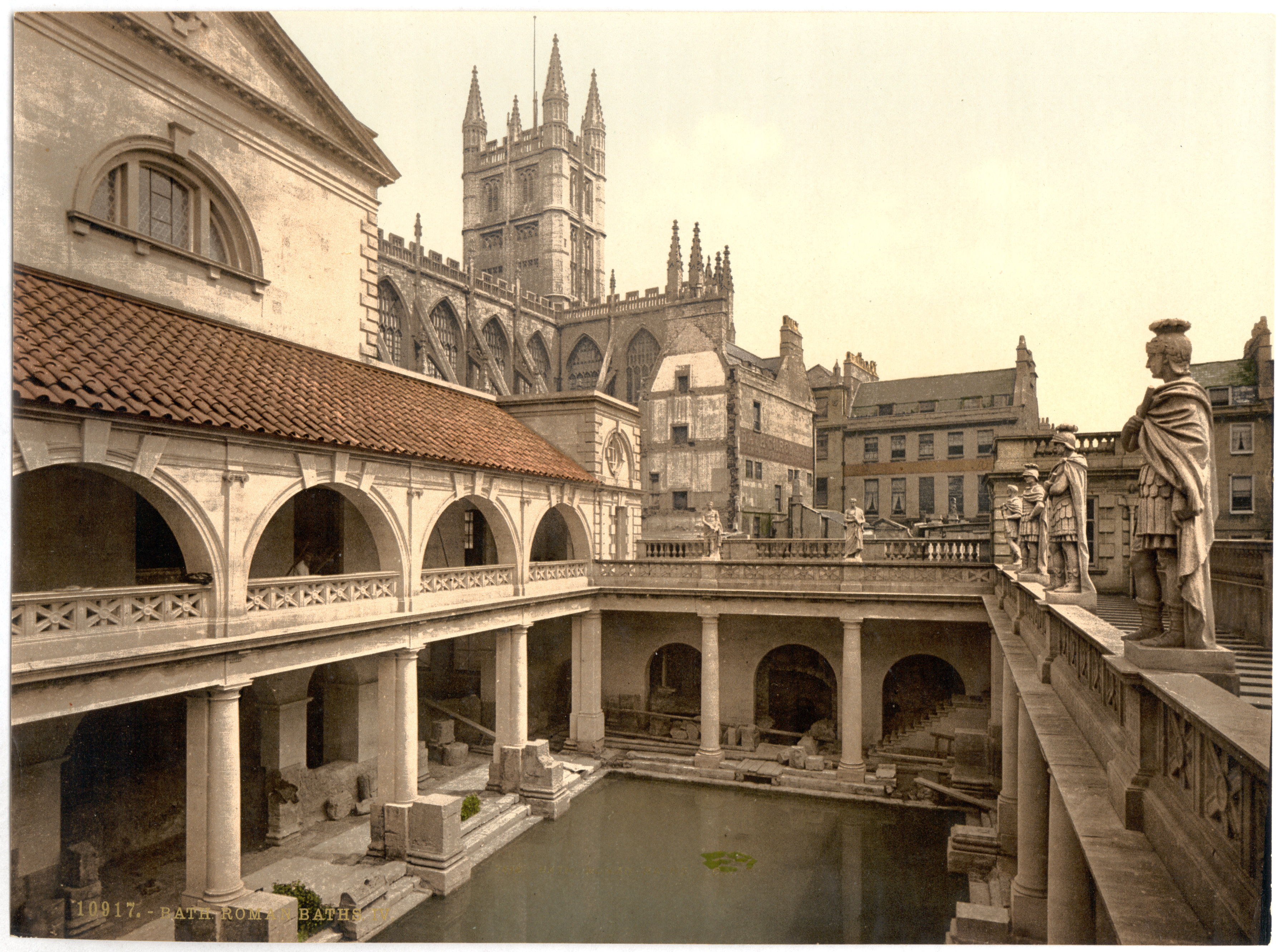
Bath, Somerset
Bath () is a city in the Bath and North East Somerset unitary area in the county of Somerset, England, known for and named after its Roman-built baths. At the 2021 Census, the population was 101,557. Bath is in the valley of the River Avon, west of London and southeast of Bristol. The city became a World Heritage Site in 1987, and was later added to the transnational World Heritage Site known as the "Great Spa Towns of Europe" in 2021. Bath is also the largest city and settlement in Somerset. The city became a spa with the Latin name ' ("the waters of Sulis") 60 AD when the Romans built baths and a temple in the valley of the River Avon, although hot springs were known even before then. Bath Abbey was founded in the 7th century and became a religious centre; the building was rebuilt in the 12th and 16th centuries. In the 17th century, claims were made for the curative properties of water from the springs, and Bath became popular as a spa town in the Georgian era. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)